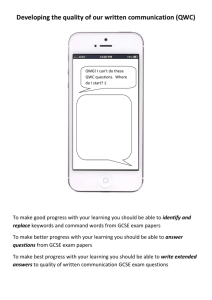
Foundation initial - Sample scheme of work and lesson plan
advertisement

© OCR 2010 Contents Introduction 3 Sample Scheme of Work: GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage 4 Sample Lesson Plan: GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage 19 Published Resources 21 2 of 22 GCSE Mathematics B Introduction In order to help you plan effectively for the implementation of the new specification we have produced sample schemes of work and lesson plans for Mathematics B. These support materials are designed for guidance only and play a secondary role to the specification. Each sample scheme of work and lesson plan is provided in Word format. You should use it as a foundation to build upon, and amend or add to the content to suit your teaching style and learners’ needs. This booklet provides examples of how to structure the teaching of this Stage; the teaching hours are suggestions only. The specification is the document on which assessment is based and specifies what content and skills need to be covered in delivering the course. At all times, therefore, this support material booklet should be read in conjunction with the specification. If clarification on a particular point is sought then that clarification should be sought in the specification itself. GCSE Mathematics B 3 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIN12 – Introducing negative numbers Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Order positive and negative temperatures Solve problems involving temperature change Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Understand and use the vocabulary of probability 4 of 22 Points to note Lists of positive and negative numbers Worksheet: each line has positive/negative numbers. Students cut them out and stick in their books in the correct order http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/maths/ Select number, then negative numbers Weather maps and lists of cities’ temperatures Although the focus is generally on temperatures, students should explore negative numbers in other relevant contexts where possible. Worksheet, or questions on whiteboard Topic World temperatures Statistics relating to the Winter of 2009/2010 FIS1 – Probability words and the probability scale Suggested teaching and homework activities Understand the probability scale Suggested resources Suggested resources Points to note Put the terms certain, likely, evens, unlikely and impossible on cards on the board Each students is given an event written on a card and places it under the relevant heading http://www.emaths.co.uk/data.htm Select ‘Probability (AB)’ Cards with probability words on Cards with events on The PowerPoint goes on to use measures of probability, which is beyond the scope of this Stage. Explain scale by relating the words to the scale (or asking students to do this) Students to place events on the scale, and can be challenged to think about ranking them by likelihood Above PowerPoint Questions from published text GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIN5 – Basic fractions Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Points to note Identify a fraction of a quantity Questions on shapes identifying shaded fractions of shapes (or shading a given fraction) Students need to understand the meaning of the numerator and the denominator to do this well. Calculate a fraction of a given quantity Questions on finding a fraction of a quantity Topic outline Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Topic Interpret scales on a range of measuring instruments GCSE Mathematics B Worksheet or questions from a textbook FIG1 - Measures and scales Suggested teaching and homework activities Use metric measurements and convert from one metric unit to another Worksheet of shapes divided into different fractions As above but students shade in a given fraction of each shape Suggested resources Work sheet matching units to items Work sheet on conversions Students to explain which items would be measured in which units Converting between metric units http://www.skillsworkshop.org/l1num/l1convertmetriclength.pdf Weighing, measuring, reading scales Practical lesson using measuring jugs, scales and balances, and tape measures Items to weigh or measure Worksheet on reading scales Points to note 5 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIA1 – Introducing patterns and sequences Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Suggested resources Points to note Students should see and describe a range of patterns, eg 99 × 99 = 9801 999 × 999 = 998001 9999 × 9999 = 99980001 Recognise and describe patterns in number Describe the rules for number sequences http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks2bitesize/maths/ Select Number, then Patterns Exercise from textbook Continue simple sequences and explain how to find the next number in a simple pattern Sequences for students to complete may be gaps in the middle not just at the end Describe in words how to find the next number in a pattern Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Calculate simple percentages of quantities without the use of a calculator Topic FIN7 – Introducing percentages as operators Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Points to note This is most likely to be linked with FIN6, in the sense that many will introduce 50% and 25% 6 of 22 Exercise from textbook Students work in pairs with individual whiteboards. One makes up a sequence; partner completes it, and describes the rule Introduce idea of simple percentages 50%, 25%, 10%, 5% and multiples Calculate multiples of 5% of quantities Spider diagrams; building up other