Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
Survivor – Planet Earth
Unit Plan
Unit Overview
Unit Title
Survivor – Planet Earth
Unit Summary
Students embark on a journey of discovery about the structure and processes of planetary geology
and explore the impact of human action, behaviour and perspectives. They investigate how we
know about the structure of the planet, the formation of natural resources and the extraction of
them from the earth and how the use of these natural resources has an impact on the environment.
The unit incorporates the ethical issues surrounding the use of these resources. Students will
research human impact on the planet including pollution, exhaustion of natural resources and global
warming.
Curriculum Links
Science
Year Level
Stage 5 Year 9
Approximate Time Needed
35 x 60 minute periods
Unit Foundation
Standards/Syllabus Outcomes
New South Wales Syllabus Outcomes
Prescribed Focus Area
5.3 Evaluates the impact of applications of science on society and the environment
Knowledge and Understanding
5.9 Relates the development of the universe and the dynamic structure of Earth to models, theories
and laws and the influence of time
5.10 Assesses human impacts on the interaction of biotic and abiotic features of the environment
5.11 analyses the impact of human resource use on the biosphere to evaluate methods of
conserving, protecting and maintaining Earth’s resources
Skills
5.13 Accesses information from a wide variety of secondary sources
5.18 Selects and uses appropriate forms of communication to present information to an audience
5.19 Uses critical thinking skills in evaluating information and drawing conclusions
5.21 Uses creativity and imagination in the analysis of problems and the development of possible
solutions
Values and Attitudes
5.26 Recognises the role of science in providing information about issues being considered and in
increasing understanding of the world around them
5.27 Acknowledges their responsibility to conserve, protect and maintain the environment for the
future
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 1 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
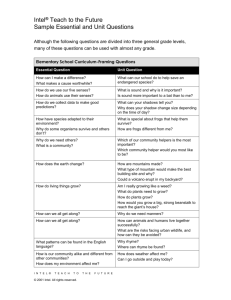
Curriculum-Framing Questions
Essential Question
Can planet Earth survive?
Unit Questions
How do geological processes change the planet?
How have geological processes affected human interaction with the
planet?
How do the short and long term implications of human actions impact
on the biotic and abiotic features of the planet?
Content Questions
What is continental drift?
What is the internal structure of the earth?
What are the effects of mining on the environment and society?
What are biotic and abiotic features of the planet?
What is an ecosystem?
How does the production of energy from renewable and non
renewable sources affect the environment?
What types of pollution exist in today’s world? What steps can be
taken to minimise pollution?
How will changes in global temperature affect the Earth?
What is the Kyoto Agreement and why did Australia delay signing the
agreement?
Do the Kyoto Protocols apply to all countries or just ‘first world’
countries?
How will the world survive if only some countries take steps to
address climate change?
Assessment Plan
Assessment Timeline
Before learning activities
begin
Brainstorming
KWL chart
Teacher Conference
Questioning
While students work on
learning activities
Brainstorming
Multimedia Rubric
Research
Teacher conference
Questioning
Group Plan
Wiki Rubric
Letter/E-mail
Kyoto Research Presentation
Student checklist of
completed tasks
Student feedback
Anecdotal notes
Blog Rubric
Debate/Forum
Newsletter
After learning activities end
Survey
Student quiz
Questioning
Rubrics - Products
Online student folio
Reflection
Evaluation
Product/unit
Assessment Summary
Assessment will be conducted over a range of tasks that will involve both group and individual work. It
will include the design of informational tools as groups and individuals. The production of multimedia
presentations, wiki and blog pages is to be teacher assessed; peer assessment would also be beneficial.
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
Assessment will also include a topic test and mini tests during the unit.
Unit Details
Prerequisite Skills
Students Prior Knowledge
Multimedia presentation, wiki development, blog development and word processing software
Flowcharting
Group work skills – understanding of the different roles of members of a group.
What conceptual knowledge and skills do students need to begin this unit?
How will students’ skills be enhanced, if necessary, to enable full participation in the unit?
Teachers’ Professional Learning
Revision of functions available through the use of programs utilised within the unit. For example
Microsoft PowerPoint*, Wikis*,Blogs*, Word*.
