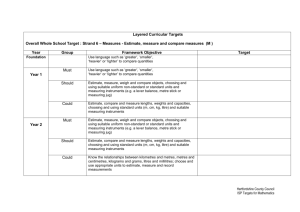
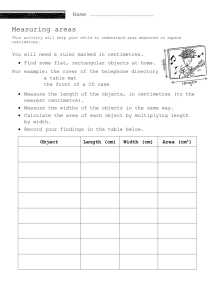
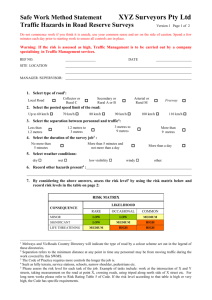
Key School Targets
advertisement
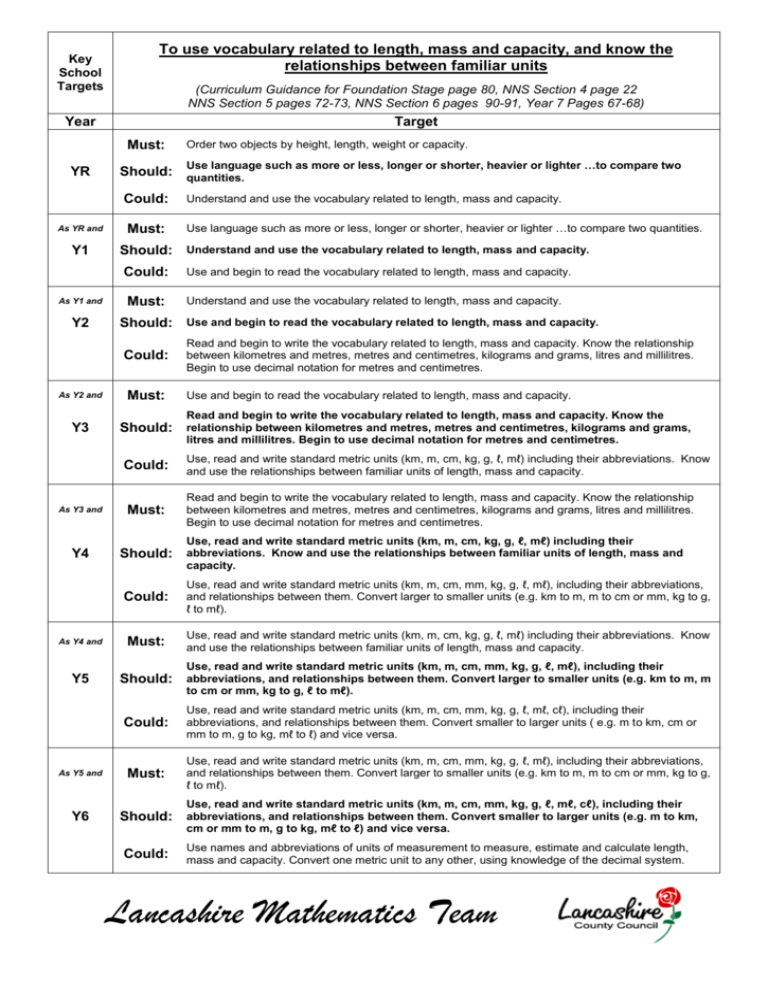
Key School Targets To use vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity, and know the relationships between familiar units (Curriculum Guidance for Foundation Stage page 80, NNS Section 4 page 22 NNS Section 5 pages 72-73, NNS Section 6 pages 90-91, Year 7 Pages 67-68) Year Target Must: YR Use language such as more or less, longer or shorter, heavier or lighter …to compare two Should: quantities. Could: As YR and Y1 Must: Y2 Must: Use language such as more or less, longer or shorter, heavier or lighter …to compare two quantities. Use and begin to read the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Understand and use the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Should: Use and begin to read the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Could: As Y2 and Understand and use the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Should: Understand and use the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Could: As Y1 and Order two objects by height, length, weight or capacity. Must: Read and begin to write the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Know the relationship between kilometres and metres, metres and centimetres, kilograms and grams, litres and millilitres. Begin to use decimal notation for metres and centimetres. Use and begin to read the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Read and begin to write the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Know the Y3 Should: relationship between kilometres and metres, metres and centimetres, kilograms and grams, litres and millilitres. Begin to use decimal notation for metres and centimetres. Could: As Y3 and Must: Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ) including their abbreviations. Know and use the relationships between familiar units of length, mass and capacity. Read and begin to write the vocabulary related to length, mass and capacity. Know the relationship between kilometres and metres, metres and centimetres, kilograms and grams, litres and millilitres. Begin to use decimal notation for metres and centimetres. Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ) including their Y4 Should: abbreviations. Know and use the relationships between familiar units of length, mass and capacity. As Y4 and Could: Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, mm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ), including their abbreviations, and relationships between them. Convert larger to smaller units (e.g. km to m, m to cm or mm, kg to g, ℓ to mℓ). Must: Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ) including their abbreviations. Know and use the relationships between familiar units of length, mass and capacity. Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, mm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ), including their Y5 Should: abbreviations, and relationships between them. Convert larger to smaller units (e.g. km to m, m to cm or mm, kg to g, ℓ to mℓ). Could: As Y5 and Must: Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, mm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ, cℓ), including their abbreviations, and relationships between them. Convert smaller to larger units ( e.g. m to km, cm or mm to m, g to kg, mℓ to ℓ) and vice versa. Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, mm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ), including their abbreviations, and relationships between them. Convert larger to smaller units (e.g. km to m, m to cm or mm, kg to g, ℓ to mℓ). Use, read and write standard metric units (km, m, cm, mm, kg, g, ℓ, mℓ, cℓ), including their Y6 Should: abbreviations, and relationships between them. Convert smaller to larger units (e.g. m to km, cm or mm to m, g to kg, mℓ to ℓ) and vice versa. Could: Use names and abbreviations of units of measurement to measure, estimate and calculate length, mass and capacity. Convert one metric unit to any other, using knowledge of the decimal system. Lancashire Mathematics Team