Biology 211 - Lab Week One: Scientific Method, Basic Chemistry for
advertisement

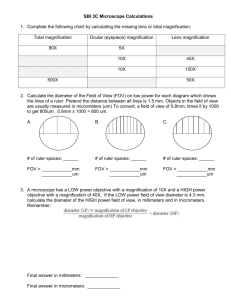
Biology 211 - Lab One: Scientific Method, Data Analysis, and Microscope Basics Reminder: Bring your textbook and a calculator – goggles NEXT week! Pre-Lab Homework: 1. Using your text (1.3), understand the steps of the scientific method and their order, and explain two important features of a good hypothesis. 2. Using this handout, describe the DEPENDENT and INDEPENDENT variables of an experiment? Which is plotted on the X-axis of a graph? Which on the Y-axis? 3. Using this handout, name and describe two diseases and two different biological molecules that will you be exploring during this lab. 4. Using your text (6.1 and appendix D) and this handout, answer the following questions about LIGHT microscopes: When were they invented? What is their magnification capacity? Name FOUR parts you have to know. Name TWO things you will be viewing in this lab. In-Lab Activity Overview a. Table/Group Discussion - Questions and Hypotheses b. Pair Analysis - Methods and Variables in a Scientific Experiment c. Working With and Graphing Scientific Data d. Introduction to Microscope Use e. Homework Table/Group Discussion - Analyzing Questions and Hypotheses Although scientific inquiry is useful and powerful, there are limitations to this approach in terms of trying to answer ALL questions. Discuss provided questions in terms of whether they can be answered scientifically. Your instructor will lead a class discussion and expect all tables/teams to participate! Pair Analysis - Methods and Variables in a Scientific Experiment Work in pairs to analyze the following experiment scenario. Answer all questions that follow to learn about important kinds of variables, and then some biology. You are the lead investigator on an FDA research grant that aims to examine whether there is a relationship between taking diet supplements that contain omega-3-fatty acids and the development of atherosclerosis. You enroll 2000 people in your study, with 1000 taking an omega-3-fatty acid supplement and 1000 taking a placebo. Every three months during your year-long study, each participant has their blood pressure tested and an ultrasound technician images and measures their femoral artery for signs of blockage. Hypothesis and Variables – Work In Pairs 1. Write an appropriate hypothesis for this experiment. Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 1 2. The dependent variable is what EXACTLY is going to be measured, counted, or observed. Given that, what is/are the dependent variable/s for this experiment? 3. The independent variable is the condition that the scientist manipulates (one being the control). Given that, what is/are the independent variable/s for this experiment? Which is the control? 4. Controlled variables are features of, in this case, the subjects that must be the similar because differences could have significant effects on the experiment outcome. Determine EIGHT controlled variables that should be taken into account for this experiment. Biology – Consult Your Book 1. Omega-3-fatty acids are a kind of unsaturated fatty acid. Which group of biological molecules do fatty acids belong to? Name two specific large molecules that fatty acids build. 2. What kinds of organisms/foods typically contain unsaturated fatty acids? Working With and Graphing Scientific Data In this exercise, you will examine provided scenario data, graph the data, interpret the data, and learn some biology. When making any graph: The independent variable is plotted on the X axis; the dependent on the Y The graph must be titled and all axes must be labeled, including units of measure Choose scales for your X and Y axes that best represent the range of your data Line Graphs are best for describing continuous data like changes over time Bar Graphs are best for describing and comparing discrete data groups Sickle Cell Disease Scenario – Bar Graph (Line Graphing Next Week!) Sickle cell disease involves a mutation in the gene that encodes part of hemoglobin. Normal people have a “glu” at a key hemoglobin location, while people with the sickle cell mutation have “val.” Researchers studied the worldwide distribution of sickle cell disease, counting the number of people with glu vs. val, and comparing different geographical locations as a function of their average annual temperature. Biology – Work in Pairs, Consult Your Book 1. Which group of biological molecules does hemoglobin belong to? What subunits are used to build members of this group? 2. Using Figure 5.17, find glu and val. What is the chemistry of each and why might changing glu to val create a problem? 