Physics topical formula set
advertisement
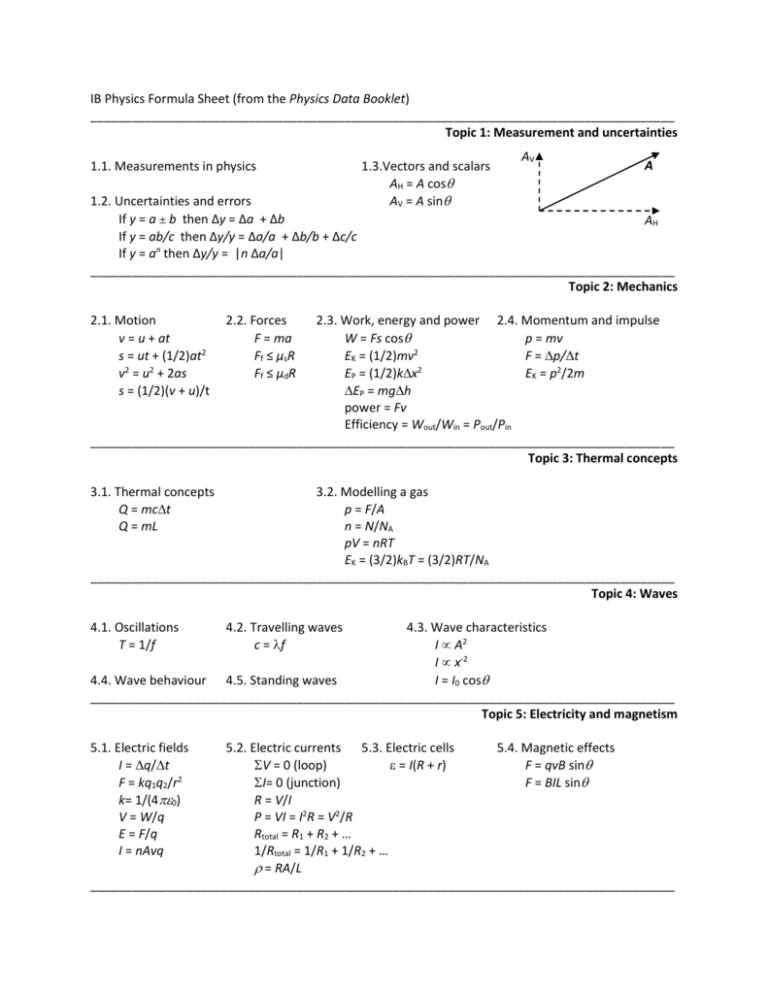
IB Physics Formula Sheet (from the Physics Data Booklet) _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 1: Measurement and uncertainties 1.1. Measurements in physics 1.3.Vectors and scalars AH = A cos AV = A sin AV A 1.2. Uncertainties and errors If y = a ± b then ∆y = ∆a + ∆b AH If y = ab/c then ∆y/y = ∆a/a + ∆b/b + ∆c/c If y = an then ∆y/y = |n ∆a/a| _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 2: Mechanics 2.1. Motion v = u + at s = ut + (1/2)at2 v2 = u2 + 2as s = (1/2)(v + u)/t 2.2. Forces F = ma Ff ≤ µsR Ff ≤ µdR 2.3. Work, energy and power 2.4. Momentum and impulse W = Fs cos p = mv EK = (1/2)mv2 F = p/t 2 EP = (1/2)kx EK = p2/2m EP = mgh power = Fv Efficiency = Wout/Win = Pout/Pin _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 3: Thermal concepts 3.1. Thermal concepts Q = mct Q = mL 3.2. Modelling a gas p = F/A n = N/NA pV = nRT EK = (3/2)kBT = (3/2)RT/NA _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 4: Waves 4.1. Oscillations T = 1/f 4.3. Wave characteristics I A2 I x-2 4.4. Wave behaviour 4.5. Standing waves I = I0 cos _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 5: Electricity and magnetism 5.1. Electric fields I = q/t F = kq1q2/r2 k= 1/(40) V = W/q E = F/q I = nAvq 4.2. Travelling waves c = f 5.2. Electric currents 5.3. Electric cells 5.4. Magnetic effects V = 0 (loop) = I(R + r) F = qvB sin I= 0 (junction) F = BIL sin R = V/I P = VI = I2R = V2/R Rtotal = R1 + R2 + … 1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … = RA/L _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 6: Circular motion and gravitation 6.1. Circular motion 6.2. Newton’s law of gravitation v = r F = GMm/r2 2 2 2 a = v /r = 4 r/T g = F/m 2 2 F = mv /r = m r g = GM/r2 _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 7: Atomic, nuclear and particle physics 7.1. Discrete energy and radioactivity E = hf = hc/E 7.2. Nuclear reactions E= m c2 7.3. The structure of matter Charge Quarks Baryon number (2/3)e u c t 1/3 -(1/3)e d s b 1/3 All quarks have a strangeness number of 0 except the strange quark that has a strangeness number of -1 Charge Leptons -1e e 0 e All leptons have a lepton number of 1 and antileptons have a lepton number of -1 Gravitational Weak Electromagnetic Strong Particles experiencing All Quarks, leptons Charged Quarks, gluons Particles mediating Graviton W +, W - , Z 0 Gluons _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 8: Energy production 8.1. Energy sources Power = energy/time Power = (1/2) Av3 8.2. Thermal energy transfer P = eAT4 max = 2.9010-3/T I = power/A albedo = total scattered power / total incident power _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 9: Simple harmonic motion 9.1. SHM 9.2. Single-slit 9.3. Interference = 2/T = /b n = d sin 2 a = - x Constructive interference: 2dn = (m + ½) x = x0 sin t; x = x0 cos t; Destructive interference: 2dn = m v = x0 cos t; v = -x0 sin t; v = ± sqrt (x02 – x2) 9.4. Resolution 9.5. Doppler effect 2 2 2 EK = (1/2)m (x0 – x ) = 1.22 /b Moving source: f ‘ = fv/(v ± us) 2 2 ET = (1/2)m x0 R = (/∆) = mN