Movement across membranes - Emmanuel Biology 12
advertisement

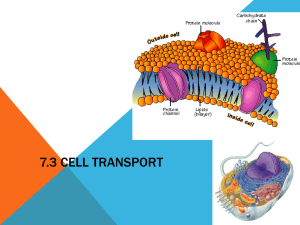
Unit 3 Biology Movement across membranes Guiding Questions 1. What are the four ways the plasma membrane maintains the cell’s internal environment? 2. What does the movement of substances across the plasma membrane depend on? 3. What is an important property of the membrane? 4. What types of molecules does this property make the membrane impermeable to? 5. How do these molecules pass through the membrane? 6. What is meant by the term differentially permeable? 7. What are the five types of processes by which molecules may pass in and out of cells? 8. 9. 10. 11. What is simple diffusion? What is the concentration gradient? When will diffusion take place? Does diffusion require energy? 12. 13. 14. 15. What four factors can make diffusion faster? How do chemical properties influence diffusion? Does water’s polar nature influence it’s passage through the plasma membrane? Why can glycerol and ethanol pass with relative ease through the membrane by simple diffusion? 16. What is osmosis? 17. Does osmosis require energy? 18. How do we define osmosis? 19. Which solution has more free water molecules, a highly concentrated solution or a less concentrated solution? 20. What concentration gradient is water diffusing along? 21. Given that the cell membrane is differentially permeable to water, will the amount of water in the external environment affect the concentration of the solution within the cell? 22. What is an isotonic solution? 23. What is a hypertonic solution? 24. What is a hypotonic solution? 25. 26. 27. 28. What happens to an animal cell in a hypotonic solution? What happens to an animal cell in a hypertonic solution? What happens to a plant cell in a hypotonic solution? What happens to a plant cell in a hypertonic solution? 29. How do large particles such as glucose or charged particles such as ions pass through the cell membrane? 30. What is this process called? 31. What are the two types of transport proteins? 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. What type of molecules do channel proteins assist to cross the membrane? Why is the lining of the pore in a channel protein hydrophilic? Are the channels selective? Does this process require energy? Does it occur against a concentration gradient? 37. What sort of signals can stimulate a gated channel protein to open or close? 38. How do carrier proteins transport molecules across the membrane? 39. What does this process require? 40. Is the relationship between the carrier protein and the transported molecule specific? 41. 42. 43. 44. What does active transport involve? Does it require energy? What does active transport allow cells to do? What organelle is in high numbers in cells that are actively transporting molecules against the concentration gradient? 45. What types of molecules are transported by exocytosis and endocytosis? 46. Do these processes require energy? 47. What are the three types of endocytosis? 48. How does endocytosis occur? 49. What is exocytosis? 50. How does exocytosis occur? 51. What is the difference between constitutive and regulated exocytosis?