Document 7672498
advertisement

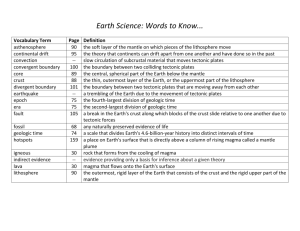
Name _________________________________ Class ________ Date __________ Plate Tectonics Unit Study Guide 1. A solid sphere of metal, mainly nickel and iron ________________________________ 2. A boundary along which two tectonic plates scrape past each other, and crust is neither formed nor destroyed ________________________________ 3. A layer of molten metal, mainly nickel and iron ________________________________ 4. An area where a column of hot material rises from deep within a planet’s mantle and heats the lithosphere above it, often causing volcanic activity at the surface______________________________ 5. A deep valley formed as tectonic plates move apart, such as along a mid-ocean ridge ________________________________ 6. The layer of rock in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents – Earth’s thickest layer ________________________________ 7. The process by which an oceanic tectonic plate sinks under another plate into Earth’s mantle ________________________________ 8. The layer of Earth made up of the crust and the rigid rock of the upper mantle, averaging about 40 kilometers thick and broken into tectonic plates __________________________ 9. An instrument that constantly records ground movements _____________________________ 10. A theory stating that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into huge plates that move and change in size over time. ________________________________ 11. The vibrations caused by an earthquake ________________________________ 12. Earth’s thinnest layer ________________________________ 13. A boundary along which two tectonic plates push together, characterized either by subduction or a continental collision. ________________________________ 14. A smaller earthquake that follows a more powerful earthquake in the same area ________________________________ 15. The layer in Earth’s upper mantle and directly under the lithosphere - rock is soft and weak ________________________________ 16. A fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other ________________________________ 17. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loop ________________________________ 18. In an earthquake, the point underground where the rocks first begin to move ________________________________ 19. One of the large, moving pieces into which Earth’s lithosphere is broken and which commonly carries both oceanic and continental crust ________________________________ 20. The force applied by an object pressing on, pulling on, or pushing against another object ________________________________ 21. The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake ________________________________ 22. The hypothesis that Earth’s continents move on Earth’s surface ________________________________ 23. A boundary along which two tectonic plates move apart, characterized by either a mid-ocean ridge or a continental rift valley ________________________________ 24. A hypothetical supercontinent that included all of the landmasses on Earth ________________________________ 25. A process in which the shaking of ground causes loose, wet soil to act like a liquid ________________________________ 26. A long line of sea-floor mountains where new ocean crust is formed by volcanic activity along a divergent boundary________________________________ 27. A process by which energy is transferred in gases and liquids, occurring when a warmer, less dense area of gas or liquid is pushed up by a cooler, more dense area of the gas or liquid. ________________________________ 28. A water wave caused by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide ________________________________ 29. A dense cloud of extremely hot gases and rock fragments ________________________________ 30. An opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt ________________________________ 31. Mountains that form as rocks move up or down along normal faults ________________________________ 32. A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air ________________________________ 33. A mountain that forms as convergent continental crust crumbles and bends ________________________________ 34. Molten rock that reaches Earth’s surface ________________________________ 35-37. List the 3 types of volcanoes: _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 38-40. List three types of plate boundaries and describe what happens at each. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________