Cells-The basic unit of life
advertisement

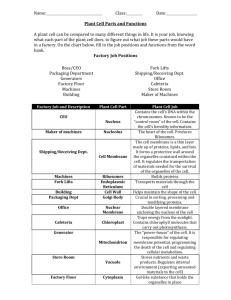
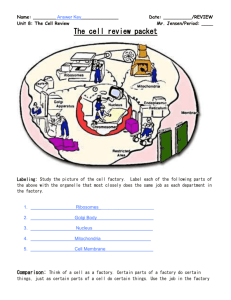
Cells-The basic unit of life The cell theory states: 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things. 3. Living cells come only from other living cells. Cell Wall- Strong and stiff in a plant cell. The cell wall allows water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and certain dissolved materials to pass through it. THIS PART OF THE CELL IS ONLY FOUND IN PLANTS and it helps provide protection & support so the plant can grow tall. ANALOGY- In a factory, the cell wall would be similar to the walls that are around the building. Cell Membrane- A thin, flexible envelope that surrounds the cell. It is the part of the cell that determines what enters and leaves the cell. In the plant cell it is just inside the cell wall. ANALOGY- In a factory, the cell membrane would be similar to the enter and exit doors. Nucleus- The “control center” or the “brain” of the cell. The nucleus controls all cell activities. ANALOGY- In a factory, the nucleus is similar to the main office & planning department. Nuclear Membrane- Thin membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell. It is similar to the cell membrane, by allowing material to flow in and out of the nucleus. ANALOGY- In a factory, the nuclear membrane is similar to the door to the main office! 1 Chromosomes- Thin threads that take up most of the space in the nucleus. They are made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that helps to pass new traits to new cells. ANALOGY- In a factory, the chromosomes are like the blueprints of the factory. An identical factory can be built from these plans. Nucleolus- “Little nucleus”. It is made up of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein. The nucleolus helps to create more RNA for the cell. ANALOGY- In a factory, the nucleolus is similar to a worker in the office. Since the blue prints can not leave the office (chromosomes), the worker (nucleolus) makes sure the jobs are carried out correctly. Cytoplasm- Thick jelly-like material that surrounds the nucleus. This material is constantly moving, protecting the different parts of the cell. ANALOGY- In a factory, the cytoplasm is similar to the factory’s floor. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- Tubular like structure that is responsible for the transportation of proteins. Some of these passageways are connected to the cell membrane. ANALOGY- In a factory, the Endoplasmic Reticulum is similar to the conveyor belts moving important parts throughout the factory and out of the factory. Ribosomes- The protein making sites of the cell. They can be found in or on the Endoplasmic Reticulum, or freely floating throughout the cell. ANALOGY- In a factory- the ribosomes can be compared to the machines in the factory that manufactures the finished products. Mitochondria- Supply most of the energy to the cell. They are known as the “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy for cells through cellular respiration. 2 ANALOGY- In a factory, the mitochondria are similar to the generator that helps create electricity for the factory. Vacuoles- A large, round, water-filled sac that floats around the cytoplasm. Vacuoles are like storage tanks; wastes, food & other materials are stored inside this organelle. Most plants and some animal cells have vacuoles. They are large in a plant cell and small in an animal cell. ANALOGY- In a factory, the vacuoles are like garbage cans (to hold waste) and grocery bags (to hold water & food). Lysosomes- Small, round structures involved with digestive activities of the cell. They are common in animal cells by not often seen in plant cells. ANALOGY- In a factory, the Lysosomes are like a garbage disposal in the factory. They help get rid of the waste in the cell. Chloroplasts- Large, irregularly shaped green structures, they are special food making structures. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. THEY ARE FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS. Chlorophyll- They capture the energy of sunlight and use it to make food for the plant cell. 3