Intrachromosomal rearrangements in avian genome evolution
advertisement

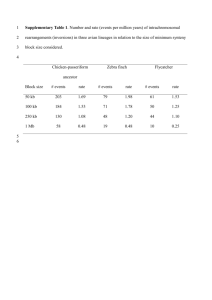
Supplementary material Supplementary table 1: Chromosomal segments identified after chromosomal alignments between chicken, turkey and zebra finch. Previously FISH-mapped chicken and zebra finch BAC clones overlapping segment locations were used to assess whether the rearrangement was consistent with physical marker order. a Segment not present. Supplementary table 2: Segment ends involved in rearrangement pathways predicted by MGR 19 . The number of times a segment end is at a breakpoint is noted for three pathways: chicken-turkey ancestor to (1) chicken, (2) turkey and (3) zebra finch. Recurring breakpoints are noted as to whether they occur only within one pathway, or more than one pathway. Note that in reality the pathway to zebra finch represents two lineages. Supplementary table 3: Reconstructed chicken-turkey ancestral organisation, and optimal pathways to each modern species' organisation as determined using the MGR tool on the GRIMM web server. Supplementary table 4: Comparison of repetitive content for classes of repeats between breakpoint regions and segments, using the breakpoint data from chicken. Supplementary Figure 1: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 1, chicken (GGA) chromosome 1 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosomes 1A and 1. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. TGU1A is positioned from 0-74Mb. Supplementary Figure 2: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosomes 6 and 3, chicken (GGA) chromosome 2 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 2. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. MGA6 is positioned from 0-56Mb. Supplementary Figure 3: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 2, chicken (GGA) chromosome 3 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 3. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 4: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosomes 9 and 4, chicken (GGA) chromosome 4 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosomes 10 and 4. MGA9 is positioned from 0-20Mb; TGU10 is positioned from 0-20.6Mb. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 5: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 5, chicken (GGA) chromosome 5 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 5. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 6: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 8, chicken (GGA) chromosome 6 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 6. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 7: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 7, chicken (GGA) chromosome 7 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 7. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 8: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 10, chicken (GGA) chromosome 8 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 8. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red. Supplementary Figure 3: Side by side chromosomal alignments between turkey (MGA) chromosome 12, chicken (GGA) chromosome 10 and zebra finch (TGU) chromosome 10. Directly matching segments are shown in blue, inversions are shown in red.