Family Meeting Models and Use
advertisement
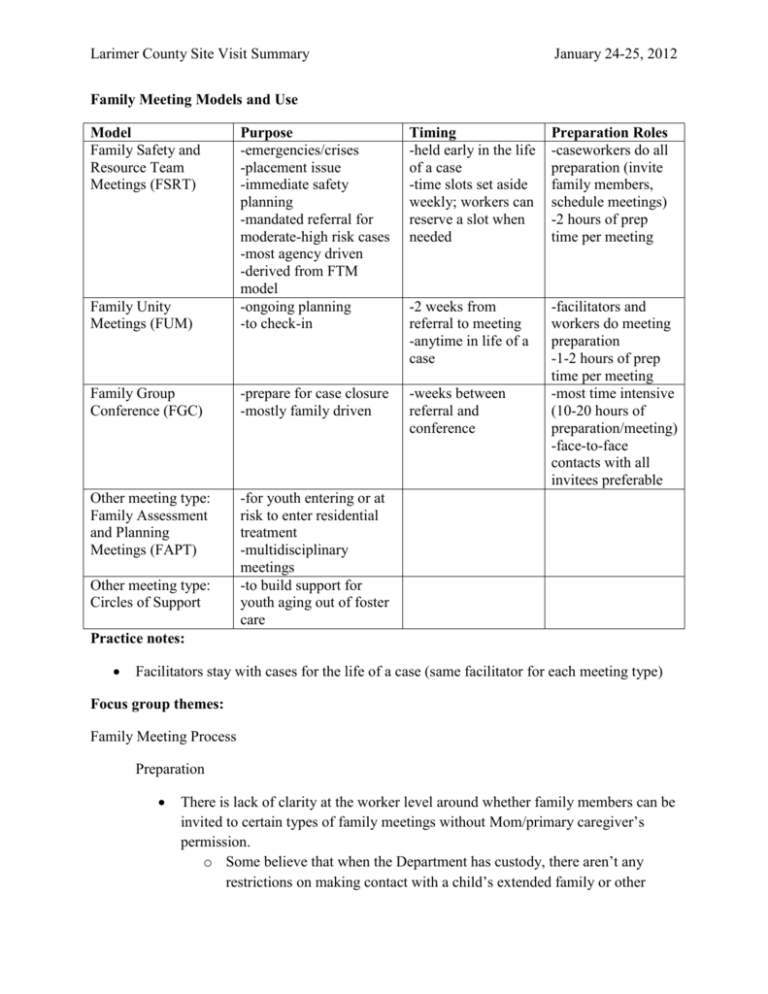
Larimer County Site Visit Summary January 24-25, 2012 Family Meeting Models and Use Model Family Safety and Resource Team Meetings (FSRT) Timing -held early in the life of a case -time slots set aside weekly; workers can reserve a slot when needed Preparation Roles -caseworkers do all preparation (invite family members, schedule meetings) -2 hours of prep time per meeting Family Unity Meetings (FUM) Purpose -emergencies/crises -placement issue -immediate safety planning -mandated referral for moderate-high risk cases -most agency driven -derived from FTM model -ongoing planning -to check-in -2 weeks from referral to meeting -anytime in life of a case Family Group Conference (FGC) -prepare for case closure -mostly family driven -weeks between referral and conference -facilitators and workers do meeting preparation -1-2 hours of prep time per meeting -most time intensive (10-20 hours of preparation/meeting) -face-to-face contacts with all invitees preferable Other meeting type: Family Assessment and Planning Meetings (FAPT) -for youth entering or at risk to enter residential treatment -multidisciplinary meetings -to build support for youth aging out of foster care Other meeting type: Circles of Support Practice notes: Facilitators stay with cases for the life of a case (same facilitator for each meeting type) Focus group themes: Family Meeting Process Preparation There is lack of clarity at the worker level around whether family members can be invited to certain types of family meetings without Mom/primary caregiver’s permission. o Some believe that when the Department has custody, there aren’t any restrictions on making contact with a child’s extended family or other Larimer County Site Visit Summary January 24-25, 2012 collaterals, and if they don’t have custody, a release of information has to be secured. FGCs are harder for facilitators to set-up than other types of meetings o May lead to referral for FUMs instead Facilitators and their supervisor are accommodating Challenge: scheduling meetings to accommodate all participant/family member schedules o Often need to be held after-hours Workers unclear and/or untrained in how to present family meetings (FSRTs) to families, especially when they are mandated Meeting Meetings are more successful when there are more family supports present A benefit of meetings is that the agency has the opportunity to share consistent information with the family group, and all parties can get on the same page. Some workers and community members feel that things are discussed in family meetings that children should not hear or be present for New workers experience anxiety over attending family meetings and may feel inadequately trained to participate o Coaches and supervisors are available to attend with workers Genograms are created with families in many meetings o Aid in family finding o Serve as lead-in to asking about family culture Facilitators are skilled and do a good job of remaining neutral Follow-up There is a lack of Spanish-speaking services and services that work with undocumented clients in the county General Most critical community stakeholders of family meetings are GALs (FGCs in particular) o Therapists and parent lawyers have also been critical of family meetings and/or challenging to incorporate into the model Caseworkers are resistant to being told to have meetings or mandated to refer There is concern that the agency may impose white, middle class norms on families of different backgrounds, such as Latino families and not respond in culturally responsive ways. Staff are doing a better job asking families about cultural and race than used to but still see room for improvement Larimer County Site Visit Summary January 24-25, 2012 o Staff not sure how to ask questions about race and/or culture. o Staff not sure what to do with information gathered from conversations about race and/or culture. Turnover makes it hard to keep workers trained in family meetings More experience with family meetings is associated with more positive perception of family meetings at the worker level Workers may have family meetings themselves (without a facilitator) if scheduling is a problem, to avoid opening a case in intake, or because they don’t like the facilitator that has been assigned Meetings are not happening as much in FAR cases o Recent policy changes (mandating referrals for moderate risk cases) may change this