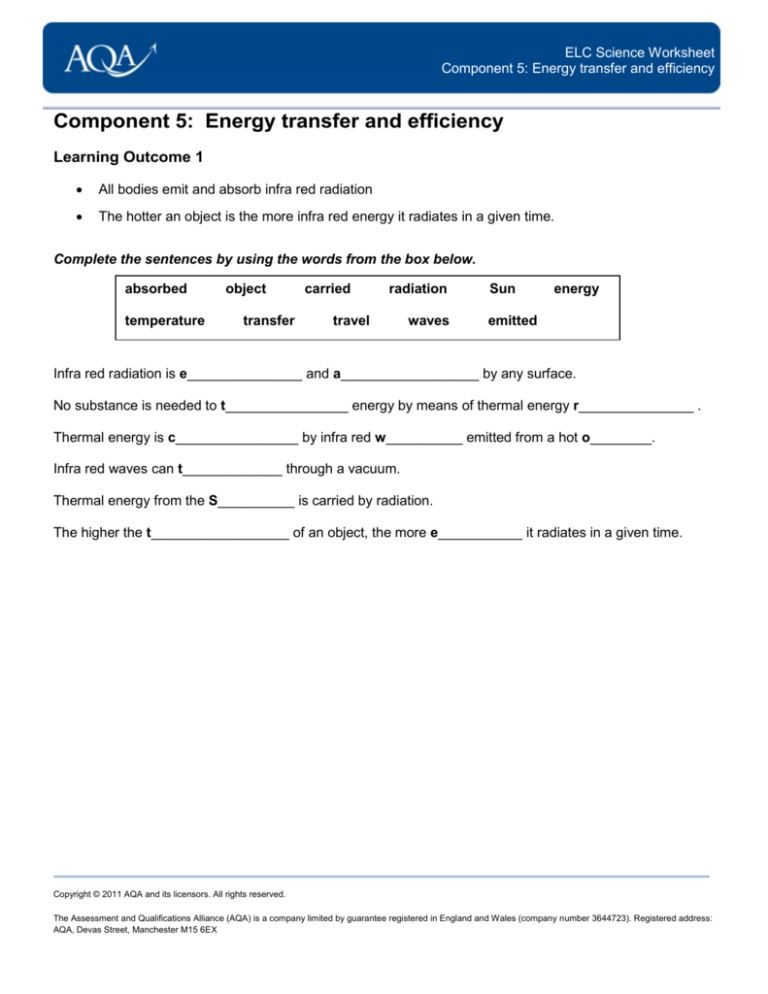
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 1
All bodies emit and absorb infra red radiation
The hotter an object is the more infra red energy it radiates in a given time.
Complete the sentences by using the words from the box below.
absorbed
temperature
object
transfer
carried
radiation
travel
waves
Sun
energy
emitted
Infra red radiation is e_______________ and a__________________ by any surface.
No substance is needed to t________________ energy by means of thermal energy r_______________ .
Thermal energy is c________________ by infra red w__________ emitted from a hot o________.
Infra red waves can t_____________ through a vacuum.
Thermal energy from the S__________ is carried by radiation.
The higher the t__________________ of an object, the more e___________ it radiates in a given time.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 2
Dark, matt surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of infra red radiation.
Light, shiny surfaces are poor absorbers and poor emitters of infra red radiation.
Light, shiny surfaces are good reflectors of infra red radiation.
Complete the sentences by using the words from the box below.
emitter
reflector
light shiny
absorber
dark matt
radiator
object
A d____________ m___________ surface is the best absorber of infra red radiation.
A l____________ s_____________ surface is the worst absorber of infra red radiation.
A light shiny surface is a good r__________________ of infra red radiation.
A dark matt surface is a good e__________________ of infra red radiation.
A light shiny surface is a poor r__________________ of infra red radiation.
A thermometer with a blackened bulb is a better a_______________ of infra red radiation than
one that has not been blackened.
Use the ideas above to explain each of the following.
