homework #2
advertisement

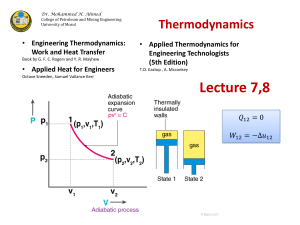
AOS 330 Homework #2 Due: 10/05/09 1. State the First Law of Thermodynamics and define/explain each term in the equation. Next define/explain the following: adiabatic process, isobaric process, isothermal process, and isochoric process in terms of the 1st Law. Rewrite the 1st law under each one of these processes. 2. The equation of state when considering a dry atmosphere is: P RT , where P is pressure, T is temperature, is the air density, and R is the Gas Constant of dry air. a.) Calculate R, only taking into account the volume fractions of the atmospheric constituents: N2, O2, Ar, and CO2 b.) Repeat the process but for the surface of Mars 3. Poisson’s equation for potential temperature is: 1000hPa T P R / Cp Derive Poisson’s equation for potential temperature from the First Law of Thermodynamics. a.) Define/explain “ ” b.) A trans-continental airline cruises at an altitude of approx. 12km, where the temperature may be -55C and the pressure approx. 200hPa. Compute the potential temperature of air at this altitude. c.) For a potential temperature of 310K compute the corresponding “T” at 700hPa, 300hPa, 100hPa 4. Prove mathematically that the potential temperature is constant for adiabatic processes i.e. = 0. (Hint: use the 1st Law of Thermo. and the equation for potential temp.) 5. Of specific interest in thermodynamic theory are cyclic processes. Explain what is meant by a cyclic process. Next using the pressure, volume diagram below explain what happens to a gas as it goes from Point A to Point B. Then, explain what happens as the gas goes from Point B to Point A. Hash out the work done on the gas and write out mathematically the net work done on this cyclic process. 6. Please define/explain the Second Law of Thermodynamics.