EnthalpyChangeMolarEnthalpyPracticeQuestions
advertisement

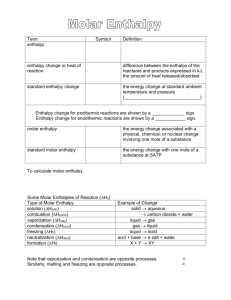
Molar Enthalpy/Enthalpy Change Practice Problems 1. In a chemistry experiment, 10.2 g of solid urea, NH2CONH2, is dissolved in pure water to make 150.0 ml of solution. A temperature change of 20.40C to 16.70C is measured in the solution (ie. the surroundings of the chemical system, which is the urea). Assume the solution is primarily distilled water. Using this data, calculate the molar enthalpy of solution for urea. (+13.7 kJ/mol) 2. A 10.1 g liquid sample of the element Gallium (Ga) is added to a 50.0 ml of distilled water. The temperature of the water changes from 24.00C to 27.80C as the Ga solidifies. Calculate the molar enthalpy of solidification for Ga. (-5.48 kJ/mol) 3. A lab technician adds 43.1 ml of concentrated 11.7 mol/L hydrochloric acid to distilled water to make exactly 500.0 ml of dilute solution. The temperature of the solution changes from 19.20C to 21.80C. Assume that the dilute solution is mainly water to calculate the molar enthalpy of dilution of hydrochloric acid. (-10.9 kJ/mol) 4. If the molar enthalpy of combustion of ethane is -1.56 MJ/mol, what is the enthalpy change in the complete combustion of (a) 5.0 mol of ethane (-7.8 MJ); (b) 40.3 kg of ethane (-2.09x103MJ) 5. The molar enthalpy of solution of ammonium chloride is +14.8 kJ/mol. What would be the final temperature of a solution in which 40.0 g of ammonium chloride is added to 200.0 ml of pure water, initially at 25.00C? (11.80C) 6. The enthalpy change for the chemical process H2O(l) H2O(g) could be described as the molar enthalpy of vapourization. Name the type of molar enthalpy that would be associated with each of the following chemical processes: a) Br2(g) Br2(l) ___________________________________________ b) CO2(s) CO2(g) _________________________________________ c) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) _________________________________ d) CH3OH(l) + 1.5O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(l) _________________________________