A thermal blanket used to keep a marathon runner warm has a light shiny outer surface.
Sandwiches wrapped in shiny aluminium foil stay cool.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
The clothing for summer sports like cricket and tennis is often white.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Emitters and absorbers
Match the beginnings with the correct endings.
Beginnings
Endings
Houses in hot countries are
often painted white
it will radiate infra red energy
more quickly
Solar panels on the roof of a
house are painted black
better than a shiny surface
Electric fires often have a
shiny metal sheet behind the
heating element
light surfaces are poor
absorbers of radiation
A car radiator is usually
painted black because
so that they absorb as much
solar radiation as possible
A matt surface absorbs infra
red radiation
because light shiny surfaces
are good reflectors of infra red
radiation.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 3
The use of kinetic theory to explain the different states of matter.
The particles of solids, liquids and gases have different amounts of energy.
All substances, solids, liquids and gases, are made from particles.
Match the description to the correct diagram
Description
Container showing particles
The particles in a solid are
very close together
vibrate in one place
usually stay in a fixed pattern
The particles in a liquid are
close together
move in all directions
have no fixed pattern
The particles in a gas are
far apart
move very quickly in all
directions
move all over the container
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
The particles of solids, liquids and gases have different amounts of energy.
Solid, Liquid and Gas
Solid
Liquid
Gas
melting
evaporating
freezing
condensing
Complete the sentences by using the words from the box below.
faster
liquid
more
solid
boiling
particles
melting
energy
gain
Solid to Liquid
When a s_______________ is heated, its p_______________ gain more energy. This makes the
particles vibrate m_______________, which weakens the forces that hold the solid together.
Eventually the particles will have enough e_______________ to break free from their fixed
positions. This is called m_______________ and the solid turns into a liquid.
Liquid to Gas
When a l_______________ is heated the particles g_______________ even more energy. Again
the particles move f_______________ which weakens and breaks the bonds holding the liquid
together. With enough energy the particles are free to move very quickly in all directions. When a
liquid turns into a gas this is called e_______________.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 4
The transfer of energy by conduction, convection, evaporation and condensation involves particles.
Thermal energy transfer
These methods of thermal energy involve particles. There are four different ways energy can be transferred
by particles:
1.
Conduction
This is the process of transferring thermal energy through solid material without any visible change in the
motion (movement) of the particles of the material
2.
Convection
This is the process of transferring thermal energy by the movement of the fluid (liquid or gas) through which
thermal energy is being transferred
3.
Evaporation
This is the process of transferring thermal energy to a liquid causing the particles to be converted to a gas.
4.
Condensation
This is the process of changing gas to a liquid.
Look at these examples below and draw a ring around the process by which thermal energy is being
transferred.
Heating up the air (gas) in a room causes it to rise and then
fall when it cools near a cold window. This movement of air
is called a current.
This example of thermal energy transfer is called
conduction convection evaporation condensation
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Thermal energy from the hot tea is being transferred
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
through the solid metal spoon.
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
This example of thermal energy transfer is called
conduction convection evaporation condensation
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Thermal energy transferred to saucepan of water causing
currents to form in the liquid.
This example of thermal energy transfer is called
conduction convection evaporation condensation
Steam (gas) turns to a liquid when it touches the cold
window.
This example of thermal energy transfer is called
conduction convection evaporation condensation
Which process is responsible for the thermal energy transfer in each of the cases below?
Answer each one by using the word conduction, convection or radiation.
1. The handle of a saucepan heats up when the pan and the contents are placed
on a cooker hot plate ___________________________
2. An object near to a gas fire becomes warm _____________________
3. The air in a room warms up when an electric heater in the room is switched on
________________________________________
4. Thermal energy travels between two objects in space ___________________________
5. Thermal energy travels through a metal bar _________________________________
6. Thermal energy travels through water _____________________________________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Complete the sentences by using the words from the box below.
conductors
reduce
insulators
material
temperature
energy
The flow of thermal energy passing through a material depends on the t_____________ difference
across the material.
