Bonding Mystery Questions Key
advertisement

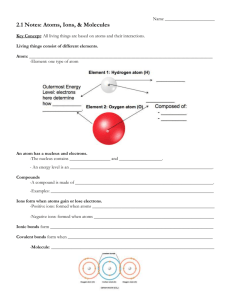
Key A calcium oxide, ionic. B diatomic nitrogen, linear, triple bonds, 180 angle, nonpolar, dispersion attractions. C water, angular, single bonds, 105 angle, polar, hydrogen bonding. D carbon tetrachloride, tetrahedral, single bonds, 109 angle, nonpolar, dispersion attractions. E carbon dioxide, linear, double bonds, 180 angle, nonpolar, dispersion attractions. F aluminium bromide, trigonal planar, single bonds, 120 angle, nonpolar, dispersion attractions. G beryllium hydride, linear, single bonds, 180 angle, nonpolar, dispersion attractions. H nitrogen trifluoride, pyramidal, single bonds, 107 angle, polar, dipole-dipole attractions. I sodium chloride, ionic. Questions: 1. How was CaO formed? (what happened in terms of valence electrons) The calcium atom gave 2 electrons to the oxygen atom. The calcium therefore became an ion with a +2 charge and the oxygen became an ion with a -2 charge. 2. How did CCl4 form? (what happened in terms of valence electrons) The carbon atom shared one electron with each of the 4 chlorine atoms and they each share one electron with carbon. 3. How many electrons are shared in an AlBr3 molecule? 6 4. Which compounds have polar bonds, but nonpolar (pure) molecules? Carbon tetrachloride has polar bonds, but it tetrahedral so behaves pure. Carbon dioxide has polar bonds, but it tetrahedral so behaves pure Aluminum bromide has polar bonds, but it tetrahedral so behaves pure Beryllium hydride has polar bonds, but it tetrahedral so behaves pure 5. Explain why NF3 molecules are polar, but AlBr3 molecules are not? NF3 is pyramidal with a pull toward the three F atoms that are at the bottom. AlBr3 is trigonal planar. The bromines are pulling the electrons, but are pulling evenly all around the molecule, so the uneven pull is dispersed (or cancels itself out). 6. What kind of intermolecular forces are seen between molecules of AlBr3? Are they weak or strong? AlBr3 is nonpolar (pure) so has only dispersion forces between the molecules. These are weak attractions. 7. What kind of intermolecular forces are seen between molecules of NF3? Are they weak or strong? NF3 is polar so had dipole-dipole attractions between the molecules. These are stronger attractions. 8. Which of the covalent compounds is most likely to dissolve in water? The polar compounds (in addition to the ionic compounds) will dissolve in water. So, nitrogen trifluoride will dissolve. 9. Which of the compounds would be the best conductors? The ionic compounds will be the best conductors, so sodium chloride and calcium oxide will conduct best. 10. Which liquid would evaporate more rapidly, CCl4 or H2O? Why? Would it have a high or low vapor pressure? The CCl4 will evaporate faster because it is pure covalent while water is polar covalent. Water has strong intermolecular attractions, so the molecules are holding on to each other making it hard for the molecules to escape and evaporate. CCl4 is heavier than water, which usually makes a liquid evaporate more slowly, but that would not be enough to overcome the difference in bonding between these two compounds.