Lecture19
advertisement

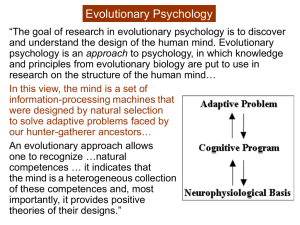
Lecture 19 Problems With Modern Research On Cognition Donald’s Observations About Cognitive Science Based on the study of two kinds of minds 1) Literate young adults 2) Computer simulations Depressing View of Human Abilities People are bad statisticians People are not logical People are bad decision makers … The Standard Social Science Model Content Free Models of Mind, e.g., Logic, Probability, etc. Information Processing Models of Cognition The Problem Space Hypothesis Rule-Based Models of Skill Page 1 of 15 Lecture 19 Evolutionary Psychology Discover & understand the design of the human mind An approach to psychology A way of thinking about psychology that can be applied to any topic with in it Mind is a collection of IP’s, designed by natural selection to solve adaptive problems faced by our hunter-gatherer ancestors Levels of Explanation Adaptive problem Cognitive Program Neuropsychological basis Page 2 of 15 Lecture 19 Where Social and Cognitive Sciences Went Astray The Standard Social Science Model (SSSM) All Specific Content Of Human Mind Originally Derives From The "Outside" Small Number Of General Purpose Mental Mechanisms have no pre-existing content built-in to their procedures not designed to construct certain contents more readily than others have no features specialized for processing particular kinds of content. Page 3 of 15 Lecture 19 Evolutionary Psychology View SSSM Is WRONG!!!!! Human minds have a standard collection of reasoning and regulatory circuits that are Functionally specialized Frequently, domain-specific Modules that are analogous to organs Design by evolution Designed to solve problem faced by our hunter-gatherer ancestors Page 4 of 15 Lecture 19 Bask To Basics (C&T) Principle 1. Brain Is A Physical System That Can Be Described As An Information Processing System Designed To Generate Behavior Appropriate To Environmental Circumstances Must Understand the Structure of Environment (Anderson, 1990) Principle 2. Brain Designed By Natural Selection To Solve Problems Faced During Our Species' Evolutionary History Disgust Our Ability To Learn Math, Drive Cars, Use Computers Is A Side-Effect Or By-Product Of Circuits That Were Designed To Solve Adaptive Problems Page 5 of 15 Lecture 19 Bask To Basics (C&T) (Cont.) Principle 3. Consciousness is just the tip of the iceberg; most of what goes on in your mind is hidden from you. Perception, Motor Control, Language Generation and Comprehension Are Extremely Complex Example: To see your mother walk, you employ specialized circuits that: (1) analyze the shape of objects (2) detect the presence of motion (3) detect the direction of motion (4) judge distance (5) analyze color (6) identify an object as human (7) recognize that the face you see is Mom's face Page 6 of 15 Lecture 19 Bask To Basics (C&T) (Cont.) ***Principle 4. Different Neural Circuits Are Specialized For Solving Different Adaptive Problems Have Specialized Neural Circuits Because The Same Mechanism Is Rarely Capable Of Solving Different Adaptive Problems Mind Consist Of A Large Number Of Circuits That Are Functionally Specialized. vision hearing sexual attraction choose nutritious food on the basis of taste and smell executive functions language reasoning problem solving Brain Is A Collection Of Specialized Modules No Disagreements About Vision, Hearing, Motor Control, … Page 7 of 15 Lecture 19 But Language, Reasoning, Learning, …, ? Page 8 of 15 Lecture 19 Principle 4 (Cont.) and 5 Reasoning Circuits And Learning Circuits Discussed Above Have The Following Five Properties: (1) Complexly Structured For Solving Specific Type Of Adaptive Problem (2) Reliably Develop In All Normal Human Beings, (3) Develop Without Any Conscious Effort And In Absence Of Any Formal Instruction (4) Applied Without Any Conscious Awareness Of Their Underlying Logic (5) Distinct From More General Abilities To Process Information Or Behave Intelligently Principle 5 Our modern skulls house a stone age mind. Computer age Industrial revolution Agricultural age Page 9 of 15 Lecture 19 Examples of Empirical Results Supporting Evolutionary Psychology Facial Expressions Language Chomsky: Universal Grammer “Poverty of the simulus” Human languages have such a complex structure that they cannot be learned just from the information available to a child Detecting Violations of Rules Probabilistic Reasoning Page 10 of 15 Lecture 19 Detecting Violations of Rules Logic and Reasoning General Content Free Mechanisms People are very bad at … Wason Selection Task IF a person goes into Boston, then that person takes the subway Boston Arlington subway cab If P, then Q Test for P(Q?) and ~Q(~P?) Huge Number of Other Examples Social Exchange (Reciprocal Altruism) Cheater detection If you take benefit B, then you must satisfy requirement R Can detect violations of If-Then rules if task is cheater detection If you are drinking beer, you must be 21 or older Beer Coke 21 or over Page 11 of 15 younger that 21 Lecture 19 Probabilistic Reasoning Company suspects 2% of its employees use illicit drugs. Company institutes random drug tests Drug test is 95% accurate; that is, P[positive test| drug use] = .95 P[negative test| no drug use] = .95 Mary Jane is selected at random; her test is positive. What is probability that Mary Jane uses illicit drugs? Gerd Gigerenzer Gigerenzer, G., Todd, P. M., & the ABC Group (1999). Simple heuristics that make us smart. New York: Oxford University Press. Probabilities verses Frequencies Fast and frugal heuristics fill part of our mind's "adaptive toolbox" of decision strategies. Together, these heuristics produce a rationality which is ecological, rather than merely logical - decision making that is welladapted to specific environmental settings or domains Page 12 of 15 Lecture 19 and specific classes of problems, rather than being universally applicable to all situations and problems. Page 13 of 15 Lecture 19 Mary Jane's Probability Test Says: "Positive" "Negative" Total Truth Clean Drug User Total 49 19 68 (5% of Col) (95% of Col) 931 1 (95% of Col) (5% of Col) 980 20 932 1000 (98% of Total) (2% of Total) For 1000 employees there would be 68 "positive" test results. But 49 of these "positive" tests would be false alarms and only 19 would be hits. P[Mary Jane is drug user | "positive" test] = 19/68 = .28 Page 14 of 15 Lecture 19 If company fired all employees with "positive" test results, for every 1000 employees they would fire 49 innocent people and only 19 guilty people. Page 15 of 15