The type of material also makes a difference.
Metals such as copper, which are good at letting thermal e________ flow through them, are called
c__________________ .
Plastic materials such as polystyrene, which are not good at letting thermal energy flow through them, are
called i_____________________ .
The thickness of the m__________________ also matters: using more layers could r________ the thermal
energy flow.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 5
The factors that affect the rate of evaporation and condensation
There are several factors which can affect the rate of evaporation and condensation.
They include:
The difference between liquid and air temperature
The surface area/volume
Type of material
Choose the correct word from each pair in the sentences below.
When you hang washing out on the line to dry, the water (condenses / evaporates) from the surface.
This happens faster when the weather is (hot / cold) and if the air is (still / windy).
The washing will dry faster if the clothes are (folded up / spread out).
Very thick clothes will dry (faster / slower) than very thin clothes.
Try to explain the following:
On a cold winter day, windows “steam up” with condensation more often than they do on a hot summer
day.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 6
The rate at which an object transfers energy by heating depends on:
surface area
the material from which the object is made
the nature of the surface with which the object is in contact.
Choose the correct word from each pair in the sentences below.
Hot water radiators have (large / small) surface area. This is to (decrease / increase) the rate at which
they can transfer thermal energy to the room.
They are usually made of (metal / plastic).
The best type of surface, if you want them to transfer energy quickly, would be a (dull / shiny) surface
which is (dark / light) in colour.
Where else would you find a radiator, other than in a room?
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
What type of surface should you stand a hot teapot or saucepan on? Explain why.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 7
The bigger the temperature difference between an object and its surroundings, the faster the rate at
which energy is transferred by heating.
Number the following in the order of the rate at energy will be transferred.
Use 1 for the fastest and 5 for the slowest.
A cup of tea at 60 °C in a room at 20 °C
_____________
An ice cream at 2 °C in a room at 22 °C
_____________
A chip pan full of oil at 150 °C in a room at 15 °C
_____________
An ice cube at 0 °C in a fridge at minus 5 °C
_____________
A casserole at 20 °C in an oven at 200 °C
_____________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 8
Heating and insulating buildings.
U-values measure how effective a material is as an insulator.
The lower the U-value, the better the material is as an insulator.
Heating and insulating buildings
The diagram shows some of the ways in which thermal energy can be lost from a house.
Heat Loss
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Complete the sentences by using the words from the box below.
double glazing
doors
roof
loft insulation
cavity
draught-proofing
windows
floors
curtains
insulated
tank
radiator
walls
Thermal energy is lost through the r____________, w____________, w____________ and the
d_____________ and f____________. To reduce heat loss, a building can be i____________.
To reduce heat loss through the roof, l____________ i____________ can be used.
C____________ wall insulation cuts down energy loss through the walls.
By d____________-p____________ windows and doors, energy losses can also be reduced.
To further reduce energy loss, d____________ g____________ can be used; this will reduce the heat lost
through windows.
Thick c____________ can also reduce energy loss.
Thermostatic r____________ valves can be used to prevent a building from over-heating and so save
energy. Also, insulating pipes and the hot water t____________ can also reduce heat loss.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
What is a U Value?
The U Value is a measurement of the rate of heat loss through a material.
The lower the U Value the better an insulator the material is.
For example, a single glazed window with standard glass will have a U Value of 5.6, while a double glazed
window with standard glass will have a U Value of 2.8, and a triple glazed window will have a U value of 1.8.
Single glazed
Double glazed
Triple glazed
U Value 5.6
U Value 2.8
U Value 1.8
Poor insulator
Good insulator
Excellent insulator
Choose the correct word from each pair in the sentences below.
U Value is the measurement of the rate of heat (loss / gain) through a material.
The lower the U Value the (better / worse) the material is as an insulator.
The best glazed window to use would be the (single / triple) glazed window.
The U Value for a single glazed window was (1.8 / 5.6)
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Put these types of insulation in order of their ‘U Value’.
