LESSON PLAN
advertisement

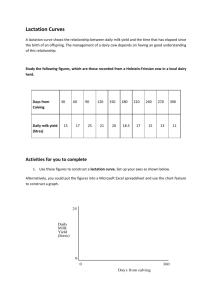
Rigor/Relevance Framework LESSON PLAN Knowledge Area and/or Course: Agricultural Science - Dairy Industry Lesson Title: Dairy Terminology No. Periods: 1-2 6 5 4 3 2 1 C D Assimilation _______ Adaptation _______ A B Acquisition __ X___ Application _______ 1 Teacher Goal(s): 2 3 4 Application 1. Have students learn appropriate vocabulary. 2. Effectively use an outline format in notebooks. 3. Recognize the different phases of a animal’s life cycle. Objectives: The student will be able to (TSWBT). (Oregon Skill Set numbers in parentheses at the end of the objective statement.) 1. Define commonly used dairy terminology. (AGPC01.01.01.01, AGPC01.01.01.02) 2. Identify different phases in the dairy animal’s life cycle. (AGPC01.03.01.01) State Standards met by Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. Category Subject Common Curr. Goal CRLS Science Science CRLS Problem Solving Life Science Life Science Teamwork Communication Heredity Organism Communication Materials, Equipment, Audio-Visual Aids: 1. PowerPoint projector. -lesson 2 slideshow 2. Photocopies of worksheet. Text books (Animal Science - James R. Gillespie), Internet, Dairy Magazines. Benchmark & Number Criteria 2 8:3 PASS PASS References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. www.ams.usda.gov/dairy www.oregon.gov/ODA/ http://www.aae.wisc.edu Hoard’s Dairyman Glenrose FFA Georgia Agricultural Education www.epa.gov/oecaagct/ag101/dairyphases.html http://www.epa.gov/oecaagct/ag101/ dairyglossary.html#lacta Knowledge: 1=awareness; 2=comprehension; 3=application; 4=analysis; 5=synthesis; 6=evaluation Application: 1=knowledge in one discipline; 2=apply knowledge in one discipline; 3=apply knowledge across disciplines; 4=apply knowledge to real-world predictable situations; 5=apply knowledge to real-world unpredictable situations 5 Anticipatory Set/Introduction/Motivation/Interest Approach: Review Yesterday’s Lesson: Yesterday we went over breeds of dairy cattle and started breed posters. Have students take out a piece of paper and label 1-10. Use the PowerPoint provided to give the quiz (1-10). KNOWLEDGE QUIZ (1-6) Name the six most popular dairy breeds in the United States. A. Aryshire B. Brown Swiss C. Guernsey D. Jersey E. Holstein F. Shorthorn 7. Which breed produces more pounds of milk per body weight than any other dairy breed? -Jersey 8. Which breed produces milk that is high in beta-carotene? -Guernsey 9. Which breed is considered a dual purpose breed? -Milking Shorthorn 10. This is one of the oldest Dairy breeds. -Brown Swiss Set: In groups, students will search for definitions of dairy terms. The handout (worksheet 2.1 ) is attached. The group of students that finds the most correct answers wins. Give students the first 10-15 minutes of class to see how many terms they can find. Once time is up, go through each term in detail. The students with the most correct answers will receive 10 extra credit points. Every student will be graded on participation and turning a paper in. Transition (Use Objective): Before we start digging into the dairy industry it is critical that we have a proper working knowledge of general terminology. 1. Define commonly used dairy terminology. 2. Identify different phases in the dairy animal’s life cycle. Strategy – Includes Teacher Activity, Student Activity, Questions/Answers and Objectives Objective 1: Teacher: Use PowerPoint to go over worksheet 2.1 Students: Correct worksheets and take notes along side the ones that are already on the worksheet. __________________________________ Q: Why do we castrate bulls? A: If you are going to fatten them for meat, they will gain better and taste better. Dairy bulls are also the meanest and most unpredictable bulls. Some farmers only breed artificially because of this. Castrating dairy bulls makes them gentler. A bull that is castrated is called a steer. Q: A gilt is to a pig as a __________ is to a cow. A: Heifer Q: Does a dairy want to have more bull (male) calves or heifer (female) calves? A: heifers, because dairy farmers produce milk and only female cattle can do that. If you were a beef rancher you would want more bulls, because they get more money/pound. Q: What is a cow? A: female dairy animal that has had a calf. When the cow has a calf it is called calving. Q: The first milk the cow gives