Quality Criteria
advertisement
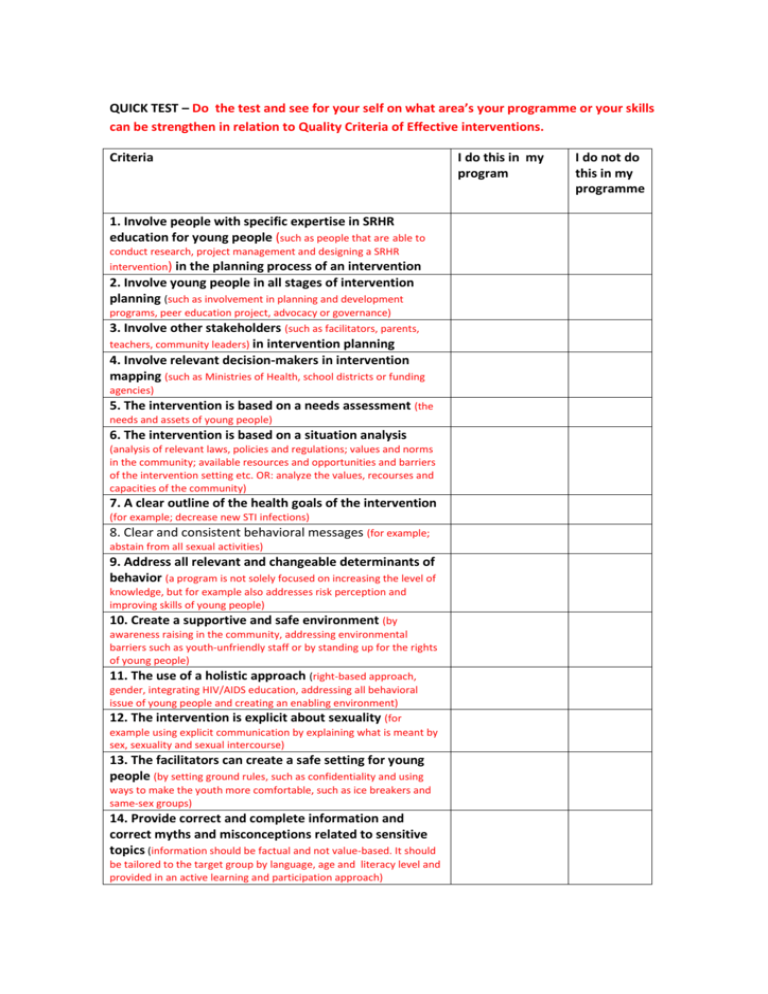
QUICK TEST – Do the test and see for your self on what area’s your programme or your skills can be strengthen in relation to Quality Criteria of Effective interventions. Criteria 1. Involve people with specific expertise in SRHR education for young people (such as people that are able to conduct research, project management and designing a SRHR intervention) in the planning process of an intervention 2. Involve young people in all stages of intervention planning (such as involvement in planning and development programs, peer education project, advocacy or governance) 3. Involve other stakeholders (such as facilitators, parents, teachers, community leaders) in intervention planning 4. Involve relevant decision-makers in intervention mapping (such as Ministries of Health, school districts or funding agencies) 5. The intervention is based on a needs assessment (the needs and assets of young people) 6. The intervention is based on a situation analysis (analysis of relevant laws, policies and regulations; values and norms in the community; available resources and opportunities and barriers of the intervention setting etc. OR: analyze the values, recourses and capacities of the community) 7. A clear outline of the health goals of the intervention (for example; decrease new STI infections) 8. Clear and consistent behavioral messages (for example; abstain from all sexual activities) 9. Address all relevant and changeable determinants of behavior (a program is not solely focused on increasing the level of knowledge, but for example also addresses risk perception and improving skills of young people) 10. Create a supportive and safe environment (by awareness raising in the community, addressing environmental barriers such as youth-unfriendly staff or by standing up for the rights of young people) 11. The use of a holistic approach (right-based approach, gender, integrating HIV/AIDS education, addressing all behavioral issue of young people and creating an enabling environment) 12. The intervention is explicit about sexuality (for example using explicit communication by explaining what is meant by sex, sexuality and sexual intercourse) 13. The facilitators can create a safe setting for young people (by setting ground rules, such as confidentiality and using ways to make the youth more comfortable, such as ice breakers and same-sex groups) 14. Provide correct and complete information and correct myths and misconceptions related to sensitive topics (information should be factual and not value-based. It should be tailored to the target group by language, age and literacy level and provided in an active learning and participation approach) I do this in my program I do not do this in my programme 15. The intervention addresses risk perception (for example by informing young people about their chances of getting STIs, HIV or becoming pregnant and by telling the negative consequences of this) 16. The intervention helps people to understand and develop their own attitude, values and awareness of social influences (for example by group discussions, providing people with persuasive arguments, interactive activities and using the modeling approach) 17. The intervention includes interactive skills training (for example by practicing saying no to unintended, unwanted or unprotected sex or negotiation skills) 18. Young people have access to individual support 19. Promoting communication with parents or other adults (for example by discussions or home-work assignments) 20. Topics in the intervention are covered in a logical sequence 21. The intervention does appeal to the target group (form and packaging, teaching strategies etc.) 22. The intervention has been tested (pre-, pilot- or post tested) 23. Efforts are made to increase adoption of the intervention (by addressing new facilitators, parents and school management) 24. The intervention is implemented by appropriate facilitators (facilitators have characteristics such as some experience with SRHR education, motivation and willingness to promote rights of young people and being youth friendly) 25. Training and support for facilitators (includes aspects like interactive teaching skills, open and non judgmental communication, learning the content, refresher courses and sharing experiences) 26. The intervention sustainable (integrating program in main policy or make it part of national/regional program) 27. Outcome evaluation (evaluating change in the behavioral determinants) 28. Process evaluation (monitor intervention’s design and implementation) Total score