percentages from easier percentages http://www.emaths.co.uk/tarsia.htm : Percentage cards Exercise from textbook Exercise from textbook The ‘Standards Unit’ Box http://nationalstrategies.standards.dcsf.gov.uk/node/47663 as being equivalent to 1 2 and 1 4 respectively. GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIA3 – Function machines and one-step equations Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Use simple function machines to deal with inputs and outputs Arithmetic practice to start Move into function machine notation Extend into determining the input from given output Mini whiteboards Sample lesson plan attached to this scheme of work Solve simple equations involving one operation Can move into algebraic notation from either function machines, replacing the input with x before showing that the machine can be removed, or balancing puzzles with equal weights on either side of the puzzles (one of which is x) Mini whiteboards Worksheet or textbook exercises Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Topic Suggested resources Suggested resources Add and subtract three-digit numbers without the use of a calculator Range of methods for doing this (traditional; splitting into hundreds, tens, units; number lines; counting on) Mini whiteboards Worksheet or textbook exercise Add and subtract numbers with up to two decimal places without the use of a calculator At this level, relate the questions to money, length or mass etc Recap previous lesson’s work on arithmetic Coins, rulers, scales – and objects to measure or weigh GCSE Mathematics B The balancing method may make the move into notation such as “2x” easier, but demonstrating division and subtraction is more difficult. FIN2 – Adding and subtracting Suggested teaching and homework activities Points to note Points to note 7 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIG6 - Maps and plans Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Use and interpret street plans and simple maps, left right and clockwise and anti clockwise Students describe their route from school to home Students have street maps: teacher questions students about the map, using left, right, clockwise, and anti-clockwise Grid references, and compass directions Introduce the idea of grid references Introduce compass directions Suggested teaching time Topic 2 hours Topic outline Find all possible ways of listing up to 4 objects 8 of 22 Points to note Can make cross-curricular links to Geography in this topic (OCR GCSE Geography A units A672, A673 and A674 or OCR GCSE Geography B unit B562) Small grids using numbers and letters on the grid Picture of compass with 8 points labelled http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks2bitesize/maths/ Select Shape, space and Measures, then Grids Exercise from textbook Street plans Web-based satellite image/mapping/street-level viewing program FIS2 – Listing objects Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Students make as many 4 digit numbers as possible from the 4 digits Introduce systematic listing Different ideas and contexts eg choices of menu Suggested resources Points to note 4 cards with different numbers Exercise from textbook GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 4 hours Topic outline Topic FIN3 & FIN4 - Multiplying and dividing Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Multiply and divide by 10,100 and 1000 without a calculator Multiply by 10, 100, 1000 Divide by 10, 100, 1000 Exercise from textbook Multiply and divide numbers with no more than one decimal digit by an integer between 1 and 10 without a calculator Multiply whole numbers and decimals by an integer Divide whole numbers and decimals by an integer Exercise from textbook Multiply and divide a threedigit number by a two-digit number. Use a variety of methods, eg ‘traditional’ algorithms, gelosia/lattice, grid, chunking for division, etc http://www.emaths.co.uk/number.htm Select “Chinese Multiplication”, Russian, or Egyptian Exercises from textbook Multiply numbers with up to two decimal digits by an integer, with (or without) a calculator Use money contexts for two decimal digits Exercises from textbook GCSE Mathematics B Points to note Recent Principal Examiners’ reports have noted that students using the grid or gelosia methods for multiplication tend to be more successful. 9 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Round numbers to a given power of 10 Suggested teaching time 3 hours Topic outline Recognise regular polygons (pentagon, hexagon, octagon) Recognise types of triangle (isosceles, equilateral, scalene) Recognise the terms circle, centre, radius, diameter and circumference Recognise simple solids (cube, cuboid, sphere, cylinder, cone) 10 of 22 Topic FIN1 – Rounding Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Place numbers on a number line and ask questions, eg what is the nearest 100? Move into decimals, again starting with money or measurement contexts Topic Newspaper and internet articles are a good source of rounded numbers Worksheet or textbook FIG4 – Recognising shapes, solids and parts of circles Suggested teaching and homework activities Points to note For each area, matching games are a good way to help learners remember the different names of the shapes and parts There may be mental associations students can make to help them remember the names “Splat” game. Write the names you want to test on the board. Two students stand by the board. Show students a picture corresponding to one of the words – the first one to “splat” the word wins, and a new challenger comes up to the front Suggested resources Points to note Flash cards Shapes and solids Mini whiteboards GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Measure and draw angles to the nearest degree Identify types of angle Recall and use angle properties Suggested teaching time FIG3 – Introduction to angles 2 hours Suggested resources Students name types of angles Students measure angles drawn on a worksheet Paired work: one student gives an angle size; partner draws it; first student checks it http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/maths/ Select Shape, space and measures, then Angles Worksheet with angles drawn: Students cut them out and stick them onto a sheet under headings acute, obtuse etc – or a similar card sorting activity Mini whiteboards, pens, protractors Pictures (of anything – could be taken by the students themselves outside the classroom). Either project them or print them, and ask students to estimate angles in the picture, and then to measure them Angle facts: straight line, round a point, opposite angles, perpendicular lines Fit together angle cards on a straight line, round a point, etc Topic Points to note Link to pictures above: ensure you have some good examples in the set illustrating the properties Exercise from textbook FIN10 - Time Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Points to note Familiarisation of 24 hour clock Use the 24 hour clock, changing to and from 12 hour clock Exercise on am/pm and 24 hour clock Analogue as well as digital Work out starting times, finishing times and intervals Problems involving time calculating intervals and start/finish times Any source of timetables on the internet Instructions (for anything) that include timings Topic outline GCSE Mathematics B 11 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIA2 - Formula Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Use formulae expressed in words or symbols Use simple word formula Discuss where formulae are used Exercise from textbook Substitute positive numbers into formula to find the value of the subject Introduce symbols into formula Exercise from textbook Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Perform calculations involving the use of brackets and the order of operations Topic Suggested resources Write a calculation on the board eg 16 + 4 × 2·12 ÷ 4 and ask students to work out the answer Discuss answers Try on scientific and non scientific calculators Introduce the order of operations Exercise from textbook Introduce brackets and the reasons for using them Exercise from textbook Points to note FIN11 - Order of operations Suggested teaching and homework activities 12 of 22 Suggested resources Points to note GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours FIS5 – Two-way tables Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Extract and use information from two-way tables including timetables Suggested teaching time Topic 2 hours Topic outline Suggested resources Introduce idea of two-way tables Students use two-way tables to answer questions http://nrich.maths.org/public/leg.php?code=5015 Bus and train timetables Mileage charts Worksheet with questions from above or exercise from a textbook Students plan a holiday or trip using a variety of two way tables Holiday brochures Topic FIN6 – Fractions, decimals and percentages Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Recall fraction to decimal conversions of simple fractions Introduce idea of conversion Use a fraction and decimal wall to show equivalence Fraction decimal dominoes Card matching Fraction/decimal wall Exercise form textbook Convert simple fractions of a whole to percentage and vice versa Use a fraction and percentage wall to show equivalence Fraction percentage dominoes Card matching Convert decimals to a percentage and vice versa Convert decimals to a percentage Convert percentages to a decimal Exercise from published text GCSE Mathematics B Points to note Points to note Links to earlier work on FIN7. 13 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIA4 - Coordinates Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Use axes and coordinates in four quadrants, including using points identified by geometrical information Drawing and labelling axes Recap on coordinates in first quadrant Introduce other quadrants Identify and plot coordinates Work sheets http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/maths Select Algebra, then Graphs: Basic Skills Plotting points to give named shapes, identify shapes from coordinates Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Make sensible estimates of a range of measures in everyday settings 14 of 22 Topic Suggested resources Points to note Exercise from published text FIG2 - Estimating angles and lengths Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Students are shown a 30 cm and 1 metre ruler. They are then asked to estimate the length/width/height of various items in the classroom Classroom and around school, eg car park Estimating angles Students given angles to estimate give 2 points if within 10°, 1 point if within 20° Worksheet Could also include length of lines Points to note GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Construct and interpret conversion graphs Suggested teaching time FIA5 - Construct and interpret simple graphics including conversion graphs 2 hours Suggested resources Introduce ideas of conversion, eg Pounds to Euros Show how to construct and use a conversion graph Fact sheets, exchange rates Unit comparisons, eg miles to km etc Reading/using simple graphs and conversion graphs Exercise from textbook Topic FIG7 & FIG8 - Reflection and reflection symmetry Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Recognise and complete reflection symmetry of 2-D shapes Understand that reflections are specified by a mirror line Introduce idea of reflection Students identity reflection symmetry Give patterns on grids for students to complete Work sheets Exercise from published text Students make up their own patterns Transform triangles and other 2-D shapes by reflection using a given line Mirror lines Reflect shapes in a given line Draw a mirror line on a diagram Worksheets Topic outline GCSE Mathematics B Points to note Points to note Mirrors may help at the early stages but are not permitted in the final examination (you may wish to allow them in the Stage Test). Tracing paper can always be used, however, and is another useful tool for completing reflections. 