TMX7051
advertisement
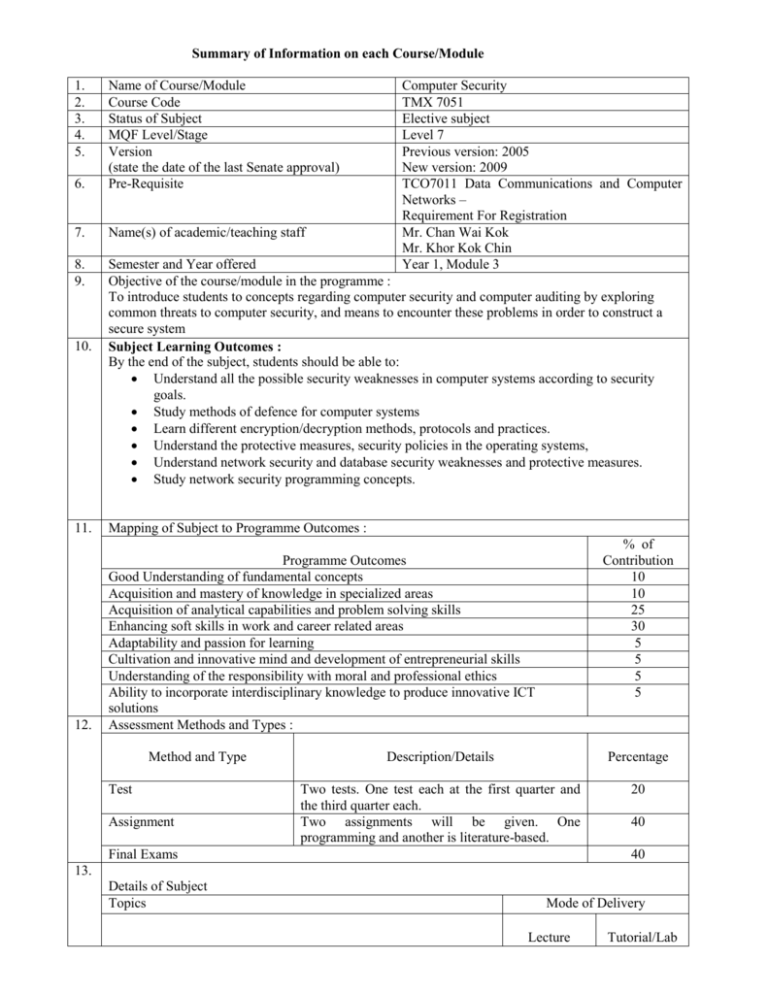
Summary of Information on each Course/Module 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Name of Course/Module Course Code Status of Subject MQF Level/Stage Version (state the date of the last Senate approval) Pre-Requisite 7. Name(s) of academic/teaching staff 8. 9. Semester and Year offered Objective of the course/module in the programme : To introduce students to concepts regarding computer security and computer auditing by exploring common threats to computer security, and means to encounter these problems in order to construct a secure system Subject Learning Outcomes : By the end of the subject, students should be able to: Understand all the possible security weaknesses in computer systems according to security goals. Study methods of defence for computer systems Learn different encryption/decryption methods, protocols and practices. Understand the protective measures, security policies in the operating systems, Understand network security and database security weaknesses and protective measures. Study network security programming concepts. 10. Computer Security TMX 7051 Elective subject Level 7 Previous version: 2005 New version: 2009 TCO7011 Data Communications and Computer Networks – Requirement For Registration Mr. Chan Wai Kok Mr. Khor Kok Chin Year 1, Module 3 11. Mapping of Subject to Programme Outcomes : 12. Programme Outcomes Good Understanding of fundamental concepts Acquisition and mastery of knowledge in specialized areas Acquisition of analytical capabilities and problem solving skills Enhancing soft skills in work and career related areas Adaptability and passion for learning Cultivation and innovative mind and development of entrepreneurial skills Understanding of the responsibility with moral and professional ethics Ability to incorporate interdisciplinary knowledge to produce innovative ICT solutions Assessment Methods and Types : Method and Type Test Assignment % of Contribution 10 10 25 30 5 5 5 5 Description/Details Percentage Two tests. One test each at the first quarter and the third quarter each. Two assignments will be given. One programming and another is literature-based. 20 Final Exams 40 40 13. Details of Subject Topics Mode of Delivery Lecture Tutorial/Lab 14. Fundamentals of Computer Auditing and Computer Security What is Computer Auditing, Security Problems in Computing 2 [Characteristics of Computer Intrusion, Kinds of Security Breaches, Security Goals and Vulnerabilities, Plan of Attack] Methods of Defence System and Security Administration, System Design, Hardware 2 Security Auditing, Software Security Auditing and Controls [Internal Auditing, Practical Approach, Writing Simple Auditing Programs] Encryption and Decryption Terminology and