Cell and Microscope Study Guide
advertisement

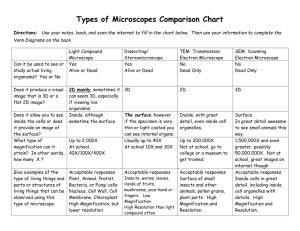
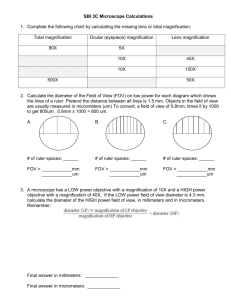
Name___________________________________________________________________Period_______ Study Guide Chapter One Test Section 1.1A. Scientists (make sure you know what they discovered and what their experiment was) 1. Robert Hooke: Observed dead cork cells under a microscope Called what he saw “cells” after the cells that monks occupied in monasteries 2. Anton von Leeuwenhoek First person to observe living cells Observed living cells in a sample of pond water 3. Francesco Redi Spontaneous Generation: In Redi’s time—the 1600s—it was commonly believed that living organisms would randomly come in to being from non-living materials. Fly/Meat Experiment: A commonly-held assumption by Redi’s contemporaries was that maggots (fly larvae) were generated in decaying meat and dead flesh. In order to test this hypothesis, Redi placed rotten meat in both an OPEN CONTAINER and in a CLOSED CONTAINER. Although adult flies tried to get into BOTH containers, they could only gain access to the meat in the OPEN CONTAINER. After some time, maggots appeared ONLY on the meat in the open container, suggesting that THE ADULT FLIES WERE THE SOURCE OF THE MAGGOTS and SPONTANEOUS GENERATION DID NOT OCCUR!! 4. Louis Pasteur Pasteurization: Process developed by Louis Pasteur after discovering that bacteria in the air could contaminate food. By superheating and then rapidly cooling food items, bacterial concentrations can be greatly reduced—prolonging shelf-life and reducing spoilage/infection. Bacteria/Broth Experiment: Preparing two flasks containing a broth (proteins, carbohydrates, etc. to support bacterial growth), Pasteur then sterilized them using high heat to kill any bacteria potentially present in the broth. Now, with both flasks bacteria free, Pasteur left one flask OPEN and left one flask CLOSED AIR-TIGHT. After some time, the OPEN FLASK HAD BACTERIAL GROWTH, while the CLOSED FLASK HAD NO BACTERIAL GROWTH. After opening the closed flask and exposing it to air, it went on to DEVELOP BACTERIAL GROWTH. This was strong evidence that bacteria is present in the air around us and led Pasteur to develop the technique for sanitizing foods called Pasteurization (see above). The results of this experiment also demonstrated that CELLS MUST COME FROM OTHER CELLS!!!! B. Cell Theory – 3 parts 1. ALL LIVING THINGS ARE COMPOSED OF ONE OR MORE CELLS 2. THE CELL IS THE MOST BASIC STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF LIFE 3. ALL CELLS ARISE FROM EXISTING, LIVING CELLS Section 1.2A. Microscopes – know what can be seen with them and magnification 1. Compound Light microscope: Uses visible light to look at a thin sample; can observe cells but not detailed organelles Eyepiece/Ocular Lens is always 10X magnification Can have objective lenses of 4X, 10X, and 40X OR 10X, 40X, and 100X To find total magnification we multiply the 10X magnification of the eyepiece and the magnification of whatever objective lens we are using o EXAMPLE: 10X (eyepiece) and 40X (objective lens):10 * 40 = 400X o The weakest magnification would be 4X objective: 10 * 4 = 40X o The strongest magnification would be 100X objective: 10 * 100 = 1000X 2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): Uses an electron beam to produce 3D, surface images of a specimen at up to 100,000X Total Magnification (think SCANNING=SURFACE) 3. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): Uses and electron beam to penetrate a thin sample and produce images of a specimen at up to 300,000X Total Magnification (think TRANSMISSION=THROUGH) B. Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes C. Plant vs. Animal Cells D. Endosymbiotic Theory: MITOCHONDRIA and CHLOROPLASTS were once distinct organisms that were absorbed into larger, pre-eukaryotic cells. Over billions of years, the symbiosis between MITOCHONDRIA/CHLOROPLASTS and the EUKARYOTIC HOST CELLS has evolved to the point that they are inseparable. MITOCHONDRIA are found in ALL eukaryotic cells, while CHLOROPLASTS are found only in eukaryotes that perform PHOTOSYNTHESIS. This implies that MITOCHONDRIA were acquired before the split of animals and plants and CHLOROPLASTS were acquired after. Organelle Functions: Centriole organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division Cilia and Flagella Used for movement/moving substances around outside of the cell Central Vacuole Maintains shape of cell, stores water, nutrients and waste Golgi Apparatus process materials manufactured by the cell Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Site of lipid synthesis Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Site of protein synthesis Ribosome produces proteins Chloroplast Captures light energy and converts to sugar Cell Wall Maintains cell shape, works with central vacuole to maintain turgor pressure Cell Membrane support, protection, controls movement of materials in/out of cell Nucleus controls cell activities Mitochondrion breaks down sugar molecules into energy Cytoplasm fluid substance that fills the interior of the cell Lysosome breaks down cellular waste products and debris (contains enzymes) Animal and Plant Cell (Eukaryotic) Bacteria (Prokaryotic) Parts of Microscope **(blank on next page for practice)**