15 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic Suggested teaching and homework activities Topic outline Draw and interpret simple frequency tables, charts, pictograms and bar charts for discrete data Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Suggested resources Points to note Collecting data, tally/frequency charts Use the tally chart to draw a bar chart collect data from the class eg number of pets owned http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/maths/ Select Handling data, then Collecting and recording Exercise from published text http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/maths/ Select Handling data, then Representing data There are opportunities to use ICT in producing the graphs as well. Pictograms Exercise from published text http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/maths/ Select Handling data, then Representing data Topic Find areas of irregular shapes by counting squares and volumes of simple shapes by counting cubes. Find the area of a rectangle. Cross-curricular links can be made to, eg Science, Business, Geography. FIG5 - Perimeter area and volume Suggested teaching and homework activities Find the perimeter of straight sided shapes. 16 of 22 FIS4 - Representing data Suggested resources Find the perimeter of straight sided shapes Measuring sides to find the perimeter Calculate one side given the perimeter and the other sides Worksheet: adding lengths to find the perimeter Measuring sides to find the perimeter Find the area of irregular shapes by counting squares Find the area of a rectangle Find the volume by counting cubes Worksheet Transparent square grid Cubes: students make models with cubes Points to note GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching 2 hours time Topic FIN8 - Ordering decimals Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Ordering decimals Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic outline Solve problems using the four operations on integer and decimal numbers using a calculator GCSE Mathematics B Suggested resources Mini whiteboards Exercise from textbook http://www.amblesideprimary.com/ambleweb/mentalmaths/numberlines.html Order decimals Give each student a mini whiteboard with a decimal written on. Five students stand at the front and the class has to place them in order Topic Points to note FIN9 - Solving problems Suggested teaching and homework activities Suggested resources Points to note A chance to introduce functional maths and a range of contexts. Identify the problem and find a strategy Students produce their own sheets of problems for others to solve Exercise from textbook A good source of problems to solve is the nrich website: http://nrich.maths.org/public/monthindex.php?mm=1 17 of 22 Sample GCSE Scheme of Work GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Suggested teaching time 2 hours Topic FIS3 - Averages and range Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Calculate the mean, median, mode and range of discrete data Suggested teaching time 2-3 hours Suggested resources Points to note Calculate the mode of discrete data Calculate the median of discrete data Calculate the mean of discrete data Calculate the range of discrete date http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/maths Select Handling data, then measures of average Exercises from textbook Students often come unstuck remembering which averages is which. A consideration of why each of the averages are used can be helpful – and of course the range is not an average. Consolidate above ideas Exercise from textbook Interpretation of these statistics is not a requirement of this Stage (see FBS2). Topic Revision, testing and feedback Topic outline Suggested teaching and homework activities Revision Revision of topics Test OCR Foundation Initial Stage Test Download the test securely from: https://interchange.ocr.org.uk Feedback Feedback on Stage Test 18 of 22 Suggested resources Points to note Worksheets ExamQuest Your examinations officer can set up a teacher/tutor account for you. GCSE Mathematics B Sample GCSE Lesson Plan GCSE Mathematics B J567: Foundation Initial Stage Function Machines and Equations OCR recognises that the teaching of this qualification above will vary greatly from school to school and from teacher to teacher. With that in mind this lesson plan is offered, as a possible approach but will be subject to modifications by the individual teacher. Lesson length is assumed to be one hour. Learning Objectives for the Lesson Objective 1 To draw one stage function machines Objective 2 To draw the inverse of one stage function machines Objective 3 To use function machines to solve one step equations Recap of Previous Experience and Prior Knowledge To know the inverse of simple functions To be able to add and subtract integers to 20 To be able to multiply and divide integers to 10 × 10 Content Time Content 5 minutes Review of single digit addition, subtraction, multiplication and division using whiteboards and, if necessary, pre-printed addition and multiplication tables. Ask questions like 3 + 5, 9 – 4, 5 × 6, 8 ÷ 2 and so on. The range of numbers can be increased depending on the ability of the group. You could use PowerPoint with a loop to present the questions; answers to be noted in exercise books. 