SOL STUDY GUIDE
advertisement
SOL STUDY GUIDE – ALGEBRA 2
PROPERTIES – SOL A2.1
Commutative ex. a b c c a b
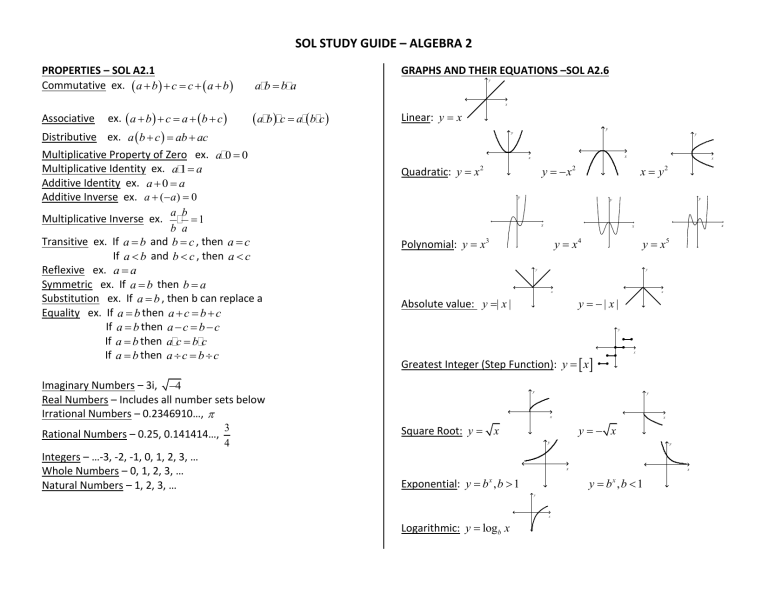
GRAPHS AND THEIR EQUATIONS –SOL A2.6
a bb a
y
x
Associative
ex. a b c a b c
a b c a b c
Distributive ex. a b c ab ac
Multiplicative Property of Zero ex. a 0 0
Multiplicative Identity ex. a 1 a
Additive Identity ex. a 0 a
Additive Inverse ex. a (a) 0
a b
1
b a
Transitive ex. If a b and b c , then a c
If a b and b c , then a c
Reflexive ex. a a
Symmetric ex. If a b then b a
Substitution ex. If a b , then b can replace a
Equality ex. If a b then a c b c
If a b then a c b c
If a b then a c b c
If a b then a c b c
Linear: y x
y
y
y
x
x
Quadratic: y x
y x
2
2
y
y
x
x
x
Polynomial: y x3
y x4
y x5
y
y
x
x
Absolute value: y | x |
y | x|
y
x
Greatest Integer (Step Function): y x
Imaginary Numbers – 3i, 4
Real Numbers – Includes all number sets below
Irrational Numbers – 0.2346910…,
Integers – …-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …
Whole Numbers – 0, 1, 2, 3, …
Natural Numbers – 1, 2, 3, …
x y
y
Multiplicative Inverse ex.
3
Rational Numbers – 0.25, 0.141414…,
4
x
2
y
y
x
x
Square Root: y x
y x
y
y
x
Exponential: y b , b 1
x
y
x
Logarithmic: y logb x
x
y b ,b 1
x
SOL STUDY GUIDE – ALGEBRA 2
SOLVING
Absolute Value – SOL A2.4 There will be 2 possible solutions!
Isolate the absolute value then split into two equations, one
equation is negated.
Ex. 2 x 4 8
Ex. 3 x 2 12
x2 4
x4 6
x46
x 4 6
x 10
x24
x 2 4
x2
x 6
x 2
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES – SOL A2.12, A2.13
The answer to a system of equations is the ordered pair(s) where
the graphs intersect. Use substitution or elimination to solve
algebraically.
The answer to a system of inequalities is where the shaded regions
intersect.
Quadratics – SOL A2.6 Roots = Zeros = Solutions = X-Intercepts
Factoring: Always look for a GCF first!
Completing the Square: Don’t forget the .
b b2 4ac
(given on SOL formula sheet)
2a
Discriminant: b 2 4ac Helps determine the roots.
b 2 4ac > 0 gives 2 real solutions
b 2 4ac < 0 gives 2 complex (imaginary) solutions
b 2 4ac = 0 gives 1 real solution
Quadratic Formula:
DOMAIN AND RANGE – SOL A2.9
Domain: x values
Range: y values
Ex. {(2,3), (4,3), (1,2)} Domain={2,4,1} Range={3,2}
What is the domain and range of function graphed?
y
Square Root – SOL A2.3 There will be 2 solutions because of the .
Ex.
