Chemistry Review - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

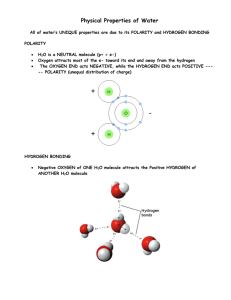
Ch. 4 - Chemistry Review Part I. Complete the following chart based on the periodic table and your knowledge of atomic structure Element Hydrogen Helium Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine Neon Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur Chlorine Argon Potassium Calcium Carbon-14 Sodium-23 Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Weight # of # of protons neutrons (p) (n) # of electrons (e-) # of electrons in outer most layer (shell) Part II. For each of the following elements / isotopes use the information from the previous chart and periodic table to 1) Draw the nucleus and put the correct number of protons & neutrons in the nucleus 2) Draw the electron shells of each atom and place the correct number of electrons in each level 1. Hydrogen 2. Helium 3. Beryllium 4. Carbon 5. Oxygen 6. Carbon-14 7. Sodium 8. Sulfur 9. Chlorine 10. Boron-11 Part III. Based on the given molecule – identify if the bond between the elements is either covalent or ionic and explain using an atomic diagram. 1. Cl2 2. KCl 3. NaF 4. CO2 Part IV. Balance the following chemical equations, so that the same number of elements on the reactant side is equal to the elements on the product side. 1. ___ H2 + ___O2 ____ H2O 6. ___ Al + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ AlCl3 2. ____ K + _____Cl2 ______ KCl 7. ___Ca(OH)2 + ___ HF ___ H2O + ___CaF2 3. ____ H2 + ____ NO ___ H2O + ___N2 8. ___ Zn + ___ H2CO3 ___ZnCO3 + ___H2 4. ___AlBr3 + ___ Cl2 ___ AlCl3 + ___ Br2 5. ___Cu + ___H2SO4 __ CuSO4 + ___ H2O + ___SO2 Part V. Answer the following questions about water 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water molecules. 3. Explain why the hydrogen and oxygen atoms don't share electrons equally in a water molecule. 4. Sketch a molecule of water showing the charges on the molecule. 5. Name 2 types of compounds that dissolve well in water. 6. What happens when an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (table salt) dissolves in water? 7. Water molecules are ___________ to other water molecules. 8. Water molecules attracting other water molecules is called _________________. 9. Cohesion of water molecules produces ________________ tension making water seem like it has a "skin" on it. Surface tension enables some _____________ to walk across the surface of the water. 10. Water molecules attracting other types of molecules is called _________________. 11. Adhesion and cohesion together enable water molecules to move ____________ through narrow tubes against the force of gravity. 12. The above property of water is called _________________. 13. Give an example of an organism using capillarity. 14. What must be true for water to change temperature? To change state? ANSWERS Part I Element Element Atomic Symbol Number Atomic Weight Hydrogen Helium Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine Neon Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur Chlorine Argon Potassium Calcium H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca 1 4 7 9 11 12 14 16 19 20 23 24 27 28 31 32 35 40 39 40 Element Hydrogen Helium Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine Neon Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur Chlorine Argon Potassium Calcium Orbitals 1s1 1s2 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s22p1 1s2 2s22p2 1s2 2s22p3 1s2 2s22p4 1s2 2s22p5 1s2 2s22p6 1s2 2s22p63s1 1s2 2s22p63s2 1s2 2s22p63s23p1 1s2 2s22p63s23p2 1s2 2s22p63s23p3 1s2 2s22p63s23p4 1s2 2s22p63s23p5 1s2 2s22p63s23p6 1s2 2s22p63s23p64s1 1s2 2s22p63s23p64s2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 # of # of protons (p) neutrons (n) 1 0 2 2 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 10 10 10 11 12 12 12 13 14 14 14 15 16 16 16 17 18 18 22 19 20 20 20 # of electrons (e-) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 # of electrons in outer most layer (shell) 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 Part II. For each of the following elements / isotopes use the information from the previous chart and periodic table to 1) Draw the nucleus and put the correct number of protons & neutrons in the nucleus 2) Draw the electron shells of each atom and place the correct number of electrons in each level 1. Hydrogen 2. Helium 3. Beryllium 4. Carbon 5. Oxygen 6. Carbon-14 7. Sodium 8. Sulfur 9. Chlorine 10. Boron-11 Part III. Based on the given molecule – identify if the bond between the elements is either covalent or ionic and explain using an atomic diagram. 