17. Bacterial Genetics III
advertisement

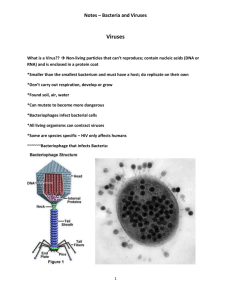
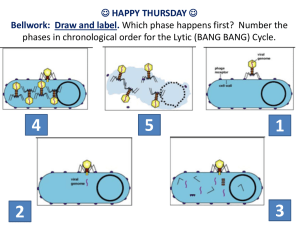
Biology 212 General Genetics Lecture 17: Bacterial Genetics III: Transduction Spring 2007 Reading: Chap. 7 pp. 259-264; 267-274 Lecture outline: 1. Lytic cycle of bacterial viruses 2. Generalized transduction 3. Lysogenic viruses 4. Specialized transduction Lecture: 1. Lytic cycle of bacterial viruses Process in which the virus infects the host cell, reproduces, then lyses the cell, releasing many progeny viruses. Examples of lytic viruses: T2, T4, P1; lambda has both lytic and lysogenic cycles 1) Virus attaches to bacteria and injects its DNA 2) Bacterial enzymes are borrowed to reproduce the phage DNA, making multiple copies 3) Bacterial DNA is broken down 4) Viral genes are transcribed into mRNAs 5) Viral mRNAs are translated into viral proteins 6) New virus particles are assembled from DNA and proteins 7) Virus causes cell lysis, releasing many progeny viruses Viruses are important to the history of molecular biology Genetic information to make progeny viruses is determined by its DNA (Hershey Chase Experiment) Viruses can mediate gene transfer between bacteria 2. Generalized transduction = Transfer of bacterial DNA from one cell to another mediated by a virus. In generalized transduction, any gene can be transferred. Process of generalized transduction is carried out be some lytic viruses, for example, P1 virus. Fig. 7.16 1) Virus DNA enters bacteria 2) Viral DNA is replicated 3) Bacterial chromosome is fragmented 1 4) Viral genes are expressed 5) As new viral particles are assembled, some accidently take up bacterial DNA. 6) Transfer of genes from one bacteria to another can be determined by selective plating Virus infects leu+ donor bacterium Some progeny viruses contain leu+ gene Introduce into leu- recipient bacterium Non-recombinants leuWon’t grow on minimal medium Recombinants leu+ Grow on minimal medium 3. Lysogenic viruses Some viruses can also undergo a lysogenic cycle in which the virus integrates and sits quietly in the bacterial chromosome. Example: lambda virus Fig. 7.22 1) Lambda virus infects the host bacteria 2) Lambda virus circularizes using cohesive ends (cos sites) 3) Lambda integrates into the bacterial chromosome. Similar regions (att sites) mediate pairing. 4) When lambda is integrated into the bacterial chromosome, it gets replicated along with the bacterial DNA 5) The lambda genes are not expressed while the virus is integrated due to action of the phage repressor protein (cI) 4. Specialized transduction: Transfer of only a select set of genes mediated by a lysogenic virus. Specialized transducing phage are produced by imprecise excision of the lambda genome from the bacterial chromosome. Transducing particles usually pick up only a neighboring gene, either gal or bio 2