Background, Classical Cryptography, Number 6 Theory Applications to Cryptography, Public Key Encryption Systems [Merkle-Hellman Knapsacks, Rivest-Shamir-Adelman Encryption], Symmetric Cryptography, Data Encryption Standard Using Encryption: Protocols and Practices Protocols, Protocols to Solve Problems [Key Distribution, Digital 4 Signatures, Contract Signing, Certified Mail, How to Use Encryption [Amount of Secrecy, Key Management, Lost (Revealed) Keys, Complexity to Encrypt, Propagation of Errors, Size of Ciphertext Protection in General-Purpose Operating Systems Protected Objects and Methods of Protection, Protecting Memory and 5 Addressing, protecting Access to General Objects, File Protection mechanisms, User Authentication Designing Trusted Operating Systems Definition of a Trusted System, Security Policies, Models of Security, 5 Design of Trusted Operating Systems, Assurance in Trusted Operating Systems, Implementation Examples Network and Telecommunication Security Threats in Networks, Detecting Threats [Security Violation, 8 Misrouted Data, Components Failure, Signal Interception], Network Security Control, Privacy Enhanced Electronic Mail, Firewalls, Multilevel Security on Networks Database Security and Auditing Security Requirements, Inference Problem, Multilevel Databases, 8 Comparison of Database and Operating System Access, Field Checks, Change Logs, Integrity Checks, User Authentication, Precision Checks, Access Control Procedures, Proposals for Multilevel Security Programming Languages for Computer Security Review of Basic Programming Concepts, Examples of the Use of 2 Programming Languages and Libraries such as Java in Writing Software for Computer Security Purposes Total 42 Total Student Face to Face Total Guided and Independent Learning Learning Time (SLT) (Hour) 42 42 Lecture (14 weeks x 3 hours) (14 weeks x 3 hours) Tutorials Laboratory/Practical 1 Presentation 2 1 24 Assignment (2 assignments) (2 assignments) 4 8 Test (2 tests) (2 tests) 3 Final Exam 10 Quizzes - 15. 16. 51 86 Sub Total Total SLT 137 / 40 = 3.425 Credit Value 3 Reading Materials : Textbook Reference Materials th Pfleeger, C. P., “Security in Computing, 4 William Stallings, “Network Security Edition”, Prentice Hall, 2007. Essentials: Applications and Standards”, Pearson International Edition, 2007. William Stallings and Lawrie Brown, “Computer Security: Principles and Practice”, Forcht, K. A., “Computer Security Pearson International Edition, 2008. Management”, 1994. Deborah, R., “Computer Security Basics”, Watne, D. A. and Turney, P. B. B., “Auditing O’Reilly & Associates, 1991. EDP Systems”, 2nd edition, Prentice-Hall, 1990. Edward, A. “Fundamentals of Computer Security”, Technology, Prentice Hall, 1994. Cooper, J. A., “Computer & Communications Security”, Mc-Graw Hill, 1989.