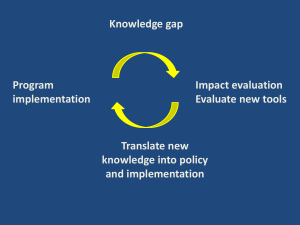
core course Antwerp
advertisement
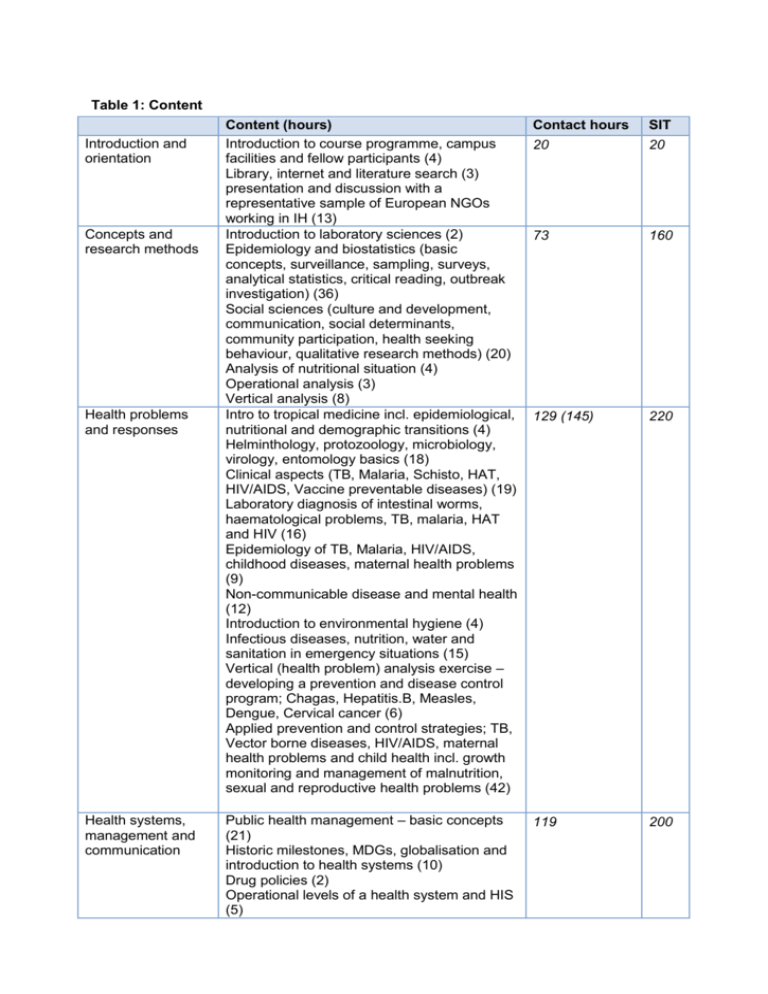
Table 1: Content Introduction and orientation Concepts and research methods Health problems and responses Health systems, management and communication Content (hours) Introduction to course programme, campus facilities and fellow participants (4) Library, internet and literature search (3) presentation and discussion with a representative sample of European NGOs working in IH (13) Introduction to laboratory sciences (2) Epidemiology and biostatistics (basic concepts, surveillance, sampling, surveys, analytical statistics, critical reading, outbreak investigation) (36) Social sciences (culture and development, communication, social determinants, community participation, health seeking behaviour, qualitative research methods) (20) Analysis of nutritional situation (4) Operational analysis (3) Vertical analysis (8) Intro to tropical medicine incl. epidemiological, nutritional and demographic transitions (4) Helminthology, protozoology, microbiology, virology, entomology basics (18) Clinical aspects (TB, Malaria, Schisto, HAT, HIV/AIDS, Vaccine preventable diseases) (19) Laboratory diagnosis of intestinal worms, haematological problems, TB, malaria, HAT and HIV (16) Epidemiology of TB, Malaria, HIV/AIDS, childhood diseases, maternal health problems (9) Non-communicable disease and mental health (12) Introduction to environmental hygiene (4) Infectious diseases, nutrition, water and sanitation in emergency situations (15) Vertical (health problem) analysis exercise – developing a prevention and disease control program; Chagas, Hepatitis.B, Measles, Dengue, Cervical cancer (6) Applied prevention and control strategies; TB, Vector borne diseases, HIV/AIDS, maternal health problems and child health incl. growth monitoring and management of malnutrition, sexual and reproductive health problems (42) Contact hours SIT 20 20 73 160 129 (145) 220 Public health management – basic concepts (21) Historic milestones, MDGs, globalisation and introduction to health systems (10) Drug policies (2) Operational levels of a health system and HIS (5) 119 200 HRM, international policy and actors (6) Nutritional policies (4) Emergency situations trends, policy and organizational aspects (11) Organization of district health services incl. community participation, resource management, financing, local health policy (18) Organisational aspects of disease control programmes (42) Table 2: Structure of the course Building blocks of the core course Introduction to health care organisation in LMIC (3 ½ weeks) Integrated TB care (1 week) HIV/AIDS: from patient to policy (1 ½ week) Vector-borne diseases: a comprehensive approach to prevention and case management (2 weeks) Targeting health of the next generation (1 week) Contents Introduction to course programme, facilities and participants Literature search Concepts and tools in public health, epidemiology and statistics International health issues Non-communicable diseases Mental health Health care seeking behaviour Epidemiology Laboratory diagnostics Clinical aspects and treatment Control strategies Health service organisation Critical reading Epidemiology Natural evolution, staging, clinical manifestations, diagnosis ART, PEP, PMTCT Organisational aspects HIV prevention and control Human resources for health International actors Pathogens, lab investigation, vector dynamics, clinical features, case definition, drugs and resistance, disease control strategies for malaria, human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), schistosomiasis and leishmaniasis Home-based treatment Disease surveillance, community participation and drug policies Critical reading Epidemiology of childhood illnesses Vaccine preventable diseases and vaccines HIV and TB in children Analysis of nutritional situation Applied prevention and control Hours (SIT) 120 45 70 90 45 strategies; child health incl. growth monitoring, EPI-IMCI and management of malnutrition Nutritional policies Critical reading Safe motherhood: a complex problem Epidemiology of maternal health requiring a systemic approach problems (1 week) Obstetric complications, infertility, abortion and post abortion care, sexual violence, family planning Applied prevention and control strategies; Operational levels in a system, HIS Monitoring and evaluation Critical reading Health care organisation in an Infectious diseases, water and emergency situation (1 week) sanitation, nutrition in emergencies Outbreak investigation and control Survey and sampling Protection Trends in emergency care Health care organisation in refugee camp Health care delivery systems for Organization of district health services defined populations (1 ½ week) incl. community participation, resource management, financing, local health policy Operationalisation of a disease control programme Infection control Qualitative research Laboratory diagnostics, blood transfusion Exams (4 half days) after 2 weeks reserved for personal study 50 50 65 65