Light Intro
advertisement

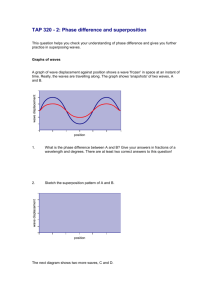
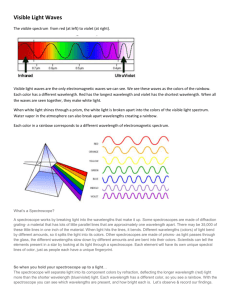
LIGHT Principles of Physics Waves created by fluctuating electric and magnetic fields Transverse waves Can travel in a vacuum – do not need a medium Travel at the speed of light in a vacuum (c = 300,000,000 m/s) Organized by frequency and wavelength http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index .php?topic=35 3.84x1014 Hz 4.82x1014 Hz Red 5.03x1014 Hz Orange 5.20x1014 Hz Yellow 6.10x1014 Hz Green 6.59x1014 Hz Blue 7.69x1014 Hz Violet Longest wavelength and lowest frequency RADIO WAVES ARE NOT SOUND WAVES Provide the signal for communications devices such as: radios, television, cell phones Micro waves are used to cook food Infrared waves are used for TV remote controls, night vision Shortest wavelength, highest frequency Cause damage to human cells because wavelength is close to atomic size Ultraviolet – sun bathing X – used to detect bone damage, baggage screening at airports Gamma – radioactive decay Waves that allow us to see color Red – longest wavelength, lowest frequency (3.84 x 1014 Hz = 384,000,000,000,000 Hz) Violet – smallest wavelength, highest frequency (7.69 x 1014 Hz = 769,000,000,000,000 Hz) Light Sources Emit light waves Produce light Sun, light bulbs, flames Illuminated Objects Most objects Actually are reflecting light People, plants, rocks, etc. Moon – source or illuminated? Intensity (brightness) = amplitude Large amplitude, a lot of energy (very hot) Small amplitude, less energy (warm) Color = frequency Order of colors = spectrum Primary colors of light – red, green and blue Red light +green light +blue light = white light Different than pigment colors (ink, paint, etc) These reflect light, they are not sources Mixing colors Applet Light can be reflected or transmitted: Materials Transparent – transmit clearly (clear glass, still water) Translucent – transmit blurry (frosted glass) Opaque – no transmission (light may be reflected or absorbed) Speed of light in a vacuum =c = 299,792,458 m/s = 2.99792458 x 108 m/s ≈ 3.00 x 108 m/s Speed of light in any other material depends on optical density (ability of a material to transmit light) Greater optical density, more light slows down Air c / 1.003 ≈ 3.00 x 108 m/s Water c/1.33 Diamond c/2.42 1. 2. 3. Put a decimal after the first non-zero number and drop any zeroes Determine the power of ten by counting the places before of after the decimal Show the places before or after the decimal using an exponent. Use a negative on your exponent if the decimal is before the number 1. Ex: 300,000,000 → 3.0 0.000345 → 3.45 2. Ex: 300,000,000 → 3.0 8 places after 0.000345 → 3.45 4 places before 3. Ex: 300,000,000 → 3.0 x108 0.000345 → 3.45 x 10-4