D_gr7_math_yearly_plan
advertisement

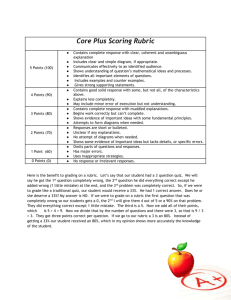
Grade 7 Mathematics Yearly Plan: Sample D 2 Another possible yearly plan could present the material in this order: September—December Chapter 1: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages A1 model and use power, base, and exponent to represent repeated multiplication 1.1 1CP Wrap-Up 16–21 51 A2 rename numbers among exponential, standard, and expanded forms 1.1 1CP Wrap-Up 16–21 51 A3 rewrite large numbers from standard form to scientific notation and vice versa 1.2 1CP Wrap-Up 22–27 51 A6 develop and apply divisibility rules for 3, 4, 6, and 9 1.3 1CP Wrap-Up 28–33 51 A4 solve and create problems involving common factors and greatest common factors (GCF) 1.4 1CP Wrap-Up 34–39 51 A5 solve and create problems involving common multiples and least common multiples (LCM) 1.4 1CP Wrap-Up 34–39 51 B5 apply the order of operations for problems involving whole and decimal numbers 1.5 1CP Wrap-Up 2.5 2.6 2CP Wrap-Up 40–45 51 92–97 98–103 107 Assessment Formative BLM 1.1 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.1 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.2 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.3 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.4 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.4 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.5 Rubric BLM 2.5 Rubric BLM 2.6 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 3 D1 identify, use, and convert among the SI units to measure, estimate, and solve problems that relate to length, area, volume, and capacity D2 apply concepts and skills related to time in problem situations throughout Ch1, Ch2, Ch8 8–51, 52–107, 330–367 throughout Ch1, Ch9 8–51, 368–419 Chapter 2: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages B6 estimate the sum or difference of fractions when appropriate 2.1 2CP Wrap-Up 58–67 107 B7 multiply mentally a fraction by a whole number and vice versa 2.2 68–75 A9 compare and order proper and improper fractions, mixed number, and decimal numbers 2.2 2.4 68–75 84–91 2.3 76–83 2.3 76–83 B4 determine and use the most appropriate computational method in problem situations involving whole numbers and/or decimals 2.4 2.5 2.6 2CP Wrap-Up 84–91 92–97 98–103 107 B2 use mental math strategies for calculations involving integers and decimal numbers 2.5 2.6 5CP Wrap-Up 92–97 98–103 249 B5 apply the order of operations for problems involving whole and decimal numbers 1.5 1CP Wrap-Up 2.5 2.6 2CP Wrap-Up A7 apply patterning in renaming numbers from fractions and mixed numbers to decimal numbers A8 rename single-digit and double-digit repeating decimals to fractions through the use of patterns and use these patterns to make predictions 40–45 51 92–97 98–103 107 Assessment Formative BLM 2.1 Rubric Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 2.2 Rubric Formative BLM 2.2 Rubric BLM 2.4 Rubric Formative BLM 2.3 Rubric Formative BLM 2.3 Rubric Formative BLM 2.4 Rubric BLM 2.5 Rubric BLM 2.6 Rubric Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 2.5 Rubric BLM 2.6 Rubric Summative BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.5 Rubric BLM 2.5 Rubric BLM 2.6 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 4 BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric B1 use estimation strategies to assess and justify the reasonableness of calculation results for integers and decimal numbers 2CP Wrap-Up 5CP Wrap-Up 107 249 B3 demonstrate an understanding of the properties of operations with decimal numbers and integers 2CP Wrap-Up 5CP Wrap-Up 107 249 D1 identify, use, and convert among the SI units to measure, estimate, and solve problems that relate to length, area, volume, and capacity throughout Ch1, Ch2, Ch8 8–51, 52–107, 330–367 Chapter 3: Outcome Chapter/Section B8 estimate and determine percent when given the part and the whole 3.1 3.2 3.3 3CP Wrap-Up 3Task A11 demonstrate number sense for percent 3.1 3CP Wrap-Up 3Task B9 estimate and determine the percent of a number 3.2 3.3 3.4 3CP Wrap-Up 3Task Pages 112–117 118–125 126–131 141 143 112–117 141 143 118–125 126–131 132–137 141 143 Assessment Formative BLM 3.1 Rubric BLM 3.2 Rubric BLM 3.3 Rubric Summative BLM 3CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 3T Task Rubric Formative BLM 3.1 Rubric Summative BLM 3CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 3T Chapter 3 Task Rubric Formative BLM 