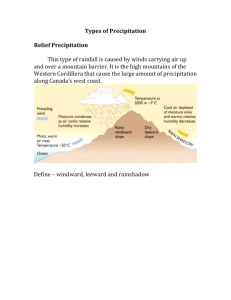
Hydrology
advertisement
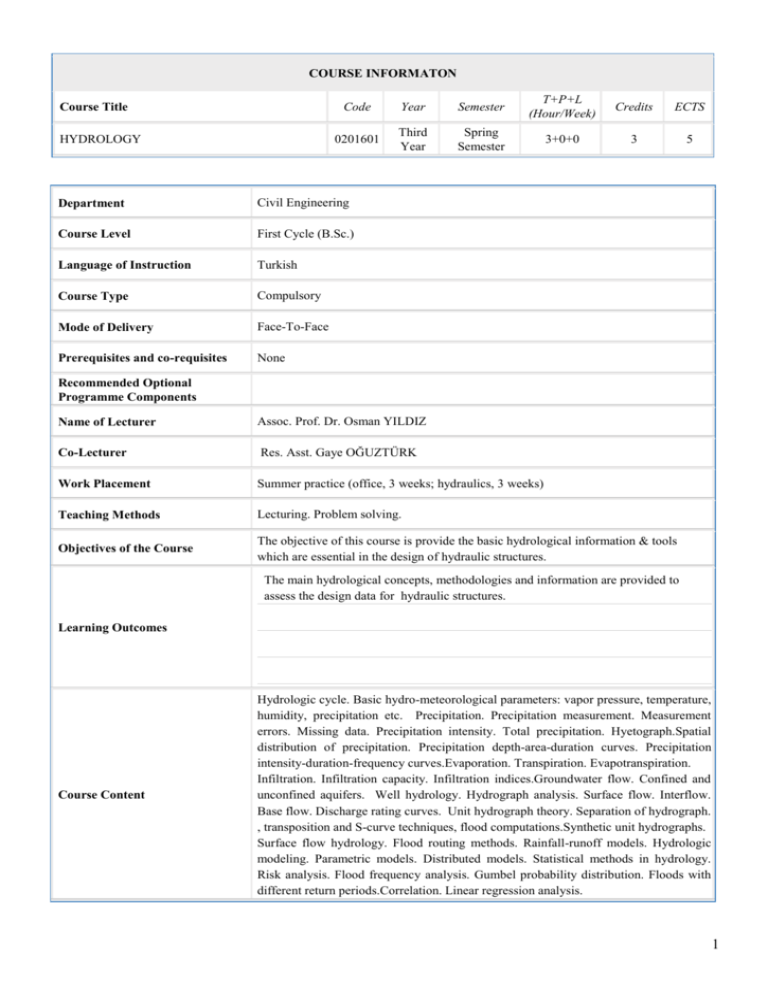
COURSE INFORMATON Course Title HYDROLOGY Code Year Semester T+P+L (Hour/Week) Credits ECTS 0201601 Third Year Spring Semester 3+0+0 3 5 Department Civil Engineering Course Level First Cycle (B.Sc.) Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face Prerequisites and co-requisites None Recommended Optional Programme Components Name of Lecturer Assoc. Prof. Dr. Osman YILDIZ Co-Lecturer Res. Asst. Gaye OĞUZTÜRK Work Placement Summer practice (office, 3 weeks; hydraulics, 3 weeks) Teaching Methods Lecturing. Problem solving. Objectives of the Course The objective of this course is provide the basic hydrological information & tools which are essential in the design of hydraulic structures. The main hydrological concepts, methodologies and information are provided to assess the design data for hydraulic structures. Learning Outcomes Course Content Hydrologic cycle. Basic hydro-meteorological parameters: vapor pressure, temperature, humidity, precipitation etc. Precipitation. Precipitation measurement. Measurement errors. Missing data. Precipitation intensity. Total precipitation. Hyetograph.Spatial distribution of precipitation. Precipitation depth-area-duration curves. Precipitation intensity-duration-frequency curves.Evaporation. Transpiration. Evapotranspiration. Infiltration. Infiltration capacity. Infiltration indices.Groundwater flow. Confined and unconfined aquifers. Well hydrology. Hydrograph analysis. Surface flow. Interflow. Base flow. Discharge rating curves. Unit hydrograph theory. Separation of hydrograph. , transposition and S-curve techniques, flood computations.Synthetic unit hydrographs. Surface flow hydrology. Flood routing methods. Rainfall-runoff models. Hydrologic modeling. Parametric models. Distributed models. Statistical methods in hydrology. Risk analysis. Flood frequency analysis. Gumbel probability distribution. Floods with different return periods.Correlation. Linear regression analysis. 1 COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics Study Materials 1 Hydrologic cycle. Basic hydro-meteorological parameters: vapor pressure, temperature, humidity, precipitation etc. 2 Precipitation. Precipitation measurement. Measurement errors. Missing data. Precipitation intensity. Total precipitation. Hyetograph. 3 Spatial distribution of precipitation. Precipitation depth-area-duration curves. Precipitation intensity-duration-frequency curves. 4 Evaporation. Transpiration. Evapotranspiration. 5 Infiltration. Infiltration capacity. Infiltration indices. 6 Groundwater flow. Confined and unconfined aquifers. Well hydrology. 7 Hydrograph analysis. Surface flow. Interflow. Base flow. Discharge rating curves. 8 MIDTERM EXAM 9 Unit hydrograph theory. Separation of hydrograph. , transposition and Scurve techniques, flood computations. 10 Synthetic unit hydrographs. 11 Surface flow hydrology. Flood routing methods. 12 Rainfall-runoff models. Hydrologic modeling. Parametric models. Distributed models. 13 Statistical methods in hydrology. Risk analysis. Flood frequency analysis. Gumbel probability distribution. Floods with different return periods. 14 Correlation. Linear regression analysis. RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook Hidroloji, Mehmetçik Bayazıt, İTÜ Yayınları. Additional Resources Engineering Hydrology, Nurunnisa Usül, METU Press (ODTÜ Yayınları). Engineering Hydrology, Victor M. Ponce, Prentice Hall. MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams Midterm Exam, Final Exam, Supplementary Exam. ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 2 Contribution of Assignments to Overall Grade 2 TOTAL 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Nr. Contribution Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 To gain the ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering to civil engineering problems. X 2 To be able to identify, model and solve civil engineering problems in consideration with safety, economy, aesthetics and environmental factors. X 3 To get familiar with modern techniques and computation methods in civil engineering. X 4 To learn measurement and evaluation methods and techniques in civil engineering. X 5 To gain the responsibility for work and labor safety in all civil engineering applications. 6 To be able to identify, analyze, and synthesize civil engineering problems and applications. 7 To have enough knowledge about construction materials. 8 To be able to conduct laboratory and site experiments, to evaluate, and to interpret experimental data. X 9 To be able to work together with other people, to adapt teamwork. X 10 To take initiative and responsibility, to work independently, and to innovate. X 11 To gain the ability for effective written and oral communication in Turkish and English. 12 To recognize the need for, and to gain the ability to engage in life-long learning. X X ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Activities Quantity Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 3 48 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 2 32 Mid-term 1 24 24 Final examination 1 24 24 Assignments Presentation / Preparing Seminar Total Work Load 128 Total Work Load / 30 (h) 4,3 ECTS Credit of the Course 5 3