RtI Glossary PaTTAN Training Module
advertisement

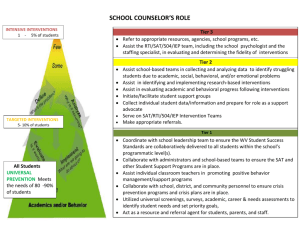
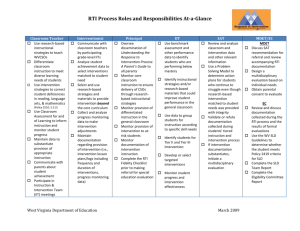
RtI Glossary Core (Reading) Program: The primary instructional tool that teachers use to teach students to read or become proficient in math and to ensure that students reach levels that meet or exceed grade level standards. It should address the instructional needs of the majority of students in the school or district. Reviews of research are available at http://reading.uoregon.edu/curricula/index.php. It is the initial tool to guide high quality instruction in the classroom. (FCRR, 2004) Differentiated Instruction: Proactively planning and providing alterations to curriculum, instruction and assessment that recognize students’ varying background knowledge, readiness, language, preferences in learning, and interests. Differentiated instruction is a process to approach teaching and learning for students of differing abilities in the same class. The intent of differentiating instruction is to maximize each student’s growth and individual success by meeting each student where he or she is, and assisting in the learning process. (http://www.cast.org/publications/ncac/ncac_diffinstruc.html) Discrepant/Discrepancy: the comparison of an individual’s performance at a point of time to the performance of peers or other established standards at that same point in time. Given equal or enhanced opportunities, the student’s current level of performance is significantly different than typical peers or identified standards. Effective Instruction: Research-based effective teaching principles include: active engagement of students, high success rates, increased content coverage, direct instruction by a teacher, carefully scaffolded instruction, instruction that addresses the critical forms of knowledge, instruction assisting in the organizing, storing, and retrieving of information, strategic instruction, explicit instruction, instruction that teaches sameness across subjects. Eligibility: Eligibility means that an individual, who by nature of his/her disability and need, requires special education and related services in order to receive an appropriate education. Intervention: Direct instruction in the area of concern. Interventions are designed to meet the identified needs of an individual and are monitored on a regular and frequent basis. Problem-solving Process: A procedure in which participants use a sequence of actions to address a problem, including: Discuss the concern. Conduct further assessments (if needed). Identify the problem. Set a measurable goal. Identify a research-based strategy that matches the data. Plan for support in establishing intervention in classroom. Monitor progress. Evaluate success of the strategy. Rate of Progress: Rate of progress is objective evidence of performance across time. The rate of skills acquisition and/or slope of improvement are the rate of progress (Iowa, 2006). Response to Intervention: “... The practice of (1) providing high-quality instruction and interventions matched to student needs and, (2) using learning rate over time and level of performance to (3) make important educational decisions. These three components of RtI are essential. (Batsche et al., 2005, p.5)” Scientifically-based Research: See page 3. Standard Protocol: Intensive, short-term (10-15 weeks) instructional interventions that follow a specified script and have research to support its effectiveness. They are typically conducted with a small group of targeted students using materials that supplement the general education curriculum (Fuchs, 2003). Standard Protocol Interventions: are research-based, have a high probability of producing change, are used in a standard manner across students, and can be orchestrated by a team. Tier 1: Benchmark/School wide: Students who are making expected progress in the general education curriculum and who demonstrate social competence. All students receive Tier 1 instruction. Tier 2: Strategic/Targeted Interventions: Academic and behavioral strategies, methodologies and practices designed for students not making expected progress in the general education curriculum and/or have mild to moderate difficulties demonstrating social competence. These students are at risk for academic failure. Tier 3: Intensive Interventions: Academic and behavioral strategies, methodologies and practices designed for students significantly lagging behind established grade-level benchmarks in the general education curriculum or who demonstrate significant difficulties with behavioral and social competence. Universal Screening: Brief (1-5 minutes per student) assessment of all students in the district to identify which students are not proficient relative to specified benchmarks (standard that corresponds with successful outcomes in the future), indicating that they are at risk for potential difficulties in language arts, mathematics, behavior, or other domains. IDEA 2004: Definition of Scientifically Based Research The Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement act of 2004 (IDEA) aligns IDEA closely to the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB), helping to ensure equity, accountability, and excellence in education for children with disabilities. IDEA 2004 addresses scientifically based research in the following context: In implementing early intervening services, LEAs may carry out activities that include: Professional development activities for teachers and other school staff to enable such personnel to deliver scientifically based academic instructional and behavioral interventions, including scientifically based literacy instruction, where appropriate… Providing educational and behavioral evaluations, services and supports, including scientifically based literacy instruction. IDEA 2004 (613(f)(2)(A)(B) While waiting for the Federal government to provide additional guidance to States within Federal regulations, specifically addressing special education and scientifically based research, LEAs may continue to rely on the definition provided in NCLB to evaluate their curricular programs. NCLB 2001: Definition of Scientifically Based Research The No Child Left Behind Act defines the term ‘scientifically based research’ (A) means research that involves the application of rigorous, systematic and objective procedures to obtain reliable and valid knowledge relevant to education activities and programs; and (B) includes research that: Employs systematic, empirical methods that draw on observation or experiment Involves rigorous data analyses that are adequate to test the stated hypothesis and justify the general conclusions drawn Relies on measurements or observational methods that provide reliable and valid data across evaluators and observers, across multiple measurements and observations, and across studies by the same or different investigators Is evaluating using experimental or quasi-experimental designs in which individuals, entities, programs, or activities are assigned to different conditions and with appropriate controls to evaluate the effects of the condition of interest, with a preference for randomassignment experiments, or other designs to the extent that those designs contain withincondition or across-condition controls Ensures experimental studies are present in sufficient detail and clarity to allow for replication or, at a minimum, offer the opportunity to build systematically on their findings Has been accepted by a peer-reviewed journal or approved by a panel of independent experts through a comparatively rigorous, objective and scientific review.” Reading First: Definition of Scientifically Based Research Scientifically based reading research is research that applies rigorous, systematic, and objective procedures to obtain valid knowledge relevant to reading development, reading instruction, and reading difficulties. This includes research that: Employs systematic, empirical methods that draw on observation or experiment; Involves rigorous data analyses that are adequate to test the stated hypothesis and justify the general conclusions drawn; Relies on measurements or observational methods that provide valid data across evaluators and observers and across multiple measurements and observations; and Has been accepted by a peer-reviewed journal or approved by a panel of independent experts through a comparably rigorous, objective and scientific review. Source: PaTTAN Training Module Resource ’06-07