3.2 Rubric BLM 3.3 Rubric BLM 3.4 Rubric Summative BLM 3CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 3T Task Rubric 5 B10 create and solve problems that involve the use of percent 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3CP Wrap-Up A10 illustrate, explain, and express ratios, fractions, decimals, and percents in alternative forms throughout Ch3, Ch4, Ch9 112–117 118–125 126–131 132–137 141 Formative BLM 3.1 Rubric BLM 3.2 Rubric BLM 3.3 Rubric BLM 3.4 Rubric Summative BLM 3CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 103–147, 148–189, 368–419 Chapter 7: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages E3 make and apply generalizations about the properties of regular polygons 7.1 7CP Wrap-Up 298–306 329 E1 recognize, name, describe, and construct polygons 7.1 10.3 10CP Wrap-Up 298–306 442–447 457 E4 make and apply generalizations about tessellations of polygons 7.2 307–313 E2 predict and generate polygons that can be formed with a transformation or composition of transformations of a given polygon 7.2 10.2 10CP Wrap-Up 307–313 436–441 457 Assessment Formative BLM 7.1 Rubric Summative BLM 7CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 7.1 Rubric BLM 10.3 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 7.2 Rubric Formative BLM 7.2 Rubric BLM 10.2 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 6 E7 make and apply generalizations about angle relationships 7.2 10.1 10CP Wrap-Up 307–313 424–435 457 E5 construct polyhedra using one type of regular polygonal face, and describe and name the resulting Platonic Solids 7.3 7CP Wrap-Up 314–320 329 E6 construct semi-regular polyhedra and describe and name the resulting solids, and demonstrate an understanding about their relationships to the Platonic Solids 7.4 7CP Wrap-Up 321–325 329 Formative BLM 7.2 Rubric BLM 10.1 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 7.3 Rubric Summative BLM 7CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 7.4 Rubric Summative BLM 7CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 7 January—March Chapter 5: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages A12 represent integers (including zero) concretely, pictorially, and symbolically, using a variety of models 5.1 5CP Wrap-Up 5Task 196–203 249 251 A13 compare and order integers 5.1 196–203 B11 add and subtract integers concretely, pictorially, and symbolically to solve problems 5.2 5.3 5CP Wrap-Up 5Task 204–210 211–218 249 251 B12 multiply integers concretely, pictorially, and symbolically to solve problems 5.4 5Task 219–227 251 B13 divide integers concretely, pictorially, and symbolically to solve problems 5.5 228–233 B14 solve and pose problems which utilize addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of integers 5.7 5Task 240–245 251 B15 apply the order of operations to integers 5.6 5CP Wrap-Up 5Task 234–239 249 251 Assessment Formative BLM 5.1 Rubric Summative BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5T Task Rubric Formative BLM 5.1 Rubric Formative BLM 5.2 Rubric BLM 5.3 Rubric Summative BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5T Task Rubric Formative BLM 5.4 Rubric Summative BLM 5T Task Rubric Formative BLM 5.5 Rubric Formative BLM 5.7 Rubric Summative BLM 5T Task Rubric Formative BLM 5.6 Rubric Summative BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5T Task Rubric 8 B1 use estimation strategies to assess and justify the reasonableness of calculation results for integers and decimal numbers 2CP Wrap-Up 5CP Wrap-Up 107 249 B2 use mental math strategies for calculations involving integers and decimal numbers 2.5 2.6 5CP Wrap-Up 92–97 98–103 249 B3 demonstrate an understanding of the properties of operations with decimal numbers and integers 2CP Wrap-Up 5CP Wrap-Up 107 249 Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 2.5 Rubric BLM 2.6 Rubric Summative BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Summative BLM 2CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 5CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Chapter 4: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages G1 identify situations for which the probability would be near 0, 1 – 4, 1 – 2 , 3 – 4, and 1 4.1 152–157 G2 solve probability problems, using simulations and by conducting experiments 4.2 4.3 4.4 4CP Wrap-Up 158–169 170–177 178–185 189 G3 identify all possible outcomes of two independent events, using tree diagrams and area models 