Bioenergetics
advertisement
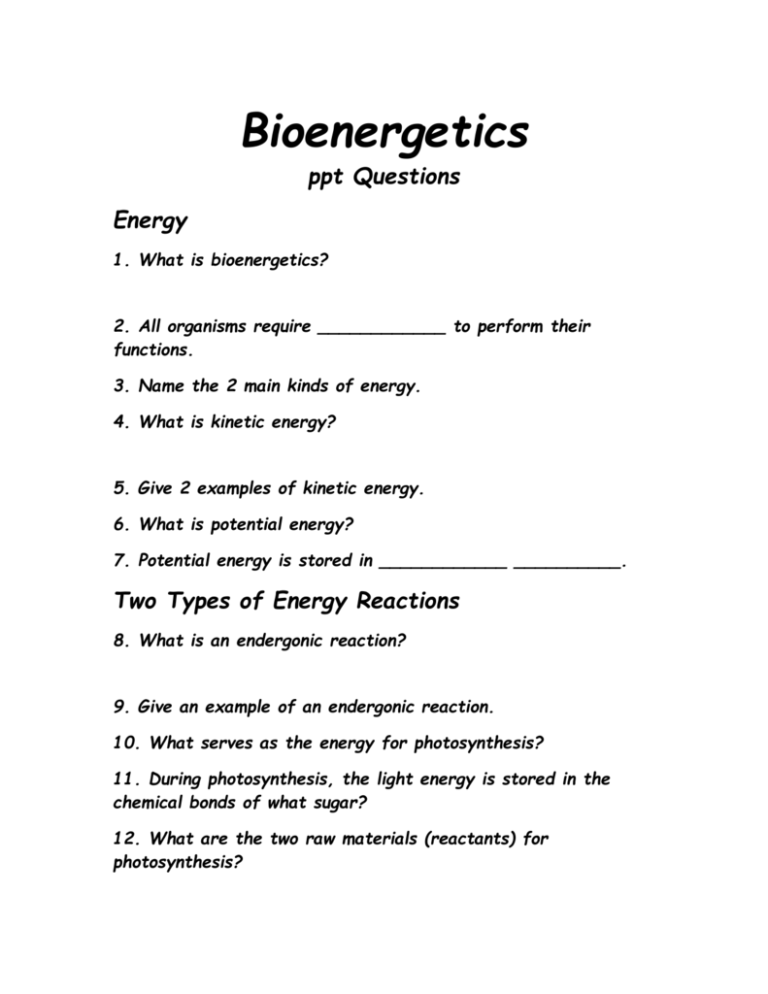
Bioenergetics ppt Questions Energy 1. What is bioenergetics? 2. All organisms require ____________ to perform their functions. 3. Name the 2 main kinds of energy. 4. What is kinetic energy? 5. Give 2 examples of kinetic energy. 6. What is potential energy? 7. Potential energy is stored in ____________ __________. Two Types of Energy Reactions 8. What is an endergonic reaction? 9. Give an example of an endergonic reaction. 10. What serves as the energy for photosynthesis? 11. During photosynthesis, the light energy is stored in the chemical bonds of what sugar? 12. What are the two raw materials (reactants) for photosynthesis? 13. What is an exergonic reaction? 14. Give an example of an exergonic reaction. 15. Where does the energy for cellular respiration come from? 16. Energy released during cellular respiration that can be used by cells is called _________. Metabolic Reactions of Cells 17. Define metabolism of cells. 18. From what compound do animals get their energy (ATP) to do cellular work? 19. Name the 2 types of metabolism. 20. Explain anabolic pathways and give an example. 21. Explain catabolic pathways and give an example. 22. The energy that drives catabolic pathways in organisms comes from breaking _____________ ___________ and producing the energy molecule ___________. Cellular Energy - ATP 23. Name the 3 components that make up ATP. a. b. c. 24. How many phosphate groups are in AT? 25. The last two phosphate groups on ATP are bonded with ___________ ___________ bonds. 26. Which phosphate bond contains the MOST energy? 27. Give the formula for a phosphate group. 28. Name the process that breaks the bonds of ATP to release energy. 29. How often does phosphorylation occur in cells? 30. What enzyme weakens the last phosphate bond so it can be broken? 31. Organisms use ___________ to break down energy-rich __________ to release the potential energy stored in its bonds. 32. Energy released from the chemical bonds of glucose are trapped & stored in ________ until a cell needs energy. 33. What does ATP stand for? 34. How much ATP do cells use? 35. What coupled reactions make ATP and then release its energy. 36. Is hydrolysis exergonic or endergonic? 37. Is energy stored or released during hydrolysis? 38. Is dehydration exergonic or endergonic? 39. Is energy stored or released in dehydration? 40. When ATP is broken down to release energy, what two things form? 41. During hydrolysis of ATP, a molecule of ___________ is added to split the ________ phosphate bond. 42. What happens to the energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP? 43. During dehydration of ATP, a molecule of ___________ is removed to join a free phosphate and __________ making more ATP again. 44. Where is the energy stored in the dehydration process to form ATP? Review 45. How many high-energy phosphate bonds does ATP have? 46. Is photosynthesis anabolic or catabolic? 47. Is photosynthesis exergonic or endergonic? 48. The breakdown of ATP is due to hydrolysis or dehydration? 49. Water is added or removed in the breakdown of ATP? 50. Which of the following are coupled reactions in organisms: a. hydrolysis - dehydration? b. Anabolism - Catabolism? c. Endergonic - Exergonic?