QuestionsCH16
advertisement

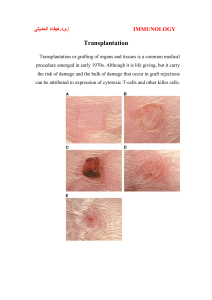
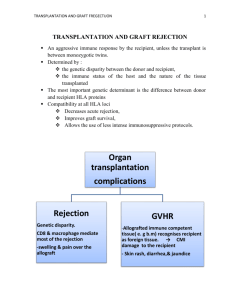
Questions for chapter 16: 1. Which of the following is a graft between nonidentical members of the same species? a. an autograft b. a syngraft c. an allograft d. a xenograft 2. When the mother and father have one haplotype in common, what is the chance that two siblings will be HLA-identical? a. 1 in 2 b. 1 in 3 c. 1 in 4 d. 1 in 5 e. 0 3. Serologic testing before kidney transplantation has revealed that the leukocytes of a prospective recipient are killed by the following anti-HLA antibodies in the presence of complement: anti-B27, anti-Al, and anti-A3. You can conclude a. that the prospective recipient expresses the B27, Al, and A3 specificities b. that the prospective recipient does not express the B27, Al, and A3 specificities c. that the potential donor and the prospective recipient are not siblings d. that the potential donor and the prospective recipient are not identical twins e. nothing 4. What is meant by direct and indirect recognition of donor MHC? 5. What type of hypersensitivity is involved in each of the following stages of allograft rejection? a. hyperacute rejection b. acute rejection c. chronic rejection 6. In transplantation of which of the following tissues is a graft-versus-host reaction most likely to occur? a. kidney b. heart c. liver d. bone marrow e. pancreas 7. How does cyklosporin A inhibit T-cell activation? 8. What is the main mechanism of rejection of discordant xenografts? 9. Regarding AB0 and Rh blood types, which one of the following is the MOST accurate? a. People with type 0 are called universal recipients because they have antibodies against H substance but not against A and B antigens b. If the father is Rh-positive and the mother is Rh-negative, hemolytic disease of the newborn only occurs when the child is Rh-negative c. People who are Rh-negative usually have antibodies to the Rh antigen because they are exposed to cross-reacting antigen located on bacteria in the colon d. If type A blood is transfused into a person with type B blood, complement will be activated and the membrane attack complex will cause lysis of the type A red cells 1-9 from: Jacqeuline Sharon: Basic Immunology 10) How does stem cell transplant differ from solid organ transplant? 11) Describe two laboratory procedures designed to reduce the risk of rejection. 10-11 from: Nairn & Helbert: Immunology for medical students.






![Immune Sys Quiz[1] - kyoussef-mci](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006621981_1-02033c62cab9330a6e1312a8f53a74c4-300x300.png)