Endocrinology 8c – Pharmacology of Oxytocin
advertisement
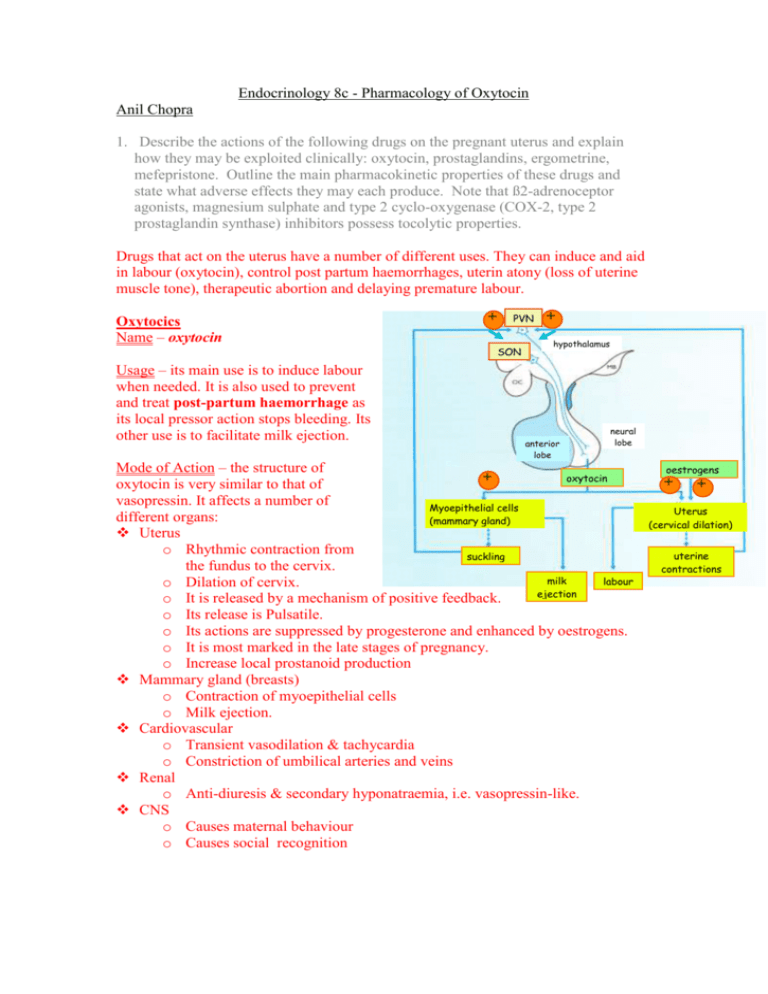
Endocrinology 8c - Pharmacology of Oxytocin Anil Chopra 1. Describe the actions of the following drugs on the pregnant uterus and explain how they may be exploited clinically: oxytocin, prostaglandins, ergometrine, mefepristone. Outline the main pharmacokinetic properties of these drugs and state what adverse effects they may each produce. Note that ß2-adrenoceptor agonists, magnesium sulphate and type 2 cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2, type 2 prostaglandin synthase) inhibitors possess tocolytic properties. Drugs that act on the uterus have a number of different uses. They can induce and aid in labour (oxytocin), control post partum haemorrhages, uterin atony (loss of uterine muscle tone), therapeutic abortion and delaying premature labour. Oxytocics Name – oxytocin Usage – its main use is to induce labour when needed. It is also used to prevent and treat post-partum haemorrhage as its local pressor action stops bleeding. Its other use is to facilitate milk ejection. + PVN SON + hypothalamus anterior lobe neural lobe Mode of Action – the structure of + oxytocin oxytocin is very similar to that of vasopressin. It affects a number of Myoepithelial cells different organs: (mammary gland) Uterus o Rhythmic contraction from suckling the fundus to the cervix. milk labour o Dilation of cervix. ejection o It is released by a mechanism of positive feedback. o Its release is Pulsatile. o Its actions are suppressed by progesterone and enhanced by oestrogens. o It is most marked in the late stages of pregnancy. o Increase local prostanoid production Mammary gland (breasts) o Contraction of myoepithelial cells o Milk ejection. Cardiovascular o Transient vasodilation & tachycardia o Constriction of umbilical arteries and veins Renal o Anti-diuresis & secondary hyponatraemia, i.e. vasopressin-like. CNS o Causes maternal behaviour o Causes social recognition oestrogens + + Uterus (cervical dilation) uterine contractions Giving birth Mating (released on orgasm) in both sexes) OT (VP) release in the brain Promotes monogamous bonds in certain mammalian species* Promotes parent-offspring bonds in certain mammalian species* Promotes social recognition memory and trust Side Effects and Pharmacokinetics Given i.v. or as an intranasal spray (generally when using it for milk ejection). It is distributed in extracellular fluid and is metabolised in the liver and kidney. Its ½ life is 5 minutes. Side effects: Compromised placental exchange of O2/nutrients foetal distress Foetus forced against an undilated cervix lacerations/trauma Uterine rupture Transient but serious hypotension with reflex tachycardia Water intoxication of mother and foetus It has been shown that vasopressin and oxytocin receptors are expressed on reward centres. These are dysfunctional in autism and activated when we see someone we love. Name – ergometrine Usage – used to treat: - Parkinson’s disease - Hyperprolactinaemia - Migraine - Late stages of labour - Patients at high risk post partum haemorrage, i.v. after delivery of the shoulders. - Post-partum atony of the uterus – oral Mode of action – it causes more prolonged series of contraction during labour and increase myometrial tone. It causes constriction of umbilical and placental vessels. Side Effects and Pharmacokinetics It is administered i.v. metabolised by the liver and has a half life of 3-4 hours. - Contra-indications o Pregnancy prior to the 3rd stage of labour o Pre-eclampsia and other vascular disease Side effects • Abdominal pain • Hypertension • Anginal pain • Nausea/vomiting Name – prostaglandins and abortifaciens. Dinoprostone, gemeprost, carboprost Usage – used in: - Induction of abortion - dinoprostone - Induction of cervical ripening – at term: dinoprostone - Post-partum haemorrhage in those resistant to oxytocin and ergometrine - cabropost Mode of Action – these stimulate contractions throughout pregnancy and cause ripening of the uterus by softening the tissue. Side Effects and Pharmacokinetics Side Effects • Potentiation of actions of oxytocin • Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea • Hypertension (PGF ), hypotension (PGE2) • Pyrexia Progesterone Receptor Blockers Name – mifepristone Usage – early therapeutic abortion (up to 63 days – 9 weeks) and softening and dilation of the cervix before suction abortion. Mode of Action – mifepristone is an antagonist at progesterone receptors. Side Effects and Pharmacokinetics It is administered orally, enters cells but distributed by binding proteins. It is metabolised by the liver and kidney and excreted in the kidneys. Its ½ life is around 20-40h. Side effects may include: - vaginal bleeding - headache Tocolytics Tocolytics reduce motility by binding to β2 adrenergic receptors in the myometrium, increasing intracellular cAMP resulting in relaxation of the uterine muscle. They are used to delay premature labour