following calving is called? A: Colostrum is vital for new born calves to receive. If they don’t get this they probably won’t live. If a cow has a lot of Colostrum her first milking after calving farmers will freeze it to use for calves in the future. Colostrum is readily absorbed and very critical! Subject Matter Outline/Problem and Solution (Application Points Lace in Throughout Lesson) (Modeling, Guided Practice, and Content) Dairy Terminology Dairy Cow - A bovine from which milk production is intended for human consumption, or is kept for raising replacement dairy heifers. __________________________________________ 1. Bull – uncastrated male dairy animal. 2. Steer – castrated male dairy animal. 3. Heifer – female dairy animal that has not had a calf. (Usually less than 18-24 months of age) A bovine female less than three years of age who has not borne a calf. Young cows with their first calves are often called first-calf heifers. 4. Calves - male or female dairy animals less than one year of age. (A young male or female bovine. Usually referred to as calves until reaching sexual maturity) 5. Cow – female dairy animal that has had a calf. (A mature female bovine. Usually referring to any dairy females that have borne a calf. Some may consider females having given birth only once as "first-calf heifers" until they have a second calf.) 6. Calving – the act of parturition in cattle. 7. Colostrum - First milk following calving. High in fat, protein, and immunoglobulin’s that may be directly absorbed by the newborn calf in its first 24 hours of life. Q: Have you seen those igloo-looking things sitting at farms? A: Those are little houses (hutches) that calves live in. Unlike beef cattle, when a dairy cow has a baby it is removed from the mother in just a few short hours. This allows the mother to produce without having to feed a calf, and allows the calf to be raised in a clean environment. 8. Hutch - An individual housing unit for young calves. Often made of white fiberglass or polyvinyl. Q: The percent of fat in the milk is called? (hint: Jerseys are known to have high quantities of this.) A: butterfat is good for making cheese. 10. butterfat - percent of fat in the milk Q: Where does the farmer’s main income come from? A: Milk Production 11. milk production - amount in pounds of milk that a cow produces during a lactation period Q: Why is it important to produce the most milk you can? A: Milk production pays (the more, the better). Milk production is the amount in pounds of milk that a cow produces during a lactation period 12. lactation - span of time that a cow is producing milk Q: An average dairy cow milks how many months in a year? A: 10 months (305 days), this is called the lactation. The other two months is called the cow’s dry period (cows rest and wait to have another calf). Q: What is the name of the system responsible for storing and producing milk? A: Mammary System Q: How many gallons of milk can the average cow give in a day? A: 6 Q: Can you breed cows to milk more? A: Yes, you can look at different pedigrees and select a bull that has the characteristics you want, and then breed your cows artificially to that bull. Q: What is culling? A: To remove a cow from the herd for low milk production, or involuntary culling of cows for reasons of health or injury. 9. dairy character - characteristics indicating that the animal will be useful in the dairy industry 13. mammary system – system in the cow responsible for storing and producing milk A. Udder - The encased group of mammary glands provided with teats or nipples as in a cow, ewe, mare or sow. Also referred to as a bag. 14. pedigree - register of lines of ancestry A. Sire - Father or male parent in a pedigree. B. Dam - Mother or female parent in a pedigree. 15. breed characteristics - physical traits that differentiate from breed from anothe 16. Cull/Cull Cow - To remove a cow from the herd. Culling reasons in clued voluntary culling of cows for low milk production, or involuntary culling of cows for reasons of health or injury. Q: How many stomach compartments do cows have? A: (4) rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasums Q: Animals having four stomach compartments are called? A: Ruminant How do farmers get the milk from the dairy cow to the storage tank? -Parlors - they come in many types: A. Flat Barn B. Walk-through C. Herringbone D. Parallel E. Swing F. Rotary __________________________________ Objective 2: Teacher: Hand out worksheet 2.2 Go over PowerPoint diagram on the typical life-cycle of a cow. Students: Fill out worksheet 2.2 and take notes. 