Exam, 2011 answers - University of Warwick

CH908
UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
MASTER OF SCIENCE EXAMINATIONS: MARCH 2011
MASS SPECTROMETRY
Time allowed 2 hours
Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered on each answer book.
Percentages in square brackets are intended as a guide to the time candidates should spend in answering the corresponding part of the question.
Answer ANY TWO QUESTIONS
1
Question 1 [50%, 25% part a, 25% part b]
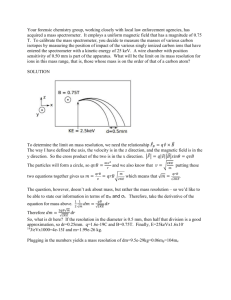
A.
(25 pts) What is the structure associated with this spectrum? i. How many carbon atoms are in the peaks at m/z 85 and 135? ii. Estimate the number of hydrogen atoms in the peaks at m/z 125, 119, 85,
69, and 31? iii. What are possible elemental compositions for the peak at m/z 135?
Answer: The isotopic cluster at 135-137 indicates one chlorine atom, and the peak at
136 indicates a maximum of 2 carbon atoms. Similar assignments can be made for lower mass ions: m/z 119: C2Cl0, 85: C1Cl1, 69: C1CL0, 31: C1CL0. There's a suspicious lack of 1 Da differences, suggesting little hydrogen. The 19 Da spacings imply Fluorine. Thus, CF, CF2, CF3, CClF2 (85), C2F4 (100), C2CLF4 (135) define the major peaks oin the spectrum. The 135 peak is therefore unlikely to be the molecular ion. Since there's no evidence for any fragments containing more than one
Cl or 2 carbons, the best guess is CClF2CF3 [Chlorophentafluoroethane).
2
b. (25 pts) What is the structure associated with this spectrum? How many carbon atoms and R+DB (double bond equivalents) are in the ion represented by the peak at
122?
Peak list:
Mass, Int.
17 1.1
26 1.23
27 2.97
37 2.65
38 5.5
39 8.12
45 6.1
49 2.46
50 24.1
51 40.89
52 6.91
53 1.46
61 1.04
62 1.08
63 1.17
65 2.2
66 1.9
73 1.92
74 9.14
75 3.3
76 6.65
77 74.48
78 8.26
94 2.78
105 99.99
106 8.4
122 82.82
123 6.2
Answer: Benzoic acid. 77, 51 indicate benzyl - but not toluyl. 105, 122 are +28 and
+17+28 from 77, so a carbonyl and a OH.
3
Question 2 [50%]
A. (15 pts) Draw a diagram of an FTICR mass spectrometer's ICR cell, label the 3 sets of plates and describe their function. What's a good calibration equation for
FTICR?
Trapping plates - to trap the ions in the z dimension
Excitation plates - to apply an RF oscillating excitation field to spin ions into a cyclotron orbit
Detection plates - attached to the amplifiers for detecting the induced sine wave of the ions in their cyclotron orbit.
Calibration equations are:
1) m/z = A/f
2
+ B/f + C
2) m/z = A/(f+B)
Where f is the detected frequency of the peak after FFT, and A,B,C are the calibration constants.
4
B. (10 pts) Calculate the approximate cyclotron frequency of a 1000 m/z ion in a 12T
FTICR mass spectrometer? f = (q B)/(2 pi M). m = 1000*1.6e-27 kg q = 1.6e-19 C
B = 12 T f = 191 kHz.
5
C. (15 pts) Draw a diagram of an electrospray quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer. Explain how the ion trap works, and explain how ions can be
"scanned" out into a detector. Why does a quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer yield lower resolving power than an FTICR mass spectrometer?
The ion trap works by trapping ions in an oscillating electric field between the endcaps and ring electrodes. If the amplitude and frequency are correct, ion trajectories inside the trap are stable. Ions can be scanned out to the detector in two ways. First, the RF amplitude can be ramped, causing lighter ions to become successively unstable in the trap and fall out. Second, a resonant RF pulse can be added on top of the main trapping field and scanned to dump the ions out of the trap.
Either way, a plot of amplitude or pulse frequency versus ion current is the resulting mass spectrum.
The resolution of a QIT depends on how precisely one can hold to the theoretical
Mathieu stability diagram. Thus, it depends on frequency stability, RF amplitude and
DC level voltages, and machining accuracy of the trap itself. It also depends on the phase-space of the ions in the trap.
The resolution of an FTICR depends on magnetic field strength and being below the high space-charge limit. Imperfections in the instrument are completely irrelevant compared to their importance in QIT.
6
D. (10 pts) In a quadrupole ion trap, using the equation below calculate the low mass cut off (LMCO) for the trap if it is run at 750 V rf
amplitude, 950 kHz, a pole-to-pole
(z - axis) minimum inner distance of 9 mm, and a z/r aspect ratio of 1.1.
LMCO is given by q z
0.908
8 eV m
2 2 r
z
2
( 2 )
Low mass cut off (LMCO) is given by q z
0.908
8 eV m
2 2 r
z
2
( 2 )
,so rearranging, we get
8 V
0.908
2 2
( r
1.1
2 2 r )
, with V = 750
Volts, ω =
2*pi*950 kHz, and z = 9/2 mm, r = z/1.1 = 4.09 mm . So: LMCO = 310 m/z
(or 3.2e-6 kg/c).
7
Question 3 [50%] a. (35 pts) Given the sequence of Substance P (RPKPQQFFGLM - NH
2
; meaning the c-terminus is amidated) and the ECD MS/MS spectrum below, assign the peaks in the mass table. b. (10 pts) When peptides are exposed to oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide, methionine tends to oxidize rapidly. Sometimes this even occurs in air. Is this peptide were oxidized, which masses would shift? How much?
Only the z9 ion moves, by +15.9949 Da. c. (5 pts) There is an additional tiny peak at m/z 337.4375. What is it?
Some students answered that it was the [M+4H]4+ ion, but it's not, it's an instrumental artifact, the second harmonic of the base peak.
8
RPKPQQFFGLM-Amidated
User AA Formula 1: C2 H3 N1 O1
Elemental Compositon: C63 H99 N18 O13 S1
MH +1 (av) MH +1 (mono)
1348.6661 1347.7354
[ – ] Main Sequence Ions c z
--- 1 R 11 ---
271.1877 2 P 10 ---
--- 3 K 9
1078.5628
496.3354 4 P 8 ---
624.3940
5 Q 7
853.4151
752.4526 6 Q 6
725.3565
899.5210
7 F 5
597.2979
1046.5894 8 F 4
450.2295
1103.6109 9 G 3
303.1611
1216.6949 10 L 2
246.1397
--- 11 M 1
133.0556
Amidated
9
Useful tables:
10
11
12