Ex.
x 2 36
x 2 48
x 36
7
6
5
(–1, 3)
x 48
2
2
x 6
4
3
2
x 4 3
1
–7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1
–1
Squaring – SOL A2.7 Check your answer for extraneous solutions!
Ex.
Ex.
x2 5
42 x 8
x2
2
5
x 2 25
x 23
2
2 x 4
x
2
x4
2
3
4
–3
–4
(–6, –5)
–5
–6
–7
x 2
2
1
–2
2
Domain: {x | -6 < x < -1}
Range: {y | -7 < x < 4}
5
6
7
x
SOL STUDY GUIDE – ALGEBRA 2
EXPONENT RULES – SOL A2.10
a 2 a 2 2a 2 can add only like terms, don't change exponent
CONICS – SOL A2.18
Formulas can also be found on the Casio!!
y
y
a (a ) a add exponents when multiplying
2
2
4
(a 2 ) 4 a8 multiply exponents when power of a power
a8
a 3 subtract exponents when dividing
a5
a 0 1 anything to the zero power = 1
1
a 1 1
a
x
Parabola: y ( x h) k
2
y
x
Circle: ( x h) ( y k ) r
2
2
2
1
a1 flip negative exponents to make positive
a 1
RADICALS AND RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS – SOL A2.3, A2.11
x
or x ( y k ) h
2
y
x
( x h) 2 ( y k ) 2
Ellipse:
1
a2
b2
y
3
Ex.
4
x 3 x 4 Exponent = Numerator and Index = Denominator
3
54 x 6 y 8 3x 2 y 2 3 2 y 2
5 2 3 5 4 2 9 2 3 5
2
2
Hyperbola: ( x 2h) ( y 2k ) 1
a
x
b
y
Only combine like terms.
2 3 5 2 3 5 10 6 6 15
COMPLEX NUMBERS (IMAGINARY) – SOL A2.3, A2.17
i 2 1 i 3 i
i4 1
MEMORIZE!!!! i1 i
FACTORING – SOL A2.5
Always look for a GCF first!!
Difference of squares: x 2 y 2 ( x y)( x y )
Difference of cubes: x3 y3 ( x y)( x 2 xy y 2 )
Sum of cubes: x3 y3 ( x y)( x 2 xy y 2 )
Trinomial: x 2 5x 6 ( x 3)( x 2) 2 x 2 3x 2 (2 x 1)( x 2)
( y k ) 2 ( x h) 2
1
a2
b2
x
SEQUENCE AND SERIES – SOL A2.16
Arithmetic: add the same difference to make the next term
Geometric: multiply the same factor to make the next term
last
Series: expression ; Plug in the numbers from the first to the
first
last into the expression, then add their values.
x4
Ex.
2
x 1
(211 ) (221 ) (231 ) (241 )
x 1
(20 ) (21 ) (22 ) (23 )
1 2 4 8 15
SOL STUDY GUIDE – ALGEBRA 2
INVERSE – SOL A2.9
Switch x and y and re-solve for y!
Ex. y 5 x 8
x 5y 8
Inverse: x 8 5 y
x 8
y
5
SCATTER PLOTS AND LINEAR REGRESSION – SOL A2.19
Line of Best Fit – line that best represents the scatter plot
Equation of the Line of Best Fit
Calculator: Stat>enter data into List I and List2
>F1 (Grph)>F1 (GPH1)>F1 (x)
Use values given for a and b to write the equation in
y = ax + b form. Use the equation to make predictions.
COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS – SOL A2.9
Take the innermost function and substitute it in the function listed
to the immediate left.
Ex. Given q x 4 x 7 and p x 2 x 8 , find p q x .
p q x p q x
p 4x 7
2 4x 7 8
8x 6
VARIATION – SOL A2.20
k is the constant and is in all variation problems
k
Direct: y kx
Inverse: y
Joint: y kxz
x
Pay attention to the order of the phrase “varies ________ as”.
Ex. If n varies directly as the cube of g. Find the constant of
variation if n = 32 when g = 2. Find g when n = 108.
n
32 108
32
Formula: k 3
3
k 3
g
(2)3
g
(2)
k 4
32 g 3 864
g 3 27
g 3 27
g 3
RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS – SOL A2.2, A2,7
Follow the same fraction rules and factor polynomials, as needed, to
simplify.
x 2 3x 18 x 3 x 6
Ex.
x6
x 3
x 3
MATRICES – SOL A2.11
2 6 1 5 1 1
Ex.
Need like dimensions.
6 10 7 8 1 2
2 6 6 18
3
Distribute scalar to all elements.
6 10 18 30
2 6
1 2
10 14 Columns of 1 must match rows of 2.
6 10
1 0
0 1 Identity
3
5
2 6
8
8 Inverse
6 10 3
1
8
8









