Title Times 14pt Bold
advertisement

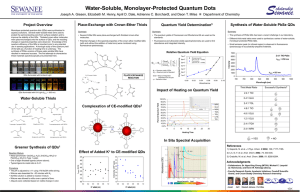
Dual-Emission Silica-Coated Quantum Dots Mixture as FRET-based Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe for detection of Zn2+ Liang Wu, Kao Zhu, Qingsheng Guo, Yuqian Liu, Qingjiang Sun* State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, School of Biological Science & Medical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China Fax: +86-25-83792349; Email: sunqj@seu.edu.cn Recently, quantum dots (QDs) have attracted widespread attention in diverse research areas due to their unique spectral properties, such as high quantum yields, exceptional resistance to photobleaching and a stable surface for further modification. Besides, their size-dependent emission spectra with broad absorption spectra allow their simultaneous excitation at a single wavelength. Utilizing these properties, different-colored QDs can be combined together to develop their applications in ratiometric fluorescence detection of protein, virus or ions. Detection of Zn2+ is a significant issue towards human health and environment due to its critical roles in many biological activities. Herein, we designed a new ratiometric fluorescence probe for Zn2+ detection in aqueous phase based on two fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) processes from different-colored QDs to meso-tetra(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphine dihydrochloride (TSPP). The probe comprises dual-emission silica-coated QDs with TSPP assembled on the surface. By adjusting the thickness of silica shell, TSPP quenches the photoluminescence (PL) of each QD dominated by FRET mechanism while other interactions are shielded. The chelation of TSPP with Zn2+ changes the absorption spectra as well as the FRET efficiency to green-emitting QDs (gQDs) and yellow-emitting QDs (yQDs) respectively, which leads to the PL recovery of gQDs and further PL quenching of yQDs. As a result, The color of the probe changes from yellow to green, which can be easily observed by the naked eye. This ratiometric probe has demonstrated to feature excellent selectivity for Zn2+ over other ions, thus potentially attractive for visual identification. Scheme 1. Schematic diagram of the ratiometric fluorescence probe for detection of Zn2+. Reference 1. Sun, Q. J.; Wang, Y. A. et al. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 717-722. 2. Sun, Q. J.; Guru, S. et al. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 737-743. 3. Xu, X. J. et al. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 2532-2535. This work was funded by NSFC and SKLB (Grants: 21005017, 21375015).








![Two-photon imaging of Zn[superscript 2+] dynamics in Please share](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012495740_1-7e131e3fc87a448a80135a30d7ebc36d-300x300.png)