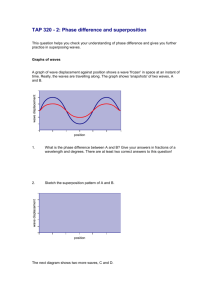
Well you might say it`s obvious - you just put the food in and it heats
advertisement

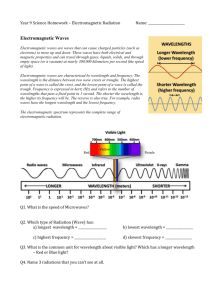
How a Microwave Oven works? « Well you might say it's obvious - you just put the food in and it heats it up. But why does it heat the food yet it doesn't heat the dish, and why is the inside of the oven always cold? A microwave oven has in it a magnetron, which is a radio transmitter. If it was on a radio mast (don't try this) it would be able to send radio signals a long way. But it is inside a metal box which keeps the signal in. The frequency of the transmitter is 2450MHz, which is a wavelength of 12cm, that's why it's micro waves, rather than short waves (several metres), medium waves (hundreds of metres) or long waves (thousands of metres). There's a good reason for the frequency being 2450 Megahertz, which I'll explain. Food has a high percentage of water, and water is famously H2O. The molecule of water has the O (Oxygen) in the middle, and the two H's (Hydrogen) stuck on it like Mickey Mouse ears at a particular angle (105 o). The H's are positive and the O is negative, so the molecule has a + and - end. It has "polarity". Polarized molecules try to line themselves up with the electrical field, like compass needles trying to point at North. But because the electrical field is changing 2,450 million times a second the molecules don't quite have time to line up one way before they have to try to line up the other way! So, anything with water in it has all these molecules being moved this way and that by the electrical field, and heated up. The dishes, walls of the oven, etc, don't pick up radio, so don't get heated up. » Source: http://www.zyra.org.uk/microw.htm 1/ Translate the words and sentence: Wavelength, stuck on, electrical field, heated up « Polarized molecules try to line themselves up with the electrical field, like compass needles trying to point at North » 2/ Explain in a few words, with the help of the text, how microwave ovens work. 3/ Explain what is a wavelength. What is the relation between wavelength and frequency? Justify the sentence: « The frequency of the transmitter is 2450MHz (megahertz), which is a wavelength of 12cm ». 4/ Do microwaves need a medium for their displacement? Give examples of waves which require and not require a medium for their displacement. 5/ Give the names, frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiations from radio waves to gamma rays. What is the wavelength range for visible light? Which radiations carry more energy (justify)? 1/ Translate the words and sentence: Wavelength, stuck on, electrical field, heated up « Polarized molecules try to line themselves up with the electrical field, like compass needles trying to point at North » 2/ Explain in a few words, with the help of the text, how microwave ovens work. The microwave oven’s magnetron generates a 2,45GHz electric microwave. Water, fat, and other substances in the food absorb energy from those microwaves in a process called dielectric heating. Water molecules are electric dipoles (they have a positive charge at one end and a negative charge at the other), and therefore rotate as they try to align themselves with the alternating electric field of the microwaves. This molecular movement is dispersed generating heat. Notice that the choice of the frequency is important: if the frequency were too low, it would not heat enough and if it were too high the radiations would not penetrate the food (the higher the frequency, the lower it penetrates, this phenomenon is known as “skin effect”). 3/ Explain what is a wavelength. What is the relation between wavelength and frequency? Justify the sentence: « The frequency of the transmitter is 2450MHz (megahertz), which is a wavelength of 12cm » Wavelength = spatial period of the wave We know that λ = c T = c / f = 3x108/2.45x109 = 30/2.45 = 12 cm 4/ Do microwaves need a medium for their displacement? Give examples of waves which require and not require a medium for their displacement. No, microwaves, like all electromagnetic waves, can travel either in a matter or in a vacuum. Waves which need a medium: sound, mechanical wave on a string or at the surface of the water... Waves which doesn't need a medium: light and more generally all the electromagnetic waves. 5/ Give the names, frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiations from radio waves to gamma rays. What is the wavelength range for visible light? Which radiations carry more energy (justify)? In order of increasing frequency (and then decreasing wavelength!) we have: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. The relation between energy and energy is E = hv (Plank's relation), this is why gamma rays are the most energetic waves.