Weather Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

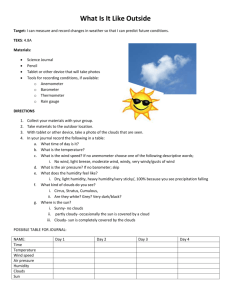
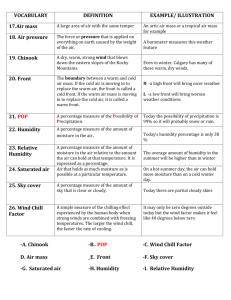
Weather Test Study Guide Answer Key Humidity and Water Vapor 1. Explain the difference between humidity and relative humidity. Humidity is the amount of moisture in the air. Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air compared with the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a given temperature. 2. What is saturation? Air is saturated when the rates of evaporization and condensation are equal The air cannot hold any more water; it will rain.. 3. What is dew point? The temperature at which air with a given amount of water vapor reaches saturation. Water will condense on objects (grass in the morning). 4. What is the relative humidity at dew point? 100% 5. Air’s ability to hold water increases as the temperature Increase. Air Masses in North America 6. A warm air mass is called a Tropical air mass. 7. A cold air mass is called a Polar air mass. 8. A dry air mass is called a Continental air mass. 9. A wet air mass coming from the ocean is called Maritime air mass 10. A cold dry air mass is called Polar Continental. 11. A cold wet air mass is called Polar Maritime. 12. A warm dry air mass is called Tropical Continental. 13. A warm wet air mass is called Tropical Maritime. Weather Instruments 14. Barometer measures Air Pressure. 15. Thermometer measures Temperature/Heat. 16. Anemometer measures Wind Speed. 17. Wind Sock and Wind Vanes measures Wind Direction. 18. Psychrometer measures Relative Humidity. 19. Hygrometer measures Humidity. Clouds 20. Nimbus means Precipitation, Rain. 21. Cirro means Thin, feathery, wispy cloud that is very high and no rain is expected. 22. Alto means medium altitude. 23. Strato means Spread Out, forms layers. 24. Puffy white clouds with flat bottoms are called cumulus. 25. Thin feathery clouds made of mostly ice are called cirrus. 26. Fog is simply a low stratus cloud. 27. Large thunderhead clouds that produce precipitation are called Cumulonimbus clouds. 28. Clouds are formed by Condensation. Fronts 29. What is the difference between an air mass and a front? An air mass is a large body of air that has the same moisture and temperature throughout. A front is the boundary that forms where two different air masses meet. 30. A front that forms when a warm air mass is trapped between cold air masses and forced to rise is called an occluded. 31. ACold Front occurs when a cold air mass meets and displaces a warm air mass. 32. How does a rain storm begin when a warm front and cold front collide? The warm front contains the water. The cold front forces the warm, wet air higher and it condenses and then falls to the ground as water. Severe Storms 33. A severe storm that forms as a rapidly rotating funnel cloud is called a Tornado. 34. Climate is temperature measured over a long period of time while weather is temperature measured at one precise moment. 35. How hot is lightning? Lightning is as hot as the surface of the sun. 36. How is lightning formed? Lightning is formed when clouds collide and either lose or gain electrons. This difference in electrons causes an electron imbalance. When the electrons flow together to balance the electron inequality, lightning occurs. 37. How is hail formed? A rising current of warm air forces water drops to rise and freeze. They then fall to the ground as hail. 38. What is the largest storm system? Hurricanes. 39. What causes most deaths in hurricanes? Storm surge. 40. What storm system has the highest wind speed? Tornadoes Weather Maps 41. Isobars indicate air pressure on a weather map. 42. A scientist that measures the formation of weather systems is a meteorologist. 43. What is an air mass? An air mass is a large body of air that has similar temperature and moisture. 44. A maritime air mass is a wet air mass that forms over water. 45. A continental air mass is a dry air mass that forms over land. 46. What is a Font? The boundary between air masses 47. As the temperature of air increases the amount of water vapor it can hold increases. Voccabulary Isobars – symbols on a weather map that indicate air pressure Front – the boundary that forms between two different air masses Air mass – a large body of air that has the same moisture and temperature Strato clouds – spread out, forms layers Cirro clouds - thin, feathery, wispy clouds that is very high and no rain is expected Cumulus clouds– puffy white clouds with flat bottoms Alto – medium altitude Nimbus - precipitation Barometer - instrument used to measure air pressure Thermometer - instrument used to measure temperature/heat Anemometer - instrument used to measure wind speed Psychrometer – instrument used to measure relative humidity Humidity – the amount of moisture in the air Relative humidity – the amount of moisture in the air compared with the maximum about of moisture the air can hold. Dew Point – the temperature of the air when the air becomes saturated Saturation – air is saturated when the air cannot hold any more water Meteorologist - a person that studies the atmosphere and forecasting the weather