File
advertisement

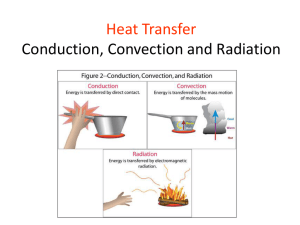
Name _________________________________________ Section _____________ Week 11: October 21, 2008 Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Student Performance Indicator: Related pages in the textbook: Key Points: Predict the heat flow between objects Chapter 4 Section 3 (4.3): pages 116-119 Conduction is the process that moves energy from one object to another when they are touching physically Convection is the process that transfers energy by the movements of large numbers of particles in the same direction within a liquid or gas Radiation is energy that travels as electromagnetic waves. I. Energy moves as heat in three ways (page 116) a. Heat is the transfer of energy from objects at a _____________________ temperature to objects at a ___________________ temperature. b. How does energy get transferred from a warmer object to a cooler one? 1. _____________________________ 2. _____________________________ 3. _____________________________ II. Conduction (page 117: the first three paragraphs) a. Conduction is the process that moves energy from one object to another when they are ________________________________________. b. If you have ever __________________________________________________, you have experienced conduction. c. Conduction occurs any time that objects at ______________________ temperatures come into contact. d. The average kinetic energy of particles in the warmer object is great than of the particles in the _____________________ object. e. As long as the objects are in contact, conduction continues until the temperature of the objects are _____________________. f. Conduction can also occur within a ________________________________________. g. In this case, energy is transferred from the ________________________ part of the object to the ______________________ part of the object. h. Example: Suppose you put a metal spoon into a cup of hot cocoa. i. Energy will be ___________________________ from the ________________ end of the spoon to the ______________________ end until the temperature of the entire spoon is the ______________________. III. Convection (page 118) a. Energy can also be transferred through the _________________________________________________. b. Convection is the process that transfers energy by the movement of large numbers of ______________________ in the ___________________________________ within a liquid or gas. c. In most substances, as the kinetic energy of particles ______________________, the particles ____________________________ over a larger area. An increased distance between particles causes a decrease in the _________________________ of the substance. d. Convection occurs when a _______________________, denser mass of the gas or liquid replaces a __________________________, less dense mass of the gas or liquid by pushing it upward. e. Convection is a cycle in nature responsible for most ___________________ and ________________ _______________________. f. Convection in air 1. Cooler, ____________________ air flows in underneath the _________________, less dense air and pushes the warmer air upward. 2. When the air ________________, it becomes ______________ dense than the ____________________ air beneath it. 3. The cooled air sinks and moves under the warmer air. g. Convection in liquids 1. Warm water that is ____________ dense than _________ water, so the warmer water is pushed upward as the cooler, denser water moves underneath. 2. When the warm water that has been pushed up cools, its density ______________________. 3. This cycle continues when this more dense water sinks, pushing warmer water up again. IV. Radiation (page 119) a. Radiation is energy that travels as _____________________________________________________________. b. Examples of electromagnetic waves include: 1. ____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ c. The ____________ is the most significant source of radiation that you experience on a daily basis. i. You can feel radiation as _____________ when radiation from the sun warms your skin. ii. The radiation emitted from the sun strikes the particles in your body and transfers ___________________. iii. The transfer of energy increases the movement of ___________________ in your skin, which you detect as an increase in _________________________________. iv. Of course, you are not the only object on Earth that absorbs the Suns’ radiation. Everything, from air to concrete, absorbs radiation that increases particle motion and produces an ____________________ in temperature. d. When radiation is emitted from one object and then is absorbed by another, the result if often a transfer of ___________________ through ______________. e. Like both conduction and convection, radiation can transfer energy from ______________ to ____________________ objects. f. *However, radiation differs from conduction and convection in a very significant way. Radiation can travel through ___________________________________, as it does when it moves from the Sun to the Earth.