Honors Chemistry- Chapter 4 Worksheet Electronic Structure 1) (a
advertisement

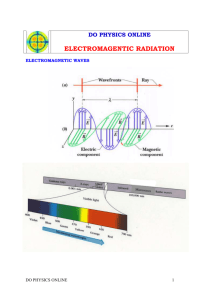
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 4 Worksheet Electronic Structure 1) (a) List the seven forms of electromagnetic radiation in order from lowest → highest frequency. (b) What is the speed of all forms of electromagnetic radiation? 2) What is the wavelength range of visible light? 3) Determine the frequency of light whose wavelength is 4.26 X 10 -7 cm. 4) (a) Which has a longer wavelength: green light or yellow light? (b) Which has a higher frequency: an X-ray or a microwave? (c) Which travels at a greater speed: UV radiation or infrared light? 5) Calculate the wavelength (in nanometers!) of electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is 7.50 X 1012 Hz. 6) In the table below, list the properties of light that favor wave vs. particle theory. Wave Theory Particle Theory 7) (a) How are wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation related? (b) How are the energy and frequency of electromagnetic radiation related? (c) Using the two equations Ephoton = hν and λν = c, derive an equation expressing Ephoton in terms of h, c, and λ. (d) Based on your answer to (c) above, how are the energy and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation related? 8) Distinguish between the ground state and the excited state of an atom. 9) According to Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen atom, how is hydrogen’s line emission spectrum produced? 10) When sodium metal is heated, a yellow spectral line whose energy is 3.37 X 10-19 J/photon is produced. (a) What is the frequency of this light? (b) What is the wavelength of this light, expressed in nanometers. 11) Describe the two major shortcomings of the Bohr Model of the Atom. 12) What is the most important piece of experimental evidence that supports the wave nature of electrons? 13) What does the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle state? 14) What is an orbital? 15) (a) What information does the principal quantum number provide? (b) How is it symbolized? 16) What information does the angular momentum quantum number provide? 17) What are the 4 orbital shapes and what does each loosely resemble? 18) What information is given by the magnetic quantum number? 19) Complete the following table. Principal Quantum Number (n) 1 2 3 4 Orbital shapes allowed # of orientations per shape Total # of electrons 20) (a) What information is given by the spin quantum number? (b) What are the possible values for this quantum number? 21) (a) What is the “rule” for the number of orbitals allowed on a given energy level? (b) What is the “rule” for the number of electrons allowed on a given energy level? 22) In the table below, describe the similarities and differences between Bohr’s Model of the Atom and the Quantum Model of the Atom. Similarities 1. 2. 3. Differences 1. 2. 3. 23) (Review Question) A photon of UV light has a wavelength of 150 nm. Calculate the energy (in Joules) of this photon. 24) What does the Aufbau Principle state about how electrons occupy atomic orbitals? 25) State Hund’s Rule. What is the other “funny” name that we use to remember Hund’s Rule? 26) (a) What is the significance of the spin quantum number? (b) State the Pauli Exclusion Principle. 27) (a) What is meant by the highest-occupied energy level (HOEL) in an atom? (b) What are inner-shell electrons? 28) Write the orbital notation and electron configuration notation for the element strontium. 29) Given that the electron configuration for chlorine is 1s22s22p63s23p5, answer the following questions: (a) How many electrons are in each chlorine atom? (b) What is the atomic number of this element? (c) How many unpaired electrons does chlorine have? (d) What is the HOEL for chlorine? (e) How many inner-shell electrons does chlorine have? (f) How many valence electrons does chlorine have? 30) How does noble-gas notation simplify writing an atom’s electron configuration? 31) When writing electron dot notation, how do you know how many dots to put around the atomic symbol? What do those dots represent? 32) Write the electron configuration notation and the noble gas notation for the element iodine. 33) Identify each of the following atoms on the basis of its electron configuration. (a) 1s22s22p1 (b) 1s22s22p5 (c) [Ne]3s2 (d) [Ne]3s23p2 (e) [Ar]4s1 (f) [Ar]4s23d6 34) What are valence electrons? 35) Write the electron configuration notation, noble-gas notation, and electron dot notation for the element actinium, Ac (atomic number 89!!). You can do it! 36) Determine the HOEL in the following elements: (a) He (b) Be (c) Al (d) Ca (e) Sn (f) Can you find a pattern from your answers to (a) to (e) 37) Do the following electron configurations represent the ground state or excited state of an atom? Which atom is it in each case? (a) 1s22s22p63s23p54s23d4 (b) 1s22s22p63s23p54s2