Wiki development, using http://www.wikispaces.com/site/for/teachers100k.
Intel® Teach Program to support professional development.
Development of evaluation tools such as checklists and rubrics.
Professional Learning Team.
Professional learning teams will be established on a grade basis.
Professional Reading.
Oz-Teacher. Net. The Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
http://rite.ed.qut.edu.au/oz-teachernet/index.php?module=ContentExpress&func=display&ceid=29.
NSW Department of Education and Training. Quality teaching framework.
https://www.det.nsw.edu.au/proflearn/areas/qt/index.htm
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Modelled
Whole class discussions involving joint constructions – creating class charts, writing and reviewing texts,
and creating multimedia products.
Guided
Providing scaffolding through small group work utilising: teacher assistance, peer mentoring, planning
scaffolds, guidance sheets (steps students need to take), class charts visible around the room. Whole
class sessions to share information and research sources with the class.
Independent
Students work individually in pairs or small groups to research and complete independent tasks.
Students utilise their planning strategies to complete their independent tasks and then conference with
the teacher.
Teacher support materials include a Curriculum Framing Question Flow Chart
See also the Unit Implementation Plan
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
Teaching and Learning Activities
In small groups students complete a brainstorming activity and create a mind map or chart of their
knowledge of the structure of the Earth. After researching appropriate information sites students create
a multimedia presentation to demonstrate to the class their understanding of Continental Drift, plate
tectonics, mid-ocean ridges and magnetic floor striping.
Students research the biotic and abiotic features of the earth. They demonstrate their understanding of
these features by creating a poster of either the carbon or nitrogen cycle.
To further their understanding of the impact of human resource use on the biosphere, students
individually map the location of coal, peat, oil deposits in Australia. Using graphic organiser software,
they then construct a flow chart showing the process of fractional distillation of crude oil.
Building on their knowledge from the previous activities students working in small groups, research
renewable and non-renewable energy sources and then create a blog as an interactive resource for
students.
Using the knowledge they have gained students debate the topic Fossil fuels are good for society or
Renewable energy is the only way to go! Students conduct independent research to validate their
position. This debate can be an intra-class or cross class activity.
Each student designs a wiki (or one wiki as a collaborative effort) to be published to students, staff and
parents of the school explaining how they can help planet Earth survive by reducing pollution using
alternative energy sources. This reinforces the idea “think globally, act locally” and could also be
distributed to local schools, libraries and community groups.
Extensions: Teachers may choose to have groups of students undertake any or all of the following
activities.
1. Students work in small teams to create a wiki. Each team takes on the role of a specific interest
group e.g. environmentalists, mining company owners; scientists and writes from their point of view.
This particular wiki will look at the question: Can the planet survive? Students conduct independent
research to validate their team’s position. The wikis can be used as a resource for other students or the
basis for a debate or forum.
2. Students are divided into small groups with each group assigned to investigate one of the effects
caused by changes in global temperature e.g. droughts, floods, economic change and natural damage
such as rising sea levels. Each group researches the predicted effects of global warming over the next
century as it concerns their assigned topic. Students use charts and graphs to illustrate the information
they have found and present it to the class.
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
3. Students research the Kyoto Agreement to find: What is it and why was it drawn up? Who does the
Agreement involve? Why did Australia delay signing the Agreement? How will the Earth survive if only
some countries take steps to address climate change? Students then design a presentation of their
choice (posters, multimedia presentation, wiki, blog, etc.) to present their information. This information
may then be used in the debate or forum process if needed.
4. After listening to all of the presentations, each student identifies what he or she thinks is the most
significant area that global warming will affect. They will then write a letter or send an email to the
Prime Minister or another world leader addressing this issue and outlining some actions the country can
take to lessen the impact of global warming.
Accommodations for Diverse Needs
Students with
Special Needs
English as a Second
Language (ESL)
Students
Gifted Students
Indigenous Groups
Use of visual and tangible aids
Open ended questioning
Peer coaching and support
Pairing of technologically more able students with those less able – within
the year group
Supporting adults or older students
Modified equipment and programs
Activities organised on rubrics at different levels of complexity
Use of visual aids to demonstrate learning put into place.
