1.20 polar bonds and molecules
advertisement

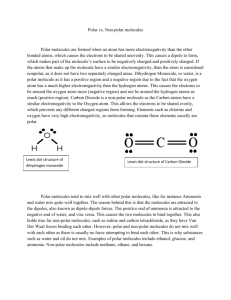
SCH 4C Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules When two atoms with very similar electronegativities bond covalently, the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms. This is called a ______________________________. Two atoms with different electronegativities can still share electrons, but in this case the sharing does not have to be equal. δ- means _______________ δ+ means _______________ When an electron pair is not shared equally, there is a buildup of negative charge around one atom, while the other atom remains more positively charged. Ions are not created, however! The electrons are more attracted to the atom with the _____________________. Using Electronegativities to Predict Bond Type EN The difference in electronegativity between two atoms is used to determine whether a bond is covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Predict the type of bond that would be made between the following atoms: a) Li and F b) Cl and Br c) H and O Polarity in Molecules If a covalent molecule has polar bonds, it may result in a _______ __________. Two things must be considered: 1) the presence of _______________ covalent bonds. 2) The _______________________________ (geometry) of the molecule. Non-polar molecules are very symmetrical and do not have charge differences within the molecule. Polar molecules have charge differences due to their less perfect geometries. Symmetry in Molecules Molecular symmetry can be determined by looking at where electron pairs are placed around a central atom. An electron pair can be either a ______________________ pair of electrons or a __________________ pair of electrons. If all of the electron areas around the central atom are the same, then the molecule has _______________________. Examples: N2 NO2 NH3 CO2 Activity: Build the following molecules with the molecular modeling kits. Complete the chart below by determining the bond type, drawing a formal Lewis structure diagram, sketch the shape of the molecule when you build it, determine if the molecule has symmetry and decide if the molecule is polar or non-polar. Molecule O2 CO2 H2O CH4 H2 HCl C2H2 CCl4 𝝙EN and bond type Lewis Structure Sketch of Shape Symmetry Molecular Polarity Properties of Polar Molecules Polar molecules can make ________________ _________ which allow like molecules to attract each other in large numbers. This is why polar substances tend to have higher melting points and boiling points than non-polar molecules. intermolecular bonds Homework: 1. Which of the following molecules are polar molecules? F2 H2 O2 H2S CO2 2. Identify the more polar bond in each of the following pairs. a) H-F and H-Cl b) N-O and C-O c) S-H and O-H d) P-Cl and S-Cl e) C-H and N-H f) S-O and P-O 3. How do intermolecular bonds help to explain why the boiling point of methane, CH4, is much lower than the boiling point of hydrogen bromide, HBr?