Total Contact Hours
advertisement
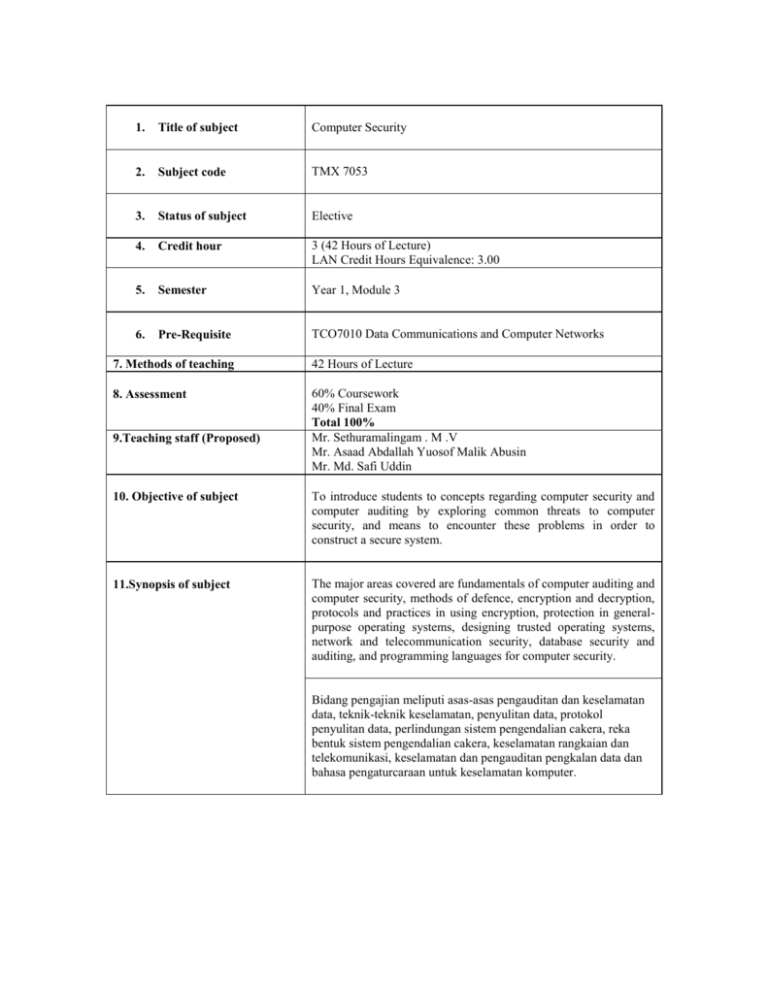
1. Title of subject Computer Security 2. Subject code TMX 7053 3. Status of subject Elective 4. Credit hour 3 (42 Hours of Lecture) LAN Credit Hours Equivalence: 3.00 5. Semester Year 1, Module 3 6. Pre-Requisite TCO7010 Data Communications and Computer Networks 7. Methods of teaching 42 Hours of Lecture 8. Assessment 60% Coursework 40% Final Exam Total 100% Mr. Sethuramalingam . M .V Mr. Asaad Abdallah Yuosof Malik Abusin Mr. Md. Safi Uddin 9.Teaching staff (Proposed) 10. Objective of subject To introduce students to concepts regarding computer security and computer auditing by exploring common threats to computer security, and means to encounter these problems in order to construct a secure system. 11.Synopsis of subject The major areas covered are fundamentals of computer auditing and computer security, methods of defence, encryption and decryption, protocols and practices in using encryption, protection in generalpurpose operating systems, designing trusted operating systems, network and telecommunication security, database security and auditing, and programming languages for computer security. Bidang pengajian meliputi asas-asas pengauditan dan keselamatan data, teknik-teknik keselamatan, penyulitan data, protokol penyulitan data, perlindungan sistem pengendalian cakera, reka bentuk sistem pengendalian cakera, keselamatan rangkaian dan telekomunikasi, keselamatan dan pengauditan pengkalan data dan bahasa pengaturcaraan untuk keselamatan komputer. 12. Learning Outcomes By the end of the subject, students should be able to : Understand all the possible security weaknesses in computer systems according to security goals. Study methods of defence for computer systems Learn different encryption/decryption methods, protocols and practices. Understand the protective measures, security policies in the operating systems, Understand network security and database security weaknesses and protective measures. Study network security programming concepts. 13.Details of subject Topics Covered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Fundamentals of Computer Auditing and Computer Security What is Computer Auditing, Security Problems in Computing [Characteristics of Computer Intrusion, Kinds of Security Breaches, Security Goals and Vulnerabilities, Plan of Attack] Methods of Defence System and Security Administration, System Design, Hardware Security Auditing, Software Security Auditing and Controls [Internal Auditing, Practical Approach, Writing Simple Auditing Programs] Encryption and Decryption Terminology and Background, Classical Cryptography, Number Theory Applications to Cryptography, Public Key Encryption Systems [Merkle-Hellman Knapsacks, Rivest-ShamirAdelman Encryption], Symmetric Cryptography, Data Encryption Standard Using Encryption: Protocols and Practices Protocols, Protocols to Solve Problems [Key Distribution, Digital Signatures, Contract Signing, Certified Mail, How to Use Encryption [Amount of Secrecy, Key Management, Lost (Revealed) Keys, Complexity to Encrypt, Propagation of Errors, Size of Ciphertext Protection in General-Purpose Operating Systems Protected Objects and Methods of Protection, Protecting Memory and Addressing, protecting Access to General Objects, File Protection mechanisms, User Authentication Designing Trusted Operating Systems Definition of a Trusted System, Security Policies, Models of Security, Design of Trusted Operating Systems, Assurance in Trusted Operating Systems, Implementation Examples Hours 2 2 6 4 5 5 7. 8. 9. 14.Text 8 Network and Telecommunication Security Threats in Networks, Detecting Threats [Security Violation, Misrouted Data, Components Failure, Signal Interception], Network Security Control, Privacy Enhanced Electronic Mail, Firewalls, Multilevel Security on Networks 8 Database Security and Auditing Security Requirements, Inference Problem, Multilevel Databases, Comparison of Database and Operating System Access, Field Checks, Change Logs, Integrity Checks, User Authentication, Precision Checks, Access Control Procedures, Proposals for Multilevel Security 2 Programming Languages for Computer Security Review of Basic Programming Concepts, Examples of the Use of Programming Languages and Libraries such as Java in Writing Software for Computer Security Purposes Total Contact Hours 42 1. Cooper, J. A. , “Computer & Communications Security”, McCompulsory Graw Hill, 1989. 2. Deborah, R., “Computer Security Basics”, O’Reilly & Associates, 1991. 3. Edward, A. “Fundamentals of Computer Security”, Technology, Prentice Hall, 1994. 1. References 2. 3. Forcht, K. A., “Computer Security Management”, 1994. Pfleeger, C. P., “Security in Computing”, Prentice Hall, 1997. Watne, D. A. and Turney, P. B. B., “Auditing EDP Systems”, 2nd edition, Prentice-Hall, 1990.