1. Cl2 2. KCl 3. NaF 4. CO2 Part IV. Balance the following chemical equations, so that the same number of elements on the reactant side is equal to the elements on the product side. 1. 2 H2 + ___O2 2 H2O 6. 2 Al + 6 HCl 3 H2 + 2 AlCl3 2. 2 K + _____Cl2 2 KCl 7. ___ Ca(OH)2 + 2 HF 2 H2O + ___CaF2 3. 2 H2 + 2 NO 2 H2O + ___N2 8. ___ Zn + H2CO3 ___ZnCO3 + ___H2 4. 2 AlBr3 + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 + 3 Br2 5. ___Cu + 2 H2SO4 __ CuSO4 + 2 H2O + ___SO2 Part V. Answer the following questions about water 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? All living things are made of water, water crucial for metabolism functions (energy) 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water molecules. Polar covalent - outer two electrons of hydrogen are pulled toward oxygen 3. Explain why the hydrogen and oxygen atoms don't share electrons equally in a water molecule. Oxygen has a greater electro-negativity and pulls the hydrogen atoms to itself - leaving the hydrogen molecules as a positive end. 4. Sketch a molecule of water showing the charges on the molecule. positive on the hydrogen sides and negative on the oxygen side 5. Name 2 types of compounds that dissolve well in water. Sugar and salt 6. What happens when an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (table salt) dissolves in water? The sodium ions are attracted to the oxygen side of the molecule and chlorides are attracted to the hydrogen 7. Water molecules are attracted to other water molecules. 8. Water molecules attracting other water molecules is called cohesion. 9. Cohesion of water molecules produces Surface tension making water seem like it has a "skin" on it. Surface tension enables some organisms to walk across the surface of the water. 10. Water molecules attracting other types of molecules is called adhesion. 11. Adhesion and cohesion together enable water molecules to move upward through narrow tubes against the force of gravity. 12. The above property of water is called capillary action. 13. Give an example of an organism using capillarity. Water is moved up the roots and stems of a plant. 14. What must be true for water to change temperature? To change state? Energy must be lost or added Zinc and lead (II) nitrate react to form zinc nitrate and lead. Zn + Pb(NO3)2 Zn(NO3)2 + Pb _______________________________________________________________ 2) Aluminum bromide and chlorine gas react to form aluminum chloride and bromine gas. 2 AlBr3 + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 + 3 Br2 _______________________________________________________________ 3) Sodium phosphate and calcium chloride react to form calcium phosphate and sodium chloride. 2 Na3PO4 + 3 CaCl2 6 NaCl + Ca3(PO4)2 _______________________________________________________________ 4) Potassium metal and chlorine gas combine to form potassium chloride. 2 K + Cl2 2 KCl _______________________________________________________________ 5) Aluminum and hydrochloric acid react to form aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. 2 Al + 6 HCl 3 H2 + 2 AlCl3 _______________________________________________________________ 6) Calcium hydroxide and phosphoric acid react to form calcium phosphate and water. 3 Ca(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 Ca3(PO4)2 + 6 H2O _______________________________________________________________ 7) Copper and sulfuric acid react to form copper (II) sulfate and water and sulfur dioxide. Cu + 2 H2SO4 CuSO4 + 2 H2O + SO2 _______________________________________________________________ 8) Hydrogen gas and nitrogen monoxide react to form water and nitrogen gas. 2 H2 + 2 NO 2 H2O + N2 1 Ca(OH)2 + 2 HF 2 H2O + CaF2 (CaF2 precipitates) 2) 1 Pb(NO3)2 + 1 K2CrO4 2 KNO3 + PbCrO4 (PbCrO4 precipitates) 3) 2 NaC2H3O2 + 1 H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2 CH3COOH (no precipitate) 4) 3 Cu(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 6 H2O + Cu3(PO4)2 copper (II) phosphate precipitates 5) 2 AgNO3 + 1 Na2CO3 Ag2CO3 + 2 NaNO3 (Ag2CO3 precipitate 6) 1 Zn + 2 H2CO3 ZnCO3 + H2 (ZnCO3 precipitates) 7) Pb(OH)2 + Hg2S no reaction; neither reagent is soluble in water Part III. Based on the given molecule – draw the bond between the elements if it is either covalent or ionic and explain any change in charges using an atomic diagram. 1. Cl2 2. KCl 3. NaF 4. CO2 Part IV. Write the Lewis dot structure for each of the following atoms 1. 5. H 2. 9. F 6. He 3. 10. N 7. Li 4. Na 11. B 8. Be Mg Ar 12. C K Part IV. Write the Lewis dot structure for each of the following atoms 1. 5. 9. 2. 6. 10. 3. 7. 11. 4. 8. 12.