answers_
advertisement

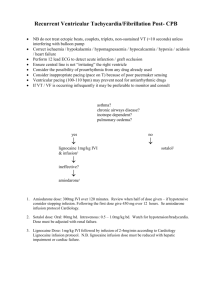
PRACTICE DOCUMENT FOR MAINTAINING STANDARDS IN PRESCRIBING AND ADMINISTERING OF DRUGS ANSWERS Name: Date: NICU Practice document: prescribing and administering of drugs. July 2013 Authors: Risk Management Team Practice Development Team Neonatal Unit Pharmacist Introduction The purpose of this document is to clarify issues around drug prescribing and administration and thereby enhance practice. It has been put together as a learning package for both medical and nursing staff in Neonatal Services. It has been compiled in response to prescribing and administrative incidents reported via the risk reporting system. Examples used are taken from actual incidents that have occurred within the service, however examples have been modified to maintain confidentiality. The document recognizes a need for back up revision following medical and nursing induction. It aims to assess your knowledge and competence regarding drug prescribing and administration and to clarify areas needing further education. All staff will be given the document following their induction. It will need to be completed and returned within two weeks for marking. Please hand it to Ruby Lopez (Neonatal Nurse) for marking. Medical staff will be expected to take it to their first Consultant appraisal for discussion. We hope you find this a useful tool. 1) a) Why is the dose calculator sheet an important safety tool? Reduces calculation and administration errors relating to miscalculation of drug doses. Provides a pre-printed intubation chart with agreed doses that is ready in the event of an emergency intubation b) When should dose calculator sheets be updated? Every Monday morning by SpR. 2) What is the significance of the purple apron when prescribing, preparing and administering drugs in neonatal services? Staff wearing the purple apron MUST not be disturbed from prescribing, preparing or administering drugs. 3) What are the standard drug administration times on the NICU for: a) BD doses 06:00, 18:00 ; 12:00, 24:00 b) TDS doses 06:00, 14:00, 22:00 c) QDS doses 06:00, 12:00, 18:00, 24:00 d) Oral supplements of vitamins, Sytron, Sodium, Potassium 12:00 4) a) What is the drug prescribing policy for NICU / SCBU? No prescriptions are to be written during the ward round, unless in an emergency b) What location on the unit (NICU) should all medication be written up? The SHO responsible for the room will leave the ward round after the ward round in that room has finished and will then start prescribing the fluids etc. They will wear purple aprons to help avoid being interrupted and will discuss the prescriptions with the nurse looking after each baby. Other prescriptions should be written in the doctors room on NICU c) What time of the day should most medication be written up? As above fluids immediately after the ward round in each room has finished. All other drugs should generally be prescribed immediately after the ward round. 5) List 5 aspects of this prescription which contravene the Addenbrooke’s Good Prescribing Guide and could lead to an error on the NICU: Dose units (mg’s) missing Dosing frequency confusing ? 24 hourly or 18 hourly No antibiotic indication No review/stop date Signature needs to be clearly written with name printed. 6) If you were responsible for administering this prescription what other information would you expect to see? Weight Hospital number Dose timings included as per standard dose times No abbreviations Benzylpenicillin rather than BenPen Prescribers signature to be written clearly and name printed Indication for antibiotic Stop/review date Dose calculation used i.e. 50mg/kg/dose 12 hourly 7) What 3 things should you expect to do / see when a prescription is cancelled? Crossed out in full Signed & printed name by prescriber cancelling prescription Dated 8) Why should original prescriptions not be amended? Usually makes prescription illegible or ambiguous Historically difficult to review prescription and see when change was made and what doses were administered on original and amended prescriptions 9) What action should be taken if the frequency of a drug changes after 2 doses? Rewrite prescription in full 10) When is the word “stat” acceptable on a drug chart? Never 11) When should maintenance dosing of caffeine be commenced following a loading dose? 12) 24 hours after loading dose (but adjusted to the nearest standard drug administration time. a) Baby Smith weighs 700g and requires a loading dose of Caffeine Citrate. The first dose is to be given on 3 January 2003 at 17h00. Prescribe this on the drug chart provided, followed by a maintenance course of caffeine. b) Baby Smith receives a loading dose of caffeine and one maintenance dose when it is noted that the documented birth weight details are incorrect. The correct weight is 750g. Show the necessary changes you would make to the prescription chart. 13) On which charts would you expect to prescribe a continuous vancomycin infusion and gentamicin doses? Vancomycin – on blue continuous vancomycin infusion prescription chart Gentamicin – on pink gentamicin chart 14) When should levels be taken once an infant has commenced a Vancomycin infusion? From 12 hours after the infusion has commenced. 15) When should levels be taken on Gentamicin? Pre 2nd dose level as either ‘level and give’ or ‘level and hold’. 