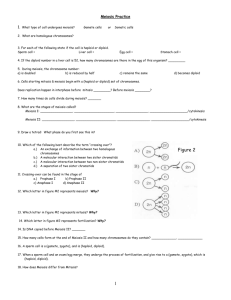
In biology, meiosis (pronounced my-oh
advertisement

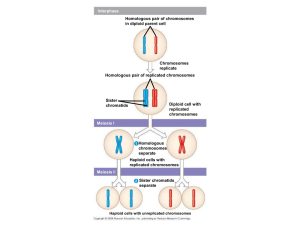
MEIOSIS (my-oh-sis) In biology, meiosis (pronounced my-oh-sis) is a process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half. In animals, meiosis always results in the formation of gametes, or sex cells, such as, sperm or egg. Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction and therefore occurs in all eukaryotes that reproduce sexually. During meiosis, long segments of DNA packaged into chromosomes, undergo DNA replication followed by two rounds of division, resulting in four haploid cells. A haploid cell contains only half the amount of chromosomes of the original cell. This is important because during fertilization, an egg and sperm join; They both need only half of the DNA (chromosomes) so that when they join, a zygote with a full set of chromosomes (diploid) is produced. Fill in the blanks: 1. A _________________ is a long segment of coiled DNA. We usually represent it as an X. 2. During _________________, a cell is divided to make 4 non-identical cells with half the number of chromosomes. 3. A _________________ cell has only half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. 4. A _________________ cell has a full set of chromosomes. 5. An example of a ________________ is a sperm or egg cell. Write a sentence for each word. (meiosis, gamete, chromosome, diploid, haploid) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Answer the following: 6. For Humans, whose normal diploid cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairsor 23 from mother and 23 from father) what is their haploid cell chromosome number? 7. What type of cell is produced from meiosis in males__________, in females___________? 8. How are each of the four daughter cells produced from meiosis different? 9. What do crossing over and independent assortment mean? 10. Why would you and your brothers and sisters be genetically unique?