Molar Enthalpy student handout
advertisement
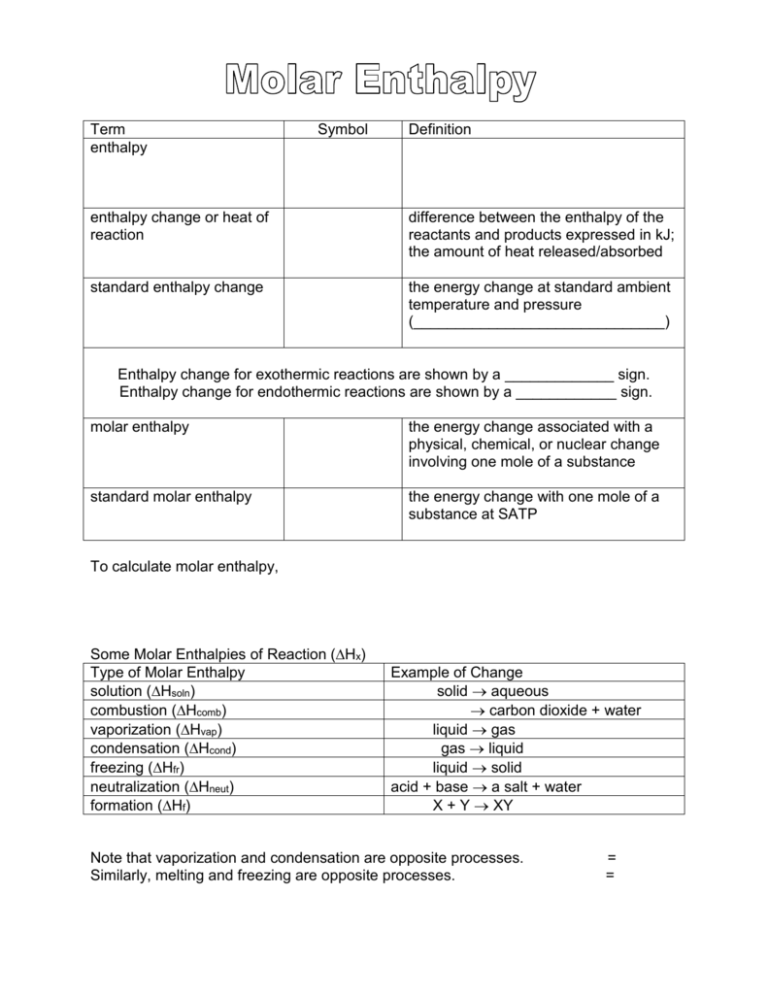
Term enthalpy Symbol Definition enthalpy change or heat of reaction difference between the enthalpy of the reactants and products expressed in kJ; the amount of heat released/absorbed standard enthalpy change the energy change at standard ambient temperature and pressure (______________________________) Enthalpy change for exothermic reactions are shown by a _____________ sign. Enthalpy change for endothermic reactions are shown by a ____________ sign. molar enthalpy the energy change associated with a physical, chemical, or nuclear change involving one mole of a substance standard molar enthalpy the energy change with one mole of a substance at SATP To calculate molar enthalpy, Some Molar Enthalpies of Reaction (Hx) Type of Molar Enthalpy solution (Hsoln) combustion (Hcomb) vaporization (Hvap) condensation (Hcond) freezing (Hfr) neutralization (Hneut) formation (Hf) Example of Change solid aqueous carbon dioxide + water liquid gas gas liquid liquid solid acid + base a salt + water X + Y XY Note that vaporization and condensation are opposite processes. Similarly, melting and freezing are opposite processes. = = Example 1: Freon-12 has a molar mass of 120.91 g/mol and Hvap of 34.99 kJ/mol. If 500.0 g of Freon is vaporized, what is the enthalpy change? Using Calorimetry to Find Molar Enthalpies A useful assumption is that the energy change of the system equals the quantity of heat that flows from the system to its surroundings, or from the surroundings to the system. This is consistent with the law of conservation of energy. H system = + lq surroundingsl Three simplifying assumptions used in the experimental technique: No heat is transferred between the calorimeter and the outside environment Any heat absorbed/released by the calorimeter is negligible. A dilute aqueous solution is assumed to have a density and specific heat capacity equal to that of pure water. density = 1.00 g/mL specific heat capacity = 4.18 J/gC Remember and since therefore Example 2: In a calorimetry experiment, 7.455 g of KCl is dissolved in 100.0 mL of water with an initial temperature of 24.1C. The final temperature of the solution is 20.0C. What is the molar enthalpy of a solution of KCl? Example 3: What mass of LiCl must have dissolved if the temperature of 200.0 g of water increased by 6.0C? The molar enthalpy of a solution of LiCl is -37 kJ/mol.