Earthquake Study Guide: Faults, Waves, and Magnitude
advertisement

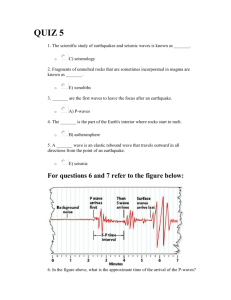
Earthquakes Occur on faults, near plate boundaries Three types of fault: normal (tension stress), reverse (compressive stresss), strike-slip (also called transform) (shear stress) Elastic rebound theory: elastic strain slowly builds up – then energy released suddenly Focus: location of earthquake at depth Epicenter: point on surface above focus Seismic waves (km/sec) 1) P-waves (like sound waves) – Primary waves- fastest 2) S-waves (shear waves)-Secondary, slower S waves cannot travel in liquids (e.g outer core) 3) Surface waves cause most damage Seismograph – instrument records ground motion Suspended weight with pen attached Rotating drum of paper When earth shakes pen records ground motion Called a seismogram Distance to epicenter Difference in arrival times of P and S waves Location of epicenter Need at least 3 seismic stations Draw circle around each station Radius of circle is distance to quake Intersection of 3 circles is location of quake Earthquake magnitudes 1) Mercalli damage scale: 1 (none) –12 (total) 2) Richter scale – log scale- measures amplitude of ground motion. Each unit= 30 times more energy. 3) Moment magnitude (best estimate of energy) = (fault slip x fault area x strength of rock) Study questions. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. What is the map location of an earthquake called? a. focus b. ground zero c. epicenter d. a bad place to be e. nexus 2. What is the point of subsurface origin of an earthquake called? a. focus b. ground zero c. epicenter d. a bad place to be e. nexus 3. Which type of earthquake wave moves the fastest? a. P-waves b. S-waves c. Love waves d. Rayleigh waves e. Permanent waves 4. Which type of earthquake wave could travel through a vacuum? a. P-waves b. S-waves c. surface waves d. all of the above e. none of the above 5. Which type of earthquake body wave cannot pass through liquids? a. P-waves b. S-waves c. Love waves d. Rayleigh waves e. surface wave 6. How much more energy does a magnitude 8 earthquake release than a magnitude 7 earthquake? a. 2 times more b. c. d. e. 10 times more 30 times more 900 times more 27,000 times more a Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C A A E B C