physical geology-vocab
advertisement

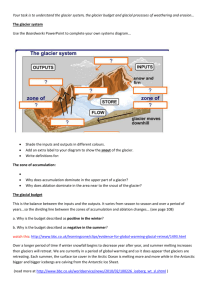
!GLG 101-Illustrated Vocabulary-Chapter 12 !Glaciers copyright 2003-Roger Weller !alpine glacier *a valley glacier !Alps *a prominent mountain range in southern Europe !arete *a skinny mountain ridge shaped on opposite sides by a series of glacial cirques !avalanche *a large mass of snow that rapidly slides down a slope !bergschrund *the large crack at the top of a valley glacier where it is pulling away from the mountain !cirque *a scoop-like depression on the side of a mountain formed by a valley glacier eroding the mountain. *[Rocky Mountains Park-Cirque-1] *[Rocky Mountains Park-Cirque-2] !continental glaciation *glaciers cover a large portion of a continent. Modern examples are Greenland and the Antarctic. !crevasse *a very large crack on top of a glacier !crustal rebound *during an ice age the weight of a thick continental glacier presses the crust of the earth down; after the glacier melts, the crust slowly rises up to its previous elevation. !drumlin *a long, skinny, cigar-shaped hill that has be sculpted by a glacier flowing over it* !erratic *a boulder far removed from its original source and deposited by a glacier. *[Yosemite-Glacial grooves and erratics-3] !esker *a snakelike ridge of water lain gravel deposited by a steam flowing beneath a melting glacier !fiord *a U-shaped glacial valley that is partially flooded by seawater !firn *glacial ice, a granular form of ice similar to the material in a "slush ball" !frost wedging *Water gets into a crack, freezes, and expands; the tremendous pressures exerted by the expansion of water into ice can cause the rock to split further. !glacial grooves *as a glacier moves across bedrock the large rocks that the glacier is dragging along gouge long grooves. *[Yosemite-Glacial grooves] !glacial plucking *the process where glacial ice is frozen in cracks and as the glacier moves, the ice pulls rock fragments out of the bedrock !glacial polish *a glacier moving across a bedrock surface can polish the bedrock by abrasion with the fine rock rock material embedded in the ice. *[Yosemite-Glacial polish-1] *[Mt. Whitney-Glacial polish-2] !glacial striations *scratches left on boulders and cobbles as they are dragged along by a glacier and rubbed against each other during the movement !glacial till *the unsorted rock debris, ranging from boulders to silt, that are left behind when a glacier melts. !glacier *a moving mass of ice on land that is at least 150 feet thick !hanging valley *a small U-shaped glacial valley exposed on the upper side of a larger U-shaped glacial valley; the smaller valley was formed in colder times by a tributary valley glacier meeting up with a larger valley glacier. !horn *a mountain with very steep slopes which was carved with cirques on three or more by valley glaciers; the most famous one is the Matterhorn in Switzerland. *[Rocky Mountains Park-Horn and Cirques] !ice ages *distinct times in the history of the Earth when major portions of the continents were covered by glaciers. !kettle *a small lake surrounded by glacial till; formed by a depression created by the melting of a large piece of glacial ice covered over with till. !lateral moraine *the piles of glacial till deposited at the terminal end of a glacier !loess *a very fine, silty material that started out as rock flour (rocks ground up by glacial action to a fine poweder), but is now a wind-deposited soil. !medial moraine *when two two valley glaciers merge to form a larger valley glacier, their area of contact is often marked by a line of glacial debris accumulated from lateral moraines of the two glaciers. !outwash plains *flat land areas covered by the silty material carried by streams flowing away from a melting glacier !permafrost ground *semipermanent frozen ground !rock flour *rock that has been crushed and ground to a fine powder by glacial action. !terminal moraine *the piles of glacial till at the base (snout) of a glacier !u-shaped valley *is created when a valley scrapes out the bottom and sides of the valley that it is moving through. *[Rocky Mountains Park-U Shaped Valley-1] !valley glacier *a glacier in a mountain valley; also known as an alpine glacier !Wisconsin Ice Age *the most recent of the Pleistocene advances of glaciers moving across North America; it ended about 15,000 years ago. !zone of ablation *the portion of a glacier below the snowline where the glacier is melting !zone of accumulation *the region of a glacier above the snow line where ice in the form of snow is being added to the glacier.