Reef notes
advertisement

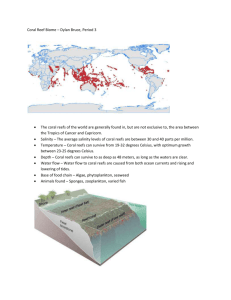
N.S.T.A. Science Objects 3 of 4 The Coral Reef Ecosystem: Interdependence *Ecology-the study of the interaction of living things with each other and their environment *Plankton: 1) Zooplankton (animal plankton) and 2) Phytoplankton (smaller chlorophyll bearing plankton often called “grasses of the sea) *Food Chains Producer (Make food from the sun’s energy…photosynthesis) Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer *All food chains have a producer and at least one consumer *Last predator in a food chain in called the apex predator *Food chains are linked to each other through food webs *Trophic level of the food pyramid *lowest concentration of energy is at the top trophic level *Recycling on the Reef *Water cycle *”Food cycle” *Carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle *Symbiosis on the reef Symbiosis Mutualism (both organisms benefit) (i.e. polyps and zooxanthellae Clownfish and anemone) Commensalism (one partner benefits and the other remains unaffected) (i.e. reef shark and remora) Parasitism (one partner benefits and the other is harmed) (i.e. reef fish and worms) 4 of 4 Coral Reef Ecosystems: Ecosystems in Crisis *Natural events that destroy the coral reef ecosystem: A. Stormy weather (i.e. hurricanes, typhoons) can destroy coral reefs B. Tsunamis (caused by underwater earthquakes) 1. Less damage is done to healthy coral that has not been Affected by human activity C. Reef raiders 1. Crown of thorns seastar (strips coral of all soft tissue) a. It’s abundance is caused from the shell collectors who collect the Great Triton (it’s main predator) thus causes the C-of-T population to increase D. Disease 1. May be caused by ocean acidification or rising water temps *Human Events that destroy the coral reef ecosystem A. Bleaching-when the polyps expel the zooxanthellae 1. Due to increase of water temperature (even 1 degree Celsius), can also be from sewage in the water, cloudy water, low O2 levels, and Other toxic material in the water 2. Coral can fix itself but become more susceptible to disease and If they die it disrupts the ecosystem B. Ocean Acidification-when CO2 in the atmosphere is absorbed into the ocean 1. Lowers the pH of the water and the concentration ion of carbonate Decreases and makes it harder for coral to form. 2. The acidity can also dissolve coral C. Runoff-toxicants and sediment in storm water runoff 1. The cloudiness in the water prevents photosynthesis 2. Overgrazing and clear cutting causes more erosion of the land and Overpopulation (more petroleum based toxicants in runoff) 3. Water from sewage plants and agriculture may stimulate algal growth a. Algal blooms cover sunlight and prevent photosynthesis in coral polyps b. Algal blooms also cause other algae to die to lack of sunlight and this dissolves O2 levels 4. Chemical Fertilizers D. Commercial Exploitation 1. Overfishing/damaging fishing techniques a. Sea cucumber delicacy (endangered now) b. Unbalanced predator/prey relationships c. Dynamite fishing and poison fishing cause excessive damage E. Invasive Species (non-native species that disrupts the balance of an ecosystem) 1. Mainly from ballast water discharge (water let off of ships when They dock…release non-native larvae, eggs, microscopic organisms F. Ship Groundings G. Tourism and Recreation 1. People who run their boats into shallow corals 2. People who stand on, touch, and/or remove coral 3. Fishing gear damage and anchor damage H. Marine Debris 1. U.S. has 10 million tons of trash that is dumped into the ocean 2. Suffocation or starvation from ingesting plastic bags 3. Choking and suffocating on plastics 4. Plastic bags can suffocate a coral reef 5. Oil spills and toxic spills damage coral reef ecosystems, too *Endangered Species A. The U.S. made it illegal to kills, hunt, injure, or harass marine mammals In 1972 B. Levels of threats: Endangered, Threatened, Species of Concern