15 minutes Use whiteboards for this activity. Read a simple scenario/story and ask them to write the answer on their whiteboards, eg “I think of a number, add 3 and the answer is 12. What is my number?” or “Some children are playing football and 5 more join in. There are now 11 playing football. How many were there originally?” or “I have some money. I spend £4. I now have £5. How much did I have to begin with?” When many are giving the correct response ask for the method used. If correct inverse is given move on without comment, allowing each student to make his/her own decisions. GCSE Mathematics B 19 of 22 Sample GCSE Lesson Plan 20 minutes Review some of the previous section’s ‘stories’. Ask the students how to write them on the board. Use ? or a rectangle or ‘stick a piece of card’ where the ‘x’ goes, eg write “? + 3 = 12” on the board. Introduce a function machine and show inverse but do not write the inverse operation in. Ask for suggestions eg +3 12 ? Repeat with other operations. Students to use whiteboards to do this. 15 minutes Review of single digit addition, subtraction, multiplication and division using whiteboards and, if necessary, pre-printed addition and multiplication tables. Ask questions like 3 + 5, 9 – 4, 5 × 6, 8 ÷ 2 and so on. The range of numbers can be increased depending on the ability of the group. You could use PowerPoint with a loop to present the questions and answers noted in exercise books. Consolidation Time Content 5 minutes Use a self-checking technique to present three equations to the students. Solutions on whiteboards or in exercise books. Three equations with different operations and three solutions. Match equation to solution. Three equations, two with same solution, third different. Find the odd one out. Write a story and a solution to give an answer of 6. Homework/ project 20 of 22 Use an exercise from an approved text book or homework book Ask each student to write 5 questions with their solutions Project: Produce a simple game, squares round perimeter of board and with ‘go forward 3’ or ‘go back 5’. Players pick a card on turn. Each card is an equation. Correct solution leads to player moving the number of squares consistent with the solution (ie ‘x’ = 3 so move forward 3 squares). Team produces game, board and cards. GCSE Mathematics B Published Resources OCR offers centres a wealth of quality published support for new specifications with a fantastic choice of ‘Official Publisher Partner’ and ‘Approved Publication’ resources, all endorsed by OCR. Publisher partners We work in close collaboration with our three publisher partners Hodder Education, Heinemann and Oxford University Press to ensure you have access to quality materials, written by experts, when you need it. The publisher partnerships are not exclusive (see Approved Publications below).All OCR endorsed resources undergo our thorough quality assurance process to ensure they cover the specification. Hodder Education is the publisher partner for OCR GCSE Mathematics B. Hodder Education is producing the following resources for OCR GCSE Mathematics B for first teaching in September 2010. OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Student Book 1 Foundation Initial & Bronze Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118506, Published: 25/06/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Student Book 2 Foundation Silver & Gold and Higher Initial & Bronze ISBN: 9781444118513, Published: 25/06/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Student Book 3 Higher Silver & Gold Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118520, Published: 25/06/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Teacher and Assessment Pack 1 Foundation Initial & Bronze Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118568, Published: 27/08/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Teacher and Assessment Pack 2 Foundation Silver & Gold and Higher Initial & Bronze Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118575, Published: 27/08/2010 GCSE Mathematics B 21 of 22 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Teacher and Assessment Pack 3 Higher Silver & Gold Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118582, Published: 27/08/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Homework Book 1 Foundation Initial & Bronze Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118537, Published: 24/09/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Homework Book 2 Foundation Silver & Gold and Higher Initial & Bronze Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118544, Published: 24/09/2010 OCR Mathematics for GCSE Specification B – Homework Book 3 Higher Silver & Gold Howard Baxter, Michael Handbury, John Jeskins, Jean Matthews, Mark Patmore ISBN: 9781444118551, Published: 24/09/2010 Dynamic Learning The unique online assessment allows you to track learners' progress, highlighting routes to achieve success. The reports not only identify students' areas of strength and weakness, but provide links to print and digital resources that will help them improve their knowledge and skills. Approved publications OCR still endorses other publisher materials, which undergo a thorough quality assurance process to achieve endorsement. By offering a choice of endorsed materials, centres can be assured of quality support for all OCR qualifications. 22 of 22 GCSE Mathematics B