Theory of Plate Tectonics
advertisement

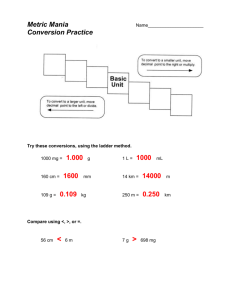
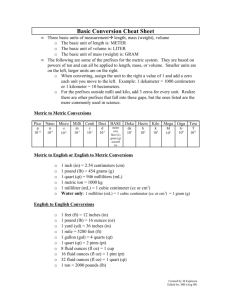
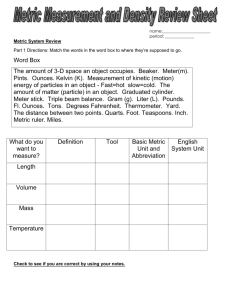
Measurement Study Guide The Big Question: How can we describe matter? Section 1 – Review of Measurement: Vocabulary: matter metric units gram meter liter metric prefixes volume mass weight balance scale graduated cylinder meniscus displacement regular-shape irregular-shape milliliter cubic centimeter Key questions/knowledge/content: 1. What are the three basic units of metric measurement for length, mass and liquid volume? 2. How do you use the metric prefixes to make smaller and large units of a measurement such as the liter, meter or gram? Give examples. 3. What do we know about a number that has a unit of length that is squared (cm2) or cubed (cm3)? 4. What would be an appropriate metric unit to use for measuring the length of your room? The length of a pencil? The distance from Essex to Manchester? 5. What is the difference between a regular-shaped and irregular-shaped object? Give examples of each. 6. Explain how you can measure the volume of regular shaped objects such as a block or ball? Do an example using the science/math format or top-down method. 7. Define the term displacement as it relates to objects in a fluid. 8. How can you use displacement to measure the volume of an object? 9. What is the relationship between a cm3 and a milliliter? 10. Compare mass and weight. Which one is determined by the force of gravity? 11. Why would you weigh (weight) less on the Moon than here in class? 12. How do you mass a liquid? Key Skills: Measure length and mass to the nearest 0.1 of centimeter and gram. Given a ruler measure and then calculate the area and volume of various regular shapes. Use the displacement method to measure the volume of irregular-shaped objects. Use a balance scale to measure the mass of liquids. Resources /Visuals : Quizlet.com/hornets7science (pw “hornets”) Measurement Review Float, Sink and Flink Metric Prefixes My website. Section 2 – Properties of Matter Vocabulary matter mass volume physical property chemical property intensive property extensive property state of matter solid liquid gas freezing point boiling point melting point Key Questions/Ideas/Content: 1. What is matter? If something isn’t matter, then what is it? 2. What are two ways to describe matter? 3. What are some properties of a 50 Kg gold cube measuring 2 cm on each side? If you cut that cube in half, which properties would change? Which properties would remain the same? 4. List at least one chemical property of wood, oil, iron and baking soda. 5. Compare the arrangement of particles in a solid, liquid and gas. 6. How does adding heat to matter affect it’s (a) volume? (b) density? 7. List the three states of matter in order of increasing energy. 8. All matter has very specific melting and boiling points. What are the melting and boiling points of water? Gold? Oxygen? ? You only have to know water but remember that this is n intensive physical property. Key skills: 1. Draw a diagram illustrating the arrangement of particles in a solid, liquid and gas. 2. Use chemical and physical properties to identify a substance. Section 3 – Density Vocabulary: density average density buoyancy neutral buoyancy positive buoyancy negative buoyancy displacement expansion contraction air bladder (fish) ballast tanks (submarine) BCD (SCUBA diving Key Questions/Knowledge/Content: 1. Define the term density? Give examples of two substances with different densities?. 2. Write the mathematical formula that is used to calculate density. 3. List the densities for pure water, ice, gold, iron and air. Use g/cm3 as your unit. 4. What are two ways to change the density of an object without changing the substance? 5. If you increase the mass of an object without changing its volume what happens to density? 6. If you increase the volume of an object without changing its mass what happens to density? 7. What is meant by the term average density? When is it used? 8. Compare the forces of gravity and buoyancy. 9. How can you predict floating, sinking and “flinking”? 10. Explain how scuba divers, fish and submarines can alter their average density. Key skills: Use the appropriate tools to determine the density of various materials and objects. Place materials with known densities in order of increasing or decreasing density. Predict if an object will float or sink of in water given their densities. Use the science/math format (aka top down method in math) to solve math problems in science.