The best insulator should be number 1 and the worst insulator should be number 7.
Two have been done for you.
Best insulation
based on U
values
Type of Insulation
U
Value
A. Hot water tank cover
4.0
1
B. Loft Insulation
0.2
2
C. Thick curtains
6.0
3
D. Double glazing
2.8
4
E. Draught-proofing
2.0
5
F. Hot water pipe lagging
4.5
6
G. Cavity Wall Insulation
0.3
7
B
C
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 9
When energy is transferred, only part of it may be usefully transferred, the rest is ‘wasted’.
Fill in the blanks in the table. Each missing word is a type of energy.
Devices
Useful energy
Wasted energy
Light bulb
L_____________ from the
H__________________ from
glowing filament.
the filament to the surroundings.
Radio
S____________
H____________
Television
L____________and
H____________
S____________
Hair dryer
H____________ and
S____________ and
K____________
H____________ of the motor.
A hot iron
H____________
L____________
Food mixer
K____________
S____________
H____________
Kettle
H____________ of the water.
H____________ transfer
from the element to the kettle
and S____________
Heater
Loudspeaker
H____________ energy
L____________ from
of the surroundings.
the glowing element.
S____________
H____________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Wasted energy is eventually transferred to the surroundings, which become warmer.
Where might the ‘wasted heat’ energy be in these examples?
Cycling
As the cyclist pedals her energy turns the wheels.
Friction between tyre and the road changes some of the
energy into wasted h___________ energy which is lost to
its surroundings.
Driving a car
C____________ energy from the burning fuel powers the
car engine. However some of the chemical energy
increases the temperature of the engine. This wasted
h______ energy is lost to its surroundings.
Light bulb in torch
Chemical energy from the torch’s battery is transformed
to e______________ energy. The filament in the light
bulb glows as useful light energy and wasted h_____
energy. The wasted heat energy is lost to its surroundings.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
The wasted energy becomes increasingly spread out and so becomes less useful.
Choose the correct word from each pair in the sentences below.
Heat from barbeque
The further the light travels from the lighthouse the
more spread out it becomes so the (more / less)
useful it is.
Sound from police siren
The further the heat travels from the barbeque to
the food, the more spread out it becomes so the
(more / less) useful it is.
The further the sound the police siren travels the
more spread out it becomes so the (more / less)
useful it is.
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
Learning Outcome 10
The greater the percentage of the energy that is usefully transformed in a device, the more efficient
the device is, e.g. the comparison between filament lamps and fluorescent tubes.
Complete the following sentences.
When devices transfer e____________, only part of it is usefully transferred to where
it is wanted.
The rest of the e______________ is transferred in some non-useful way or wasted.
Usually the e_____________ is wasted to the surrounding as h____________
Concept of energy conservation:
The energy that is w_________________ does not disappear; it is changed into a
non-useful form.
The non-useful energy in a light bulb is h____________ .
The non-useful energy in a liquidiser is h______________ .
Efficiency of some energy transfers. Energy is measured in units called joules (J).
Device and amount of
energy supplied to it
Useful energy
produced
Wasted energy
Filament light bulb 100 J
20 J as L___________
______ J as heat
Low energy light bulb 25 J
___J as light
5 J as heat
Electric kettle 2000 J
1800 J to h____ the
water
100 J to h______ the
element
Electric drill 500 J
Television 200 J
300 J as kinetic
(movement) energy
20 J as light and sound
200 J as h_________
150 J as h________
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX
ELC Science Worksheet
Component 5: Energy transfer and efficiency
The greater the proportion of e_______________ supplied to a device that is usefully
transferred, the m__________ efficient the device is.
A car engine is 20% e___________________ . This means that a lot more energy is
w_______________ than is used to drive the car forward.
A microwave is 60% efficient. This means that out of every 100 joules of electrical
energy supplied, 60 joules are used to heat the food. What happens to the other 40
joules?
Copyright © 2011 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723). Registered address:
AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX