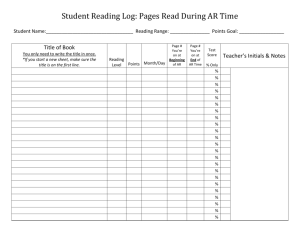
Reference for a specific web page
advertisement

How To: Cite and Reference Using Harvard - The purpose of referencing - Ways of introducing references into text - Quoting - Using reporting verbs in text - Bibliographic referencing - Other sources of help - Example of bibliography For appointments contact: T: 0141 273 1230 E: AskLDC@gcu.ac.uk www.gcu.ac.uk/ldc © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment 2011 Citing and Referencing Whenever you refer to the work or ideas of someone else, you must acknowledge this in two places – in the main body of the text (citing) and at the end of your work in the alphabetical list of references. This practice is called referencing. Information provided in this document relates to the Harvard System of referencing. The Harvard System uses the author’s surname and date of publication for referencing purposes in the text. Information can be drawn from a wide range of sources including: books, journals, newspapers, videos and the Internet. Always check the referencing guidelines provided by your Programme Organiser or Lecturer. If you have a choice to adopt a certain style you must keep to it throughout the assignment. The purpose of referencing Referencing allows the reader to verify quotations and data and consult the sources used. Referencing ensures that plagiarism is avoided and demonstrates the range of reading undertaken. Plagiarism is when you use someone’s ideas, thoughts and words without acknowledging the source. References are required when you: Quote - use someone’s exact words Summarise - sum up someone else's arguments or ideas Paraphrase - put another author's material into your own words Copy - use illustrations such as: diagrams, tables, charts or maps © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 1 Ways of Introducing References into the Text References can be introduced into the text in various ways and certain rules apply. Ideally this information should be integrated into the text so that it does not break up the flow of the writing. EXPLANATION Author's name occurs naturally in the sentence, only use the surname and place bracket round the year Author’s name does not appear naturally in the sentence, place surname and publication inside bracket Using two names inside text use ‘and’ Using two names in the bracket use ‘&’ The author is unknown use ‘Anon’ but be wary of unauthored work. In newspaper articles or websites, if there is no author, use the name of the newspaper. In websites where there is no author use the website host address. Often websites do not have a date, but always check the home page of the website. Be wary of using unauthored work. Occasionally the same author will write more than one article in the same year. Use ‘a’, ‘b’ etc. EXPLANATION When there are more than two authors use: 'et al' (note italics) NB: All names should appear in the references. If you refer to a source in another text, refer to both sources. For example, you may mention but you need to tell the reader that you have not read Freud’s actual work. If you quote one source in another text, note the actual page you read Journals are often published as ejournals. Cite in text as hard copy using author and year (refer to page 6, Bibliographic referencing). EXAMPLE Morgan (1997) suggested that ... A recent study (Smith, 2003) found or In a recent study it was found… (Smith 2003) Harris and Jones (2001) have commented on … (Harris & Jones 2001) It has been observed ( Anon, 2001) that … A recent study described ... (The Herald, 2011, p4) The Health and Safety Executive ( 2011) states that… In his first article Grayson (1997a) indicates … Grayson (1997b) further argued that... EXAMPLE An additional theory was developed (Hughes et al., 2002)… Freud (1888, cited in Smith, 2000) Porter (1997, cited in Feeley, 2001, p12) (Murphy, 2001) © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 2 Reporting Verbs Make the text more interesting for the reader Make your meaning clearer Help establish the discussion Highlights what the author has done Note the tense used depends on the context. EXAMPLE - THE AUTHOR (YEAR) EXPLANATION Analyses/analysed Examine closely Compares/compared Discusses in terms of similarities and differences Comments/Commented Give an opinion or reaction Concludes/Concluded Bring argument to a close Criticises/Criticised Express disagreement Demonstrates/Demonstrated Show clearly by giving proof / evidence Examines Look at in detail Discusses/Discussed Consider and offer opinion Illustrates/Illustrated Offer an example/s Indicates/ Indicated Offer a explanation Notes/Noted Make mention of Observes/Observed Note through comments Points out/Pointed out Giving an opinion Suggests/Suggested Put forward an idea Summarise/Summarised Present the main points Validates/Validated Prove the accuracy of something Verifies/Verified Check the accuracy Further reporting verbs can be found at http://www.job-analysis.net/G053.htm © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 3 Quotations are the exact words used in the source, whether it be a book, journal, newspaper or website. Quotes should be used sparingly to make significant points and should be integrated well within the text. EXPLANATION Short quotations - less than a line, use single quotation marks and incorporate quote into text; use author, year and page number If you leave words out then indicate by … using three dots Double inverted commas should be used for reporting direct speech. EXAMPLE Burns (2000, p3) explained that ‘Research is a systematic investigation to find answers to a problem’. ‘…most reinsurers have consistently lost money’ At the World Economic Forum 2011, Gates talked about ‘polio eradication…which is spearheaded by the World Health Organisation…’ Graph illustrating natural change Diagrams, graphs or illustrations should have a title and include the words (adapted from, Author's name, date of publication and page number where possible) ** No page number here as from website (Adapted from Office for National Statistics, 2007) Bibliographic Referencing When writing essays or reports you are expected to include Bibliographic information in a list at the end of the assignment. You may be asked to produce: A Reference List - this includes all sources you refer to in your text. A Bibliography - this lists all materials consulted, including works not cited in the text. When using the Harvard System references are listed in bibliographies or reference lists alphabetically by authors' names. © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 4 EXPLANATION EXAMPLE Book Author's surname, and initials., Year of publication. Title (in italics - you can underline in handwritten work). Edition - if not the first. Place of publication: Publisher. Texts by the same author. List these in chronological order - most recent year first. More than one text has been published by an author in the same year letters should be added to differentiate - (1997a) (1997b). Angus, S., 1999. A Study Skills Guide. 2nd ed. Glasgow: Pierce Press. Angus, S.,2001, Study Skills Revised. Glasgow: Pierce Press. Angus, S., 1999. A Study Skills Guide.2nd ed. Glasgow: Pierce Press. Grayson, J. (1997a) ‘Place of residence, student involvement, and first year marks’. The Canadian Journal of Higher Education. 27, pp. 1-24 Grayson, J. (1997b). ‘Academic achievement of first-generation students in a Canadian university’. Research in Higher Education 38, pp. 659-676 Reference to a contribution in a book Contributing author‘s Surname, Initials., Year of publication. Title of contribution followed by In: Initials. Surname of author or editor of publications followed by editor(s) Title of book. Edition - if not the first. Place of publication: Publisher, Page number(s) of contribution. Banz.CZ., 1995. Social Dimensions of software development. In: J.A. ANDERSON, ed. Annual review of software management and development. Newbury Park, CA: Sage, pp. 502-510 and/another example is the following: Barr, T., 1987. Critical Analysis Skills. In: P.W. HOLLOWAY, ed. Developing Skills for Higher Education. London: Palmer Print, pp. 45 - 52. © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 5 Government Department or Organisation Name of body which produced the document. Year of publication. Title of publication Place of publication: Publisher, Report No - if relevant. Scottish Enterprise. 2001. Scottish Economic Growth. Glasgow: Scottish Enterprise, (WW40). Article in a Journal Author's surname, and initials., Year of publication. Title of Article, Title of Journal, Volume number and (part number), Page numbers of contribution. O'Brien, M., 2001. Searching the Internet Successfully. The Internet Journal, 8 (2), pp. 211-219. Newspaper Article Author's surname and initials or newspaper article, Year of publication. Title of Article. Title of Newspaper, Date - day and month, Page numbers / Column number. Full text journal or newspaper article from the internet Author’s surname and initials, Year of publication. Title of article. Title of publication. [Type of medium in square brackets] Date of publication. Available from: URL [Date accessed in square brackets] Full text journal from a database on the internet Author’s surname and initials. Year of publication. Title of article. Title of publication. Volume (Issue Nr). [Type of medium in square brackets] Available from: database followed by the URL [Date accessed in square brackets] Farrar, S., 2004. Cash crises lead to student depression. The Times Higher Education Supplement. 16 April, p. 5 Lyons, W., 2004. The 10 trends that will shape 2005. news.Scotsman.com. [online]. Wednesday 22nd December. Available from: http://news.scotsman.com/uk.cfm?id=1456172004 [Accessed 26th August 2005] Clancy, P. and Goastellec, G., 2007. Exploring Access and Equity in Higher Education: Policy and Performance in a Comparative Perspective. Higher Education Quarterly. 