3. What other INFECTIOUS disease influences sickle cell? Introduction to Light Microscopes Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 2 Remove microscope from the cupboard, carrying it by the arm and base. Review the basic parts of the microscope that you need to know: oculars, objectives, stage, coarse vs. fine focus, lamp/light source, on/off, light intensity switch, condenser. Most microscopes in this lab have 10X oculars, and four different objectives: 4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X. Total magnification = ocular magnification X objective being used. Basic Techniques – Work In Pairs 1. Carefully clean the lenses and oculars using provided lens paper and cleaner. 2. Turn on your microscope and rotate the objectives such that you are looking through the 4X lens; adjust intensity to mid-range (i.e. visible but not blinding). 3. Place your “letter e” slide in the slide holder, using the joystick to center the “e” in middle of the stage opening. Using COARSE focus, bring image into clear view. 4. When satisfied, rotate the objectives such that you are looking through the 10X lens and – using COARSE and then FINE focus – bring the image into clear view. When “e” is in focus, complete the following: Using joystick, move slide to the right; how does what you see move? Is image in the ocular inverted relative to the specimen on the stage? 5. Now, rotate objectives such that you are looking through the 40X objective lens and – using ONLY THE FINE focus – bring the image into clear view. You may have to increase the light intensity. When “e” is in focus, complete the following: Is “working distance” (specimen to objective) greater with 10X or 40X? What is the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION of the letter you are seeing? If the oculars were 20X, what would the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION be? 6. Remove “e” slide and rotate back to the 4X objective lens. Place the clear ruler as flat as you can on the stage, focusing on its mm marking edge. In mm units, what is the diameter of the circular field of view? Repeat this measurement for the 10X and the 40X objective. Cells are usually measured in microns (um); convert all mm’s to um’s. What is the relationship between field of view size and magnification? 7. Remove the ruler and rotate back to the 4X objective lens. Find your “threads” slide and focus on a region where you see threads crossing. Using 4X objective, are both threads in focus at same time? With 10X? Does the 4X or 10X objective have a shorter depth of field? Homework Read your text, 1.3 section called “Case Study in Scientific Inquiry…” and figure out: 1. What is the question? What is the hypothesis being tested? 2. What organism is being used and where was this study conducted? 3. What was the dependent variable? The independent variable? The control? 4. What kind of graph was chosen for this study? Why? Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 3 5. What was the major conclusion researchers made from this study? Lab One: Biological Molecules & Cells - Turn In As Pairs At End of Lab Pair Member Names: 1. Methods and Variables in a Scientific Experiment This question is worth 3.5 pts. For every mistake, 0.5 pts. will be subtracted! a. Hypothesis: b. Dependent Variable(s): c. Independent Variable(s) – circle CONTROL: d. EIGHT Controlled Variables: i. v. ii. vi. iii. vii. iv. viii. e. Fatty acids are _____________ that build _____________ and _____________. f. Name two foods that would contain unsaturated fatty acids: i. ii. Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 4 2. Sickle Cell Graphing and Problems This question is worth 3.5 pts. For every mistake, 0.5 pts. will be subtracted! a. Hemoglobin is a _________________ built from ______________________. b. Why might changing glu to val create a problem? c. What other INFECTIOUS disease influences sickle cell & human evolution? How might this relate to the data - explain? Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 5 3. Microscope Skills This question is worth 3 pts. For every mistake, 0.5 pts. will be subtracted! Question When you move slide right, the image in the ocular moves… Your Answer(s) Is the image in the ocular inverted relative to the specimen? Is working distance greater with 40X OR 10X objective? Total magnification of last “e” operation? Diameter – in mm AND um – of field of view using 4X objective. Diameter – in mm AND um – of field of view using 10X objective. Diameter – in mm AND um – of field of view using 40X objective. What is relationship between field of view size and magnification? Are threads in focus using 4X objective? Are threads in focus using 10X objective? Does the 4X or 10X objective have a shorter depth of field? Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab One, page 6