17. Ruminant - Animals having four stomach compartments - rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasums - through which food passes in digestion. These animals chew their cud or regurgitate partially digested food for further breakdown in the mouth. Ruminant animals include cattle, sheep, goats, deer and camels. 18. Parlor - The specialized area on the dairy farm where milking is performed. Parlors come in many types: G. Flat Barn H. Walk-through I. Herringbone J. Parallel K. Swing L. Rotary __________________________________________ Stages of a dairy cows life: (1) birth to calving (2) first calf dams (3) mature lactating cows (4) dry periods A cow typically remains in the dairy herd till about 5 years of age, although many cows are capable of remaining productive in the herd for 12 to 15 years. Following birth, the calf is usually removed from her dam (cow) after only a few hours. The newborn calf is fed milk or milk replacer until weaning at 6 to 8 weeks of age. The calf will then be raised until it reaches appropriate breeding weight at about 15 months of age. Heifers are then maintained and continue to grow through their gestation. They usually calve, or give birth, at about 24 months of age. However, they do not reach mature size until at least 4 years of age. Q: How long does it take until a cow will have a baby after getting pregnant? A: 9 months. This is called the gestation period. Q: Why is it important that cows have calves each year? A: By having calves allows cows to continue producing milk. It also gives them a two month break to rest. Q: How old should a calf be before it is weaned from milk? A: 6-8 weeeks. Q: How old should a heifer be when breeding for the first time? A: 15 months. A heifer should have her first calf at 24 months. With a 9 month gestation period, being bred at 15 months allows the heifer to calve by 24 months. Closure/Summary/Conclusion (Tie in Objectives) Having knowledge of the terminology used in the dairy industry will serve as a foundation for the rest of the unit. If you can become familiar with these terms, it will help you to understand the dairy industry as a whole. Knowledge of terminology will also help for future class discussions and assignments. It is also important to understand different phases of a cow’s life and to understand their life-cycle. Students will be responsible for all the terms discussed today. Evaluation: (Authentic forms of Evaluation, Quizzes, or Written Exam) Students will be held responsible for all terms discusses in class. These terms will show up on a quiz the following period and throughout the dairy unit as we discuss the dairy industry. Student will also be responsible for these terms on the dairy unit final exam. Assignments: (Student Activities Involved in Lesson/Designed to Meet Objectives) Attached to this lesson are two worksheets that students must complete (Worksheet 2.1 Dairy Terminology & Worksheet 2.2 Dairy Cow Life-Cycle). Students will be required to fill this out before the end of the class. They will have a chance to do it on their own at first and after 10-15 minutes, we will go over all the terms in class and make sure they found the correct answers. Students will be required to write down a few definitions that are not on the worksheets as well. This will require them to pay attention throughout the period and not just copy down notes. Lesson Reflection I felt the lesson went well. A lesson on terminology can be a challenging to teach, but having a handout that didn’t require the students to write everything out really helped them keep up and pay attention. I also felt that letting students work on the terms before I went over them challenged the students to think on their feet and search in different books, magazines, and the internet for correct definitions. It also gave them a chance to work in groups and develop team work skills. Having examples (pictures) of the terms that were discussed would also help students visualize what was taught. If I had been closer to a dairy farm this would have been a good lesson to go and have students discover first hand some of the dairy terminology.