4.4 4CP Wrap-Up 178–185 189 G4 create and solve problems, using the numerical definition of probability 4.2 4.3 4.4 4CP Wrap-Up 158–169 170–177 178–185 189 G5 compare experimental results with theoretical results 4.2 4.4 158–169 178–185 Assessment Formative BLM 4.1 Rubric Formative BLM 4.2 Rubric BLM 4.3 Rubric BLM 4.4 Rubric Summative BLM 4CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 4.4 Rubric Summative BLM 4CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 4.2 Rubric BLM 4.3 Rubric BLM 4.4 Rubric Summative BLM 4CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 4.2 Rubric 9 4CP Wrap-Up 189 G6 use fractions, decimals, and percents as numerical expressions to describe probability 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4CP Wrap-Up 152–157 158–169 170–177 178–185 189 A6 develop and apply divisibility rules for 3, 4, 6, and 9 1.3 1CP Wrap-Up 28–33 51 A10 illustrate, explain, and express ratios, fractions, decimals, and percents in alternative forms throughout Ch3, Ch4, Ch9 103–147, 148–189, 368–419 BLM 4.3 Rubric Summative BLM 4CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 4.1 Rubric BLM 4.2 Rubric BLM 4.3 Rubric BLM 4.4 Rubric Summative BLM 4CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 1.3 Rubric Summative BLM 1CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Chapter 6: Outcome F1 communicate through example the distinction between biased and unbiased sampling, and firstand second-hand data F2 formulate questions for investigation from relevant contexts F3 select, defend, and use appropriate data collection methods and evaluate issues to be considered when collecting data F4 construct a histogram Chapter/Section Pages 6.1 6CP Wrap-Up 256–261 289 6.1 256–261 6.1 6CP Wrap-Up 256–261 289 6.2 262–268 Assessment Formative BLM 6.1 Rubric Summative BLM 6CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 6.1 Rubric Formative BLM 6.1 Rubric Summative BLM 6CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 6.2 Rubric 10 F5 construct appropriate data displays, grouping data where appropriate and taking into consideration the nature of the data F6 read and make inferences for grouped and ungrouped data displays F7 formulate statistics projects to explore current issues from within mathematics, other subject areas, or the world of students F8 determine measures of central tendency and how they are affected by data presentations and fluctuations F9 draw inferences and make predictions based on the variability of data sets, using range and the examination of outliers, gaps, and clusters 6.2 6.3 6CP Wrap-Up 262–268 269–275 289 6.3 269–275 Formative BLM 6.2 Rubric BLM 6.3 Rubric Summative BLM 6CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 6.3 Rubric 6CP Wrap-Up 289 Summative BLM 6CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 6.4 6CP Wrap-Up 276–283 289 Formative BLM 6.4 Rubric Summative BLM 6CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 6.4 276–283 Formative BLM 6.4 Rubric 11 Mid-March—June Chapter 8: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages D5 demonstrate an understanding of the relationships among diameter, radii, and circumference of circles, and use the relationships to solve problems 8.1 C1 describe a pattern, using written and spoken language and tables and graphs 8.1 8CP Wrap-Up 8Task 334–345 365 367 C2 summarize simple patterns, using constants, variables, algebraic expressions, and equations, and use them in making predictions 8.1 8CP Wrap-Up 8Task 334–345 365 367 C8 determine if an ordered pair is a solution to a linear equation 8.1 9.2 334–345 381–389 C3 explain the difference between algebraic expressions and algebraic equations 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 8Task 346–353 365 367 C4 solve one- and two-step single-variable linear equations, using systematic trial 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.1 346–353 365 372–380 C5 illustrate the solution for one- and two-step linear equations, using concrete materials and diagrams 8.2 9.1 334–345 346–353 372–380 Assessment Formative BLM 8.1 Rubric Formative BLM 8.1 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 8T Task Rubric Formative BLM 8.1 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 8T Task Rubric Formative BLM 8.1 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 8T Task Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.1 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.1 