Advanced Chem Lecture #6
advertisement

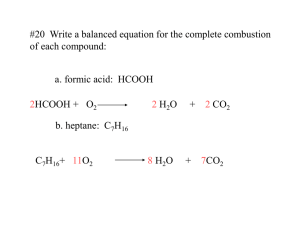
Advanced Chem Lecture #6 Percent Composition Suppose we need to verify the purity of a substance First determine what percentage of mass should come from each element Then determine what percentages are actually contributed Use percent composition to determine mass of elements in molecule Mass % element X = moles X in formula x molar mass of x (g/mol) mass (g) of 1 mol compound X 100 Note that the individual components ALWAYS add up to 100% Glucose (C6H12O6). Determine mass percent. How many grams carbon in 16.55g? Determination of Empirical Formula Can determine empirical formula of unknown compound from masses of elements An analytical chemist investigating a compound decomposes it into simpler substances, finds the mass of each component element, converts these masses to numbers of moles, and then mathematically converts the moles to whole-number subscripts. This procedure yields the empirical formula, the simplest wholenumber ratio of moles of each element in the compound. Analysis shows that an unknown compound contains 0.21mol Zn, 0.14mol P, and 0.56mol O. Determine empirical formula. First, divide by smallest subscript. If any subscripts are still not integers, multiply through by the smallest integer that will make them all integers. Zn0.21P0.14O0.56 / 0.14 Zn1.5P1.0O4.0 * 2 = Zn3P2O8 Note that since we multiplied all the subscripts by two, we did not change the relative amounts of moles in each Different substances can have the same empirical formula but different molecular Name Formaldehyde Acetic Acid Lactic Acid Erythrose Ribose Glucose Molecular Formula CH2O C2H4O2 C3H6O3 C4H8O4 C5H10O5 C6H12O6 Multiple 1 2 3 4 5 6 g/mol 30.03 60.05 90.08 120.1 150.13 180.16 Use biologoical preservative vinegar 5% solution forms in muscle during exercise forms during sugar metabolism nucleic acid component cellular nutrient Balancing Chemical Equations Vitamin C (176.12g/mol) is a compound of C,H,O found in citrus fruits. When a 1.000g sample is placed in a combustion chamber and burned, following data obtained: Mass CO2 after combustion: 85.35g Mass CO2 before combustion: 83.85g Mass H2O absorber after combustion: 37.96g Mass H2O absorber before combustion: 37.55g What is the molecular formula for Vitamin C? Find mass of CO2 added, from this, can use mass fraction of C to find carbon content in vitamin C. Similarly, find mass of H from mass fraction of H2O added. Mass of vitamin C (1.000g) minus C and H gives mass of O. Knowing grams of each, calculate moles of each, construct empirical formula, determine whole-number multiple from given molar mass, then give molecular formula Mass CO2 = 85.35-83.85 = 1.50g CO2 Mass H2O = 37.96-37.55 = 0.41g H2O Mass C = 1.50g CO2 * (12.01gC/44.01gCO2) = 0.409g C Mass H = 0.41g H20 * (2.016g H/18.02g H2O) = 0.046g H Mass vitamin - mass C - mass H = mass O = 0.545g Divide grams by molar mass to give mols 0.0341 mol C, 0.046mol H, 0.0341mol O Preliminary formula: C0.0341H0.046O0.0341 Divide by smallest subscript: C1H1.3O1 Multiply through by 3: C3,H4O3 Molar mass vitamin C / molar mass emprical = 2 (Empirical * 2) = C6H8O6 Check Stoichiometry Can use example from combustion reaction above to balance.