ESI for “Novel preparation of nanocrystalline magnesia
advertisement
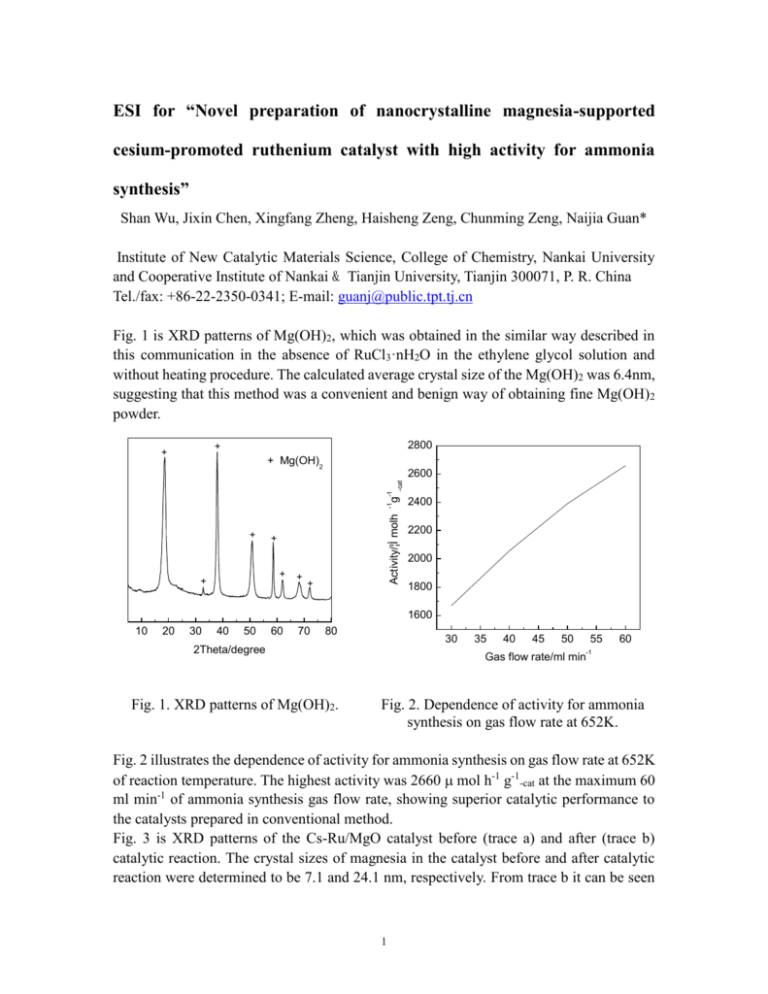
ESI for “Novel preparation of nanocrystalline magnesia-supported cesium-promoted ruthenium catalyst with high activity for ammonia synthesis” Shan Wu, Jixin Chen, Xingfang Zheng, Haisheng Zeng, Chunming Zeng, Naijia Guan* Institute of New Catalytic Materials Science, College of Chemistry, Nankai University and Cooperative Institute of Nankai & Tianjin University, Tianjin 300071, P. R. China Tel./fax: +86-22-2350-0341; E-mail: guanj@public.tpt.tj.cn Fig. 1 is XRD patterns of Mg(OH)2, which was obtained in the similar way described in this communication in the absence of RuCl3·nH2O in the ethylene glycol solution and without heating procedure. The calculated average crystal size of the Mg(OH)2 was 6.4nm, suggesting that this method was a convenient and benign way of obtaining fine Mg(OH)2 powder. 2800 + + + Mg(OH)2 + + + + + -cat Activity/¦Ì molh g -1 -1 2600 + 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 30 2Theta/degree Fig. 1. XRD patterns of Mg(OH)2. 35 40 45 50 55 60 -1 Gas flow rate/ml min Fig. 2. Dependence of activity for ammonia synthesis on gas flow rate at 652K. Fig. 2 illustrates the dependence of activity for ammonia synthesis on gas flow rate at 652K of reaction temperature. The highest activity was 2660 mol h-1 g-1-cat at the maximum 60 ml min-1 of ammonia synthesis gas flow rate, showing superior catalytic performance to the catalysts prepared in conventional method. Fig. 3 is XRD patterns of the Cs-Ru/MgO catalyst before (trace a) and after (trace b) catalytic reaction. The crystal sizes of magnesia in the catalyst before and after catalytic reaction were determined to be 7.1 and 24.1 nm, respectively. From trace b it can be seen 1 that the promoter, cesium compound, was present on the catalyst in the amorphous state after catalytic reaction. + Cl2p - CsNO3 + MgO - + - - + a - + - - + + b b a 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 210 2Theta/degree 205 200 195 190 Binding energy/eV Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Cs-Ru/MgO Fig. 4 XPS spectra of Cl2p of Cs-Ru/MgO before (trace a) and after (trace b) (trace a) before catalytic reaction and catalytic reaction. sample-P (trace b). Fig. 4 is the XPS spectra of Cl2p of the Cs-Ru/MgO catalyst (trace a) before catalytic reaction and sample-P (trace b). The sample-P was prepared by impregnating commercial magnesia product, as the Ru content of 4.3 wt%, with RuCl3·nH2O aqueous solution for 12h and dried slowly, then maintained in an oven at 383 K overnight. The sample-P was not treated with any reduction process. By qualitative comparison, most chlorine in the Cs-Ru/MgO catalyst is found to have been eliminated efficiently, forming one of the three main factors insuring the high activity of the catalyst. In summary, this method reported in the communication was confirmed to be efficient, facile and economical in dispersing Ru, preparing nanocrystalline magnesia, and removing chlorine, thus deserving being further investigated. 2