61 ( 2). [online]. Available from: http://www.swetswise.com/eAccess/viewToc.do?title ID=92191&yevoID=1946926 [Accessed 10th April 2008] © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 6 Reference for a specific web page Author’s surname and initials. Year of publication. Document title. [Type of medium in square brackets] Available from: URL [Date accessed in square brackets] Document in pdf format Author’s surname and initials. Year of publication. Title of document. [Type of medium in square brackets] Available from: URL [Date accessed in square brackets] E-Book Author’s surname and initials, Year of publication. Title of Book Edition – if not the first Place of publication: Publisher [Type of medium in square brackets] Available from: URL [Date accessed in square brackets] Monash University. 2008. Essay Writing. Language and Learning Online. [online]. Available from: http://www.monash.edu.au/lls/llonline/writing/genera l/essay/index.xml [Accessed 17TH April 2008] University of New South Wales. 2007. Transition Signals in Writing. The Learning Centre Homepage. [online] Available from: http://www.lc.unsw.edu.au/onlib/pdf/transsig.pdf [Accessed 17th April 2008] Chalker, S. and Weiner, E., 1998. The Oxford Dictionary of English Grammar. Oxford: University Press. [online] Available from: http://www.oxfordreference.com/views/ENTRY.html ?subview=Main&entry=t28.e1353 [Accessed on 04.April 2008] Email Communication Author’s surname and initials. Title of the Email Type of medium in square brackets Message to: Recipient Date sent [date accessed] Personal Communication Wilson, Margaret. Essay Writing Tips for Students. [online]. Message to: Esther Smith. 03.07.07. [02.02.08]. Personal Communication Blog Lisa. 2008. Book Review: the Longman Practical Stylist. 30.01.08 Book Reviews. Humanities and Social Science Library. [online]. Available from: Author’s surname and initials. Year. Title of the blog entry. Date when the blog was written Title of the Blog [Type of medium in square brackets] Available from: URL [Date accessed] http://blogs.ntu.edu.sg/library/hss/index.php/archive s/category/book-reviews [Accessed on: 04.03.08] © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 7 If there is no author, either corporate or individual, try to avoid using the example as it is difficult to establish authenticity. Useful sources of additional information CGU’s website on Refworks http://www.refworks.com/rwathens/help/Refworks.htm#QuickStartGuide. pdf Harvard and Numeric explanations, University of Sussex http://www.sussex.ac.uk/library/infosuss/referencing/index.shtml Guidelines on reference listing, the Harvard system, University of Thames Valley http://www.tvu.ac.uk/lrs/guides/harvard.html#further Guide to citing references (Harvard, Numeric, Footnotes) and Referencing Software, University of Birmingham http://www.i-cite.bham.ac.uk/ Citing references – The Harvard System and Legal Material, Bournemouth University http://www.bournemouth.ac.uk/library/using/harvard_system.html © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 8 Example Bibliography Baren-Cohen, S., 2003. The essential difference: men, women and the extreme male brain. London: Allen Lane. Barnes, S., 2001. Questionnaire design and construction. Bristol Institute of Learning and Technology. [online] http://www.cros.ac.uk/question_design.pdf#search=%22belief%20questions%20% 20Barnes%202001%22 Accessed on 30 August 2006. Clancy, P. and Goastellec, G., 2007. Exploring Access and Equity in Higher Education: Policy and Performance in a Comparative Perspective. Higher Education Quarterly. 61 ( 2). [online]. Available from: http://www.swetswise.com/eAccess/viewToc.do?titleID=92191&yevoID=1946926. [Accessed 10th April 2008] Cottrell, S., 2005. Critical thinking skills. Basingstoke: Palgrave. Effective Learning Service, 2003. Annual questionnaire, 2002/3. Glasgow: Glasgow Caledonian University. Farrar, S., 2004. Cash crises lead to student depression. The Times Higher Education Supplement. 16 April. p 5 Field, J., 2004. Articulation and credit transfer in Scotland: taking the academic highroad or a sideways step in a ghetto? Journal of Access Policy and Practice. 1 (2), pp. 85-99 [online] Available from: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/niace/japp. Accessed on 18 August 2006 Gillett, A., 2008. Writing Paragraphs. Using English for Academic Purposes Website. [online]. Available from: http://www.uefap.com/writing/writfram.htm [Accessed 10th April 2008] Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE), 2002. Good practice guidance for senior managers and practitioners. (November 2002/48) [online]. Available from: http://www.hefce.ac.uk/Pubs/hefce/2002/02_48.htm#exec. [Accessed on 2nd March 2006] Illeris, K., 2006. What is special about adult learning? In: P. Sutherland and J. Crowther, eds. Lifelong Learning. London: Routledge, 15-24 Wilding, R. and Morelli, A., 2006. Preparing for Dissertations. 22th November. 2008. Study Zone Blog. [online]. Available from: http://mycommunity.newport.ac.uk/blogs/studyzone/archive/2006/11/22/2201.aspx. [Accessed 17th April 2008] © Glasgow Caledonian University School of Engineering and Built Environment (LDC) 2012 9