Moving observer: f ‘ = f(v ± uo)/v Pendulum: T = 2 sqrt (l/g) ∆f/f = /∆ v/c Mass-spring: T = 2 sqrt (m/k) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 10: Fields 10.1. Describing fields W = q∆Ve W = m∆Vg 10.2. Fields at work Vg = -GM/r; Ve = kq/r g = -∆Vg/∆r; E = -∆Ve/∆r EP = mVg = -GMm/r EP = qVe = kq1q2/r 2 FG = Gm1m2/r FE = kq1q2/r2 Vesc = sqrt (2GM/r) Vorbit = sqrt (GM/r) _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 11: Electromagnetic induction 11.1. Induction = BA cos = -N ∆/∆t = Bvl = BvlN 11.2. Power generation 11.3. Capacitance Irms = I0/2 C = q/V Vrms = V0/2 Cparallel = C1 + C2 + … = RC R = V0/I0 = Vrms/ Irms 1/Cseries = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … q = q0e-t/ Pmax = I0V0 C = 0A/d I = I0e-t/ 2 Pavg = (1/2) I0V0 E = (1/2)CV V = V0e-t/ p/s = Np/Ns = Is/Ip _____________________________________________________________________________________ Topic 12: Quantum and nuclear physics 12.1. Interaction of matter with radiation 12.2. Nuclear physics 2 E = hf P(r) = || ∆V R = R0A1/3 Emax = hf - ∆x∆p h/4 N = N0e-t E = -13.6/n2 eV ∆E∆t h/4 A = N0e-t mvr = nh/2 sin = /d _____________________________________________________________________________________ Option A: Relativity A.1. Beginnings of relativity x’ = x – vt u’ = u - v A.2. Lorentz transformations A.3. Spacetime diagrams = (1 – v2/c2)-1/2 = tan-1(v/c) x’ = (x – vt); ∆x’ = (∆x – v∆t) t’ = (t – vx/c2); ∆t’ = (∆t – v∆x/c2) u’ = (u – v)/(1 – uv/c2) ∆t = ∆t0 L = L0/ (ct’)2 – (x’)2 = (ct)2 – (x)2 A.4. Relativistic mechanics (HL only) A.5. General relativity (HL only) 2 E = m0c ∆f/f =g∆h/c2 2 E0 = m0c Rs = 2GM/c2 EK = ( - 1)m0c2 ∆t = ∆t0/sqrt(1 – Rs/r) p = m0v E2 = p2c2 + m02c4 qV = ∆EK _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Option B: Engineering physics B.1. Rigid bodies and rotational dynamics = Fr sin = 2f I = mr2 f = I + t = I f2 = I2 + 2 = It + (1/2)t2 L = I EKrot = (1/2)I2 B.2. Thermodynamics Q = U + W U = (3/2)nRT S = Q/T pV5/3 = const W = pV pV5/3 = const W = pV = Wuseful/Einput carnot = 1 – Tcold/Thot B.3. Fluids and fluid dynamics (HL only) B.4. Forced vibrations and resonance (HL only) B = fVfg FD = 6rv Q = 2(Estored/Edissipated/cycle) P = P0 + fgd R = vr/ Q = 2fres(Estored/Ploss) Av = constant (1/2) v2 + gz + p = const _____________________________________________________________________________________ Option C: Imaging C.1. Introduction to imaging 1/f = 1/v + 1/u P = 1/f m = hi/ho = -v/u M = i/o C.2. Imaging instrumentation M = i/o M = fo/fe Mnear point = D/f + 1 Minfinity = D/f C.3. Fibre optics n = 1/sin c attenuation = 10 log (I/I0) C.4. Medical imaging (HL only) Lf = 10 log (I1/I0) I = I0 e-x µx1/2 = ln 2 Z = pc _____________________________________________________________________________________ Option D: Astrophysics D.1. Stellar quantities d(parsec) = 1/p(arc-second) L = AT4 B = L/(4d2) D.2. Stellar evolution max = 2.910-3 m K L M3.5 D.3. Cosmology z = /0 v/c z = R/R0 – 1 v = H0d T 1/H0 D.4. Stellar processes (HL only) D.5. Further cosmology (HL only) v = sqrt(4G/3) r c = 3H2/(8G) _____________________________________________________________________________________