Rubric 12 C6 graph linear equations, using a table of values 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.2 C7 interpolate and extrapolate number values from a given graph 8.2 9.2 C9 construct and analyse graphs to show how change in one quantity affects a related quantity 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.3 9CP Wrap-Up 346–353 365 381–389 346–353 381–389 346–353 365 390–396 415 B16 create and evaluate simple variable expressions by recognizing that the four operations apply in the same way as they do for numerical expressions 8.3 8CP Wrap-Up 8Task 354–361 365 367 B17 distinguish between like and unlike terms 8.3 354–361 8.3 354–361 B18 add and subtract like terms by recognizing the parallel with numerical situations, using concrete and pictorial models D1 identify, use, and convert among the SI units to measure, estimate, and solve problems that relate to length, area, volume, and capacity throughout Ch1, Ch2, Ch8 Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.3 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 9CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 8.3 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 8T Task Rubric Formative BLM 8.3 Rubric Formative BLM 8.3 Rubric 8–51, 52–107, 330–367 Chapter 9: Outcome C4 solve one- and two-step single-variable linear equations, using systematic trial Chapter/Section 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.1 Pages 346–353 365 372–380 Assessment Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.1 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 13 C5 illustrate the solution for one- and two-step linear equations, using concrete materials and diagrams 8.2 9.1 C6 graph linear equations, using a table of values 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.2 C7 interpolate and extrapolate number values from a given graph 8.2 9.2 346–353 381–389 C8 determine if an ordered pair is a solution to a linear equation 8.1 9.2 334–345 381–389 C9 construct and analyse graphs to show how change in one quantity affects a related quantity 8.2 8CP Wrap-Up 9.3 9CP Wrap-Up D3 develop and use rate as a tool for solving indirect measurement problems in a variety of contexts 9.4 9CP Wrap-Up 404–411 415 D4 construct and analyse graphs to show change in one quantity affects a related quantity 9.4 9CP Wrap-Up 404–411 415 D2 apply concepts and skills related to time in problem situations A10 illustrate, explain, and express ratios, fractions, decimals, and percents in alternative forms throughout Ch1, Ch9 8–51, 368–419 103–147, 148–189, 368–419 throughout Ch3, Ch4, Ch9 346–353 372–380 346–353 365 381–389 346–353 365 390–396 415 Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.1 Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Formative BLM 8.1 Rubric BLM 9.2 Rubric Formative BLM 8.2 Rubric BLM 9.3 Rubric Summative BLM 8CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric BLM 9CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 9.4 Rubric Summative BLM 9CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 9.4 Rubric Summative BLM 9CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric 14 Chapter 10: Outcome Chapter/Section Pages Assessment Formative BLM 7.2 Rubric BLM 10.1 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 10.2 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric E7 make and apply generalizations about angle relationships 7.2 10.1 10CP Wrap-Up 307–313 424–435 457 E8 make and apply generalizations about the commutativity of transformations 10.2 10CP Wrap-Up 436–441 457 10.4 448–453 Formative BLM 10.4 Rubric 10.4 448–453 Formative BLM 10.4 Rubric E9 make and apply informal deductions about the minimum sufficient conditions to guarantee that a given triangle is of a particular type E10 make informal deductions about the minimum sufficient conditions to guarantee that a given quadrilateral is of a particular type, and to understand formal definitions of the various members of the quadrilateral family E1 recognize, name, describe, and construct polygons 7.1 10.3 10CP Wrap-Up 298–306 442–447 457 E2 predict and generate polygons that can be formed with a transformation or composition of transformations of a given polygon 7.2 10.2 10CP Wrap-Up 307–313 436–441 457 Formative BLM 7.1 Rubric BLM 10.3 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric Formative BLM 7.2 Rubric BLM 10.2 Rubric Summative BLM 10CP Chapter Problem Wrap-Up Rubric