1.3RefractionOfLight - ECF Saint Too Canaan College
advertisement

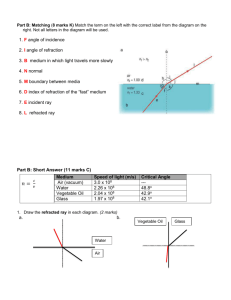
ECF Saint Too Canaan College S.3 Physics Unit 1 Light Rays 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Light as rays Reflection of light Refraction of light Lenses In this unit, we will learn the ray model of light how a plane mirror forms images how light is refracted at the boundary between two media how lenses form images 1.3 Refraction of light When a light ray travels from air to glass, it bends towards the normal. When a light ray travels from glass to air, it bends away from the normal. incident ray normal angle of incidence air glass angle of refraction refracted ray Laws of refraction How much a ray is bent depends on the media. If we know the direction of the incident ray, we can find the direction of the refracted ray using the laws of refraction (折射定律). 1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal all lie on the same plane, 2. Snell's law: sin i constant sin r The constant depends on the media across which light ray travels. Refractive index If the light ray travels from air to other media, the constant is called the refractive index (折射率). sin i n sin r When the light ray travels from air to glass, the equation is rewritten as: ng sin a sin g a air Here a and g stand for air and glass. glass g 1 The following table gives the refractive indices of some media. Medium Vacuum Air Water Perspex Glass Diamond Refractive index 1 1.00 1.33 1.5 1.5-1.7 2.4 In general, the Snell's law can be expressed as n1 sin 1 = n2 sin 2 where 1 and 2 stand for the two media that light crosses. Example 1 A light ray passes from air into water. The angle of incidence is 30o. What is the angle of refraction in water? The refractive index of water is 1.33. Example 2 Find the refractive index of material X in the following figure. 2 Example 3 A light ray passes from air into alcohol. The refractive index of alcohol is 1.36. Find the angle of refraction. Example 4 Find the refractive index of the semicircular block in the following figure. Example 5 A light ray passes from air into a medium at a certain angle as shown in the following table. Complete the table. Medium Refractive index Angle of incidence Water 1.33 50o Glass 1.5 Diamond Angle of refraction 30.7o 50o 18.5o 3 Example of refraction of light 1. Bent chopstick The chopstick in the figure looks bent when dipped in water. Actually it is straight, it appears bent because of refraction. 2. Shallower in water Swimming pools always look shallower than they really are. The depth as seen by the observer is called the apparent depth. Example 6 A rock is placed in a bucket which is just not seen by us. We can see it when water is added into the bucket. Draw a ray diagram to show how we can see the rock. rock water 4 Example 7 A Kingfisher is hunting for a fish. It sees a fish in the water as shown in the following figure. However, it is only the image of the fish. Draw a ray diagram to show the real position of the fish. Example 8 An Indian is hunting for a fish. However, he is not aiming at the place where the fish appears to be (position A). (a) Where should he aim at, above or below A? (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the real position of the fish. A 5 Exercise Fig 2e 1 To an observer standing at poolside, the bottom of the pool seems to be at a higher position (Fig 2e), i.e. the pool looks ________________. 2 The depth as seen by the observer is called the _______________ depth. In Figure 2e, the apparent depth is ______________ than the real depth of the swimming pool. 3 The bucket as shown appears to be shallower when filled with water (Fig a). The object at the bottom of the bucket therefore appears (Fig b). Fig a Fig b (a) Draw a ray diagram in Figure c to show how the observer sees the object. (b) How does the image different from the object? (a) Fig c (b) The image appears ____________ and ___________ to the water surface. 6