Volcano Test Study Guide
advertisement
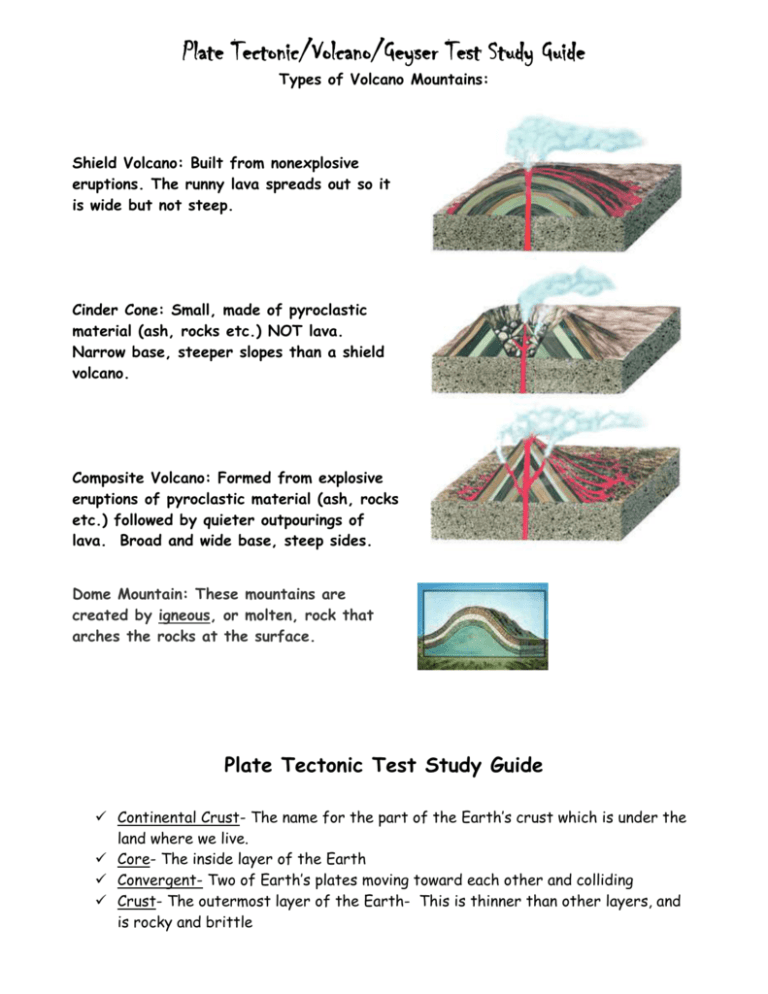
Plate Tectonic/Volcano/Geyser Test Study Guide Types of Volcano Mountains: Shield Volcano: Built from nonexplosive eruptions. The runny lava spreads out so it is wide but not steep. Cinder Cone: Small, made of pyroclastic material (ash, rocks etc.) NOT lava. Narrow base, steeper slopes than a shield volcano. Composite Volcano: Formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material (ash, rocks etc.) followed by quieter outpourings of lava. Broad and wide base, steep sides. Dome Mountain: These mountains are created by igneous, or molten, rock that arches the rocks at the surface. Plate Tectonic Test Study Guide Continental Crust- The name for the part of the Earth’s crust which is under the land where we live. Core- The inside layer of the Earth Convergent- Two of Earth’s plates moving toward each other and colliding Crust- The outermost layer of the Earth- This is thinner than other layers, and is rocky and brittle Divergent- Two of Earth’s plates moving away from each other- When plates move apart, molten rock rises and cools, which creates new crust. Mantle- The middle layer of the Earth- It comprises most of the earth’s mass. Oceanic Crust- The name for the part of Earth’s crust which is under the ocean Plate Tectonics- This is a geological theory which says that the surface of Earth is broken into large plates. Transform- Two of Earth’s plates moving horizontally against each other- An example is the San Andreas Fault in California. Extinct volcanoes have not erupted in recorded history and probably never will again. Dormant volcanoes are not currently erupting but have erupted at some time in recorded history. Active volcanoes are in the process of erupting or show signs of erupting in the near future. Scientists predict volcanic eruptions: They measure earthquakes because they occur closer together and become stronger before an eruption. They also measure the slope of a volcano because it may bulge before an eruption. They collect gases and use satellite images which can measure temperature changes. Volcanoes get hotter as magma pushes closer to the surface. A geyser is a hot spring with narrow spaces in its plumbing which erupts periodically and forcibly ejects hot water. A hot spring has an open plumbing system and the superheated water is able to rise freely to the surface. Old Faithful is the name of a famous geyser in Yellow Stone National Park.