Strong buddy groups set up.
Extra help from peers.
Appropriate resources including Internet sites; a variety of ways available
to demonstrate their learning, support personnel, help of peers
Put into groups of students with superior language skills
Use of Blooms Taxonomy
More challenging tasks, extended investigation in related topics of the
learner’s choice
Open-ended tasks (research into the Kyoto protocol) or projects that allow
for deeper analysis and evaluation of issues.
Activities organised on rubrics at different levels of complexity.
Creation of their own rubrics will allow greater ownership of their learning.
The class wiki in particular could be used to showcase work from gifted
students
Opportunities to act as mentors.
A wiki page dedicated to indigenous peoples survival on the planet before
European settlement.
A deeper look into the effects of global warming on the less populated
areas of Australia.
Materials and Resources Required for Unit
Technology – Hardware (Click boxes of all equipment needed)
Camera
X Computer(s)
Digital Camera
Laser Disk
Printer
X Projection System
X DVD Player
Scanner
X Internet Connection
Television
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
VCR
Video Camera
Video Conferencing Equip.
Other
Page 5 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
Technology – Software (Click boxes of all software needed)
X Web Page/wiki Development
X Database/Spreadsheet
Image Processing
Desktop Publishing
X Internet Web Browser
E-mail Software
Encyclopedia on CD-ROM
X Multimedia
X Word Processing
X Other Digital Learning
Objects
Australian Government Geoscience Australia
http://www.ga.gov.au/urban/factsheets/volcanoes.jsp
Australian Museum
http://www.amonline.net.au/biodiversity/what/ecosystem.htm
Australian Academy of Science
http://www.science.org.au/nova/027/027key.htm
CSIRO
www.csiro.au/
United State Department of the Interior
http://walrus.wr.usgs.gov/tsunami/basics.html
Discovery School
http://school.discovery.com/lessonplans/programs/biomes_sea/
National Geographic
http://www.nationalgeographic.com/xpeditions/lessons/07/g912/co2.html
Public Broadcasting Service
http://www.pbs.org/now/classroom/globalwarming.html
Internet Resources/
Communication Tools
ThinkQuest
http://library.thinkquest.org/C0111040/Types/types.php
CNN
http://cnnstudentnews.cnn.com/2001/fyi/lesson.plans/03/05/climate.talks/
U.S. Geological Survey
http://www.usgs.gov/
Online resources from The Le@rning Federation
Nuclear power
The nuclear power series enables students to explore various aspects of
nuclear energy.
Wind power
This series enables students to explore the conversion of wind energy into
electricity.
Wind farm: cool solutions
Students investigate the advantages and disadvantages of establishing a wind
farm in a coastal community. They explore other options such as solar power
or extension of coal-fired power. Students gather facts and opinions from local
residents such as a dairy farmer, small business owner, young family and
retired people. Using this information they look at the relationship of energy
options to global warming and climate change.
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6 of 7
Intel® Teach Program
Designing Effective Projects
Green machine
In the Green machine series, students investigate the connection between a
vehicle’s features and its greenhouse gas emissions and assemble a vehicle
that meets specific targets for fuel consumption. Students are required to
consider the responsibilities of Australian drivers within the context of global
warming and its possible effects on planet Earth.
Wind farm: pros and cons
Students investigate the advantages and disadvantages of establishing a wind
farm in a coastal community by gathering facts and opinions from local
residents such as a dairy farmer, small business owner, young family and
retired people. Students use this information to decide whether to proceed with
the development by considering issues of ecological sustainability, economic
development, social responsibility, lifestyle and visual impact.
For details on how to access these online resources go to
www.thelearningfederation.edu.au
See also Resources for full list of internet sites
Other Resources
DVD: An Inconvenient Truth (Released February 2007 by Paramount Classics &
Participant Productions)
Credits
Brett Loughman participated in an Intel® Teach Essentials Course, which resulted in this idea for a
classroom project. A team of teachers expanded the plan into the example you see here.
© Copyright NSW Department of Education and Training 2008.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
© 2000-2007 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7 of 7