16) a) The first dose of Gentamicin is prescribed and given to a term baby with no concerns about renal function at 16h20 on 14 June. When is the first level due? Before 2nd dose 16:20 on 15th June b) When is the second dose due? Immediately following the level being taken. c) When is the third dose due? Once pre 2nd dose level has been confirmed, the timing of the 3rd dose can be confirmed. If level <2mg/L then next dose can be given at a standard administration time 18:00 on 16th June. If level >2mg/L then level needs to be rechecked and dose held until result is <2mg/L d) What needs to be checked before administering gentamicin? All aspects included on the double checking prompt. e) What action would you take if there is a discrepancy from the gentamicin double checking prompt? Complete a CIR form resolve issue and complete form on the back of the gentamicin prescription chart 17) For a continuous vancomycin infusions what actions should be taken if Vancomycin levels are? 18) a) <10mg/l - Increase daily dose and rate by 50% b) 10 to <15mg/l - Increase daily dose and rate by 25% c) 15 to 25mg/l - No change to dose d) > 25 to 30mg/l - Decrease daily dose and rate by 25% e) >30mg/l - Stop infusion and recheck level until <25mg/L and recommence infusion at lower rate. Where should 18 hourly drugs OTHER than Vancomycin and Gentamicin be prescribed? On the ‘Once only’ chart section 19) An infant, Baby Smith born at 26/40 (DOB 01.01.12) weighing 750g is to be treated with a continuous vancomycin infusion. There is no indication of renal impairment and his creatinine is <50micromol/L. Using the drug charts attached (see appendices) prescribe the loading dose which would be due to be given at midnight on 03.01.12. What would the Vancomycin maintenance dose and infusion rate be? 20) What drugs is a continuous infusion of Vancomycin incompatible with? Albumin, amphotericin, benzylpenicillin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, dexamethasone, furosemide, heparin, phenytoin, sodium bicarbonate 21) Prescribe 2 doses of Gentamicin for the same baby with the first dose due to be given at 2pm on 02.01.12 (see appendices). 22) If a drug dosage needed changing after 2 doses, how would you amend the prescription? Cross off original prescription (dating and signing prescription) Rewrite prescription in full 23) Baby Smith weighing 750g is diagnosed with a PDA. The decision is made to treat with ibuprofen IV. Prescribe this drug on the attached drug chart with the first dose to be given at 18.00hrs on 08.01.03. Dose will be 7.5mg/day. 24) What would you monitor prior to and following administration of ibuprofen? Renal function Platelets Abdomen (for signs of distension) Signs of infection Coagulation defects 25) What is the correct dose of Morphine / kg: a) As an infusion? 5-40microgram/kg/hour b) As a loading dose? 100microgram/kg 26) Where can you find information on prescribing Morphine? NICU handbook Dose calculator sheets IV monograph Intubation charts Pocket cards 27) Baby Smith requires a morphine loading dose and subsequent continuous infusion. If she weighs 750g prescribe a morphine loading dose and infusion on drug and infusion charts provided. The loading dose (100 microgram / kg / dose) is to be given at 1pm on 08.01.03 followed immediately by a standard continuous infusion (diluent is dextrose 10%). Loading dose is 75 microgram (or can be given as dose banded dose) Maintenance infusion is 750microgram morphine in 50ml dextrose 10%. 0.25-2ml/hr = 5-40microgram/kg/hr 28) Baby Smith needs to be fluid restricted. Represcribe the Morphine infusion at double strength. Maintenance infusion is 1.5mg morphine in 50ml dextrose 10%. 0.125-1ml/hr = 5-40microgram/kg/hr 29) A decision to wean Baby Smith off Morphine is made following a good post op recovery. Paracetamol is prescribed to maintain pain relief as needed. Prescribe this on the attached chart accordingly. Paracetamol IV dose will be 7.5mg/kg (5.6mg) 6 hourly 30) What is the correct dose of Metronidazole / kg for a baby that is 45 days old: 7.5mg/kg/dose 12 hourly 31) Baby Smith is being treated for suspected NEC. Prescribe a course of Metronidazole. Dose = 5.6mg 12 hourly Need to include indication, start date and review date on prescription. 32) Prescribe hydrocortisone for an 800g infant for the management of hypotension. Dose is 2-6mg/kg/day divided into 4 hourly doses e.g. 800microgram/dose 4 hourly 33) Prescribe an insulin infusion for a baby who weighs 930g, where the normal insulin prescription range has not proven to be effective. Use 25units/kg (23units) in 50ml sodium chloride 0.9% e.g. >18mmol/L 14-18mmol/L 10-14mmol/L 8-10mmol/L <8mmol/L 0.2units/kg/hour 0.15units/kg/hour 0.1units/kg/hour 0.05units/kg/hour Stop = = = = 0.4ml/hr 0.3ml/hr 0.2ml/hr 0.1ml/hr Other sensible answers are acceptable 34) Baby Smith weighing 750g requires 3mmols / kg / day of Sodium and 2mmols / kg / day of Potassium adding to his 10% Dextrose. He is on 120mls / kg of fluid. Calculate his requirements and prescribe these as you would expect to see them on the fluid chart provided. Dextrose 10% 500ml containing Sodium chloride 12.5mmol (3mmol/kg/day) Potassium chloride 8.3mmol (2mmol/kg/day) 35) Where would you go for guidance if you needed information relating to the prescription or administration of a drug / infusion? NICU handbook NICU pharmacist IV Monographs Medicines Information 36) 37) What would you do if you noted a discrepancy between the monograph and the handbook? Complete CIR form Discuss prescription with Consultant Discuss with NICU pharmacist List 10 things you would check on a prescription prior to administering a drug. Legibility of prescription Name and Hospital number are correct Weight is correct Dose is calculated correctly When was last dose administered Is frequency correct (e.g. dose frequency need changing with age) Prescription has been signed by prescriber Are any levels or results due before dose can be given Is route of administration